Tests
1st tests to order
erect lumbar spine x-ray
Test
Upright anteroposterior and lateral plain radiographs are a quick and simple investigation that may give valuable information; however, they are not routinely recommended for nonspecific back pain.[64][65][66][67][68] Plain radiographs are recommended if recent significant trauma, osteoporosis, or age over 70 years.[65] For all other instances of low back pain (LBP), such as spinal malignancy, infection, fracture, cauda equina syndrome, or ankylosing spondylitis or another inflammatory disorder, the preferred modality is lumbar MRI.[64][65]
Result
osteoporosis, fractures, or vertebral metastases; degenerative changes (osteophytes, disk space narrowing, foraminal stenosis, endplate sclerosis, ligament calcification) may be seen
MRI spine
Test
Provides an excellent assessment of the discal pathology, nerve root compression, canal compression due to hypertrophied ligamentum flavum, and the facet joints.[62]
Correlation of changes seen on different MRI sequences with the histopathological findings is known as Modic classification: type 1 - decreased signal intensity on T1-weighted MRI and an increased signal on T2-weighted images indicates acute or subacute inflammatory changes; type 2 - increased signal intensity on T1-weighted images and isointense or slightly increased signal on T2-weighted images indicates chronic repetitive trauma; type 3 - decreased signal activity on both T1- and T2-weighted imaging corresponds to advanced degeneration with reactive osteosclerosis.[77]
These findings should always be interpreted with caution because, even in the presence of degenerative findings, MRI of the spine alone is not an absolute indicator of the patient’s symptoms.[72][74][75][76][95]
High-intensity zone (HIZ) lesions are hyperintense signal changes on T2-weighted images, located within the posterior annulus of the disk and visible on both axial and sagittal views. HIZ lesions are variably present in painful degenerative disks. They reflect entities as diverse as annular tears, trapped nucleus pulposus herniations, or even focal degenerative myxoid change within the outer annulus.[88][89][90] This heterogeneity probably explains why HIZ lesions have been shown to be inconsistent as sensitive markers for discogenic pain.[92][91][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: T2-weighted MRI spine: sagittal view (left) demonstrates 2 level disk dehydration at L4-5 and L5S1 with a moderate reduction in disk height; axial views (right) demonstrate constitutionally narrow canal at L4-5 with a moderate disk prolapse and a large disk prolapse at L5S1 level with left S1 root compressionFrom the collection of Dr N. Quiraishi [Citation ends].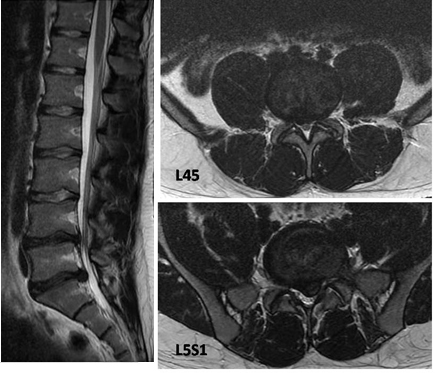 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: T2-weighted MRI spine: sagittal view (left) demonstrates degenerate disks; axial view (right) demonstrates left-sided L5S1 foraminal narrowingFrom the collection of Dr N. Quiraishi [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: T2-weighted MRI spine: sagittal view (left) demonstrates degenerate disks; axial view (right) demonstrates left-sided L5S1 foraminal narrowingFrom the collection of Dr N. Quiraishi [Citation ends].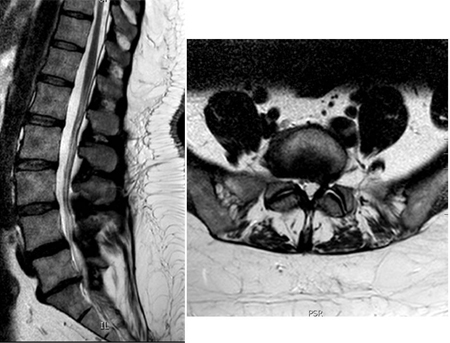 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: MRI spine: degenerate L4-5 disk with a disk bulge and L5S1 disk with a high-intensity zoneFrom the collection of Dr N. Quiraishi [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: MRI spine: degenerate L4-5 disk with a disk bulge and L5S1 disk with a high-intensity zoneFrom the collection of Dr N. Quiraishi [Citation ends].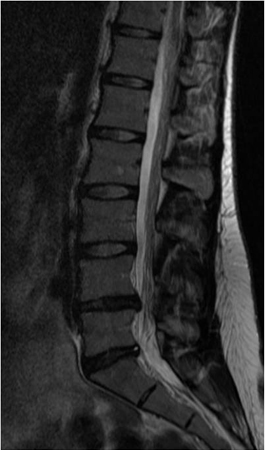
Result
signs of degeneration (decreased signal on T2-weighted images [black disk]), evaluation of disk height, presence or absence of annular tears, endplate changes
Investigations to avoid
dermatomal somatosensory evoked potentials
Recommendations
Do not perform dermatomal somatosensory evoked potentials to diagnose radiculopathy in the neck or back.[63]
nerve conduction studies
Recommendations
Nerve conduction studies alone cannot be used to diagnose radiculopathy. Needle electromyography would also be necessary to determine the disease process.[63]
Rationale
Electromyography and nerve conduction studies are suggested to have limited use for diagnosing lumbar disk herniation with radiculopathy.[62]
Tests to consider
CT spine
Test
Indicated if MRI is contraindicated, in post-operative cases to assess the implant positioning or surgical fusion, and in conjunction with a myelography or discography.[62]
Result
facet arthritis, tropism, assessment of canal dimensions
flexion/extension spine x-rays
Test
May be obtained to aid the diagnosis if there is a suspicion of spondylolisthesis. Useful to stage instability (stage 2 of the Kirkaldy-Willis classification) to assess any abnormal motion with flexion and extension.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Spondylolisthesis: flexion/extension viewsFrom the collection of Dr N. Quiraishi [Citation ends].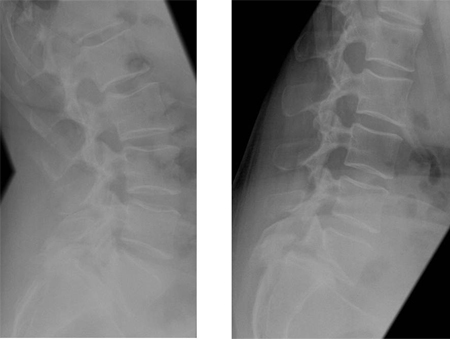
Result
abnormal movement (lumbar motion segment instability)
single photon emission computed tomography
Test
Marker of pathologies that cause an increased blood flow locally such as inflammation (e.g., diskitis), reactive changes due to proximity to a tumor, or degenerative changes (e.g., facet joint inflammation).
Useful when other imaging modalities are negative but pathology (not necessarily discogenic) is still suspected. This investigation allows for identification of an underlying pathology but is not specific. However, it gives a false negative in multiple myeloma.
Result
increased tracer uptake may be present
CT myelogram
Test
Allows for better assessment of stenotic segments in the spinal canal and the nerve root foramina.[62] Although traditional CT scans are performed in the supine position, the myelogram can be performed with the patient upright. It is an invasive investigation and involves injection of a contrast material into the epidural space. It is not commonly performed though is a useful adjunct to CT scans.
Result
central canal, lateral recess, or foraminal compromise
discography
Test
A useful functional imaging tool to evaluate the annular pathology and to determine whether the pain is concordant and whether or not the disk is the pain generator. The main limitation of the procedure is its reliance on subjective pain responses from the patient. Suitable candidates for discography are patients with chronic LBP (>3 months), those whose symptoms have not been improved by conservative treatment or other minimal invasive procedures (facet joint injections, nerve root block, sacroiliac injections), and patients who are candidates for a possible interventional treatment aimed at reducing the discogenic pain. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Discography: a patient presents with back and right leg pain that did not respond to a trial of conservative management. MRI (left, sagittal T2-weighted image) demonstrates multiple degenerate disks with loss of normal hydration, reduced signal, and loss of the nuclear-annular transition, with a normal disk height. A 3-level discography at L3-4, L4-5, and L5S1 (middle, AP radiograph; right, lateral radiograph) reveals a low-pressure injection with degenerate annular tears at all 3 levels, with 5/5 pain concordance at L5S1; 3/5 at L4-5; and 0/5 at L3-4From the collection of Dr N. Quiraishi [Citation ends].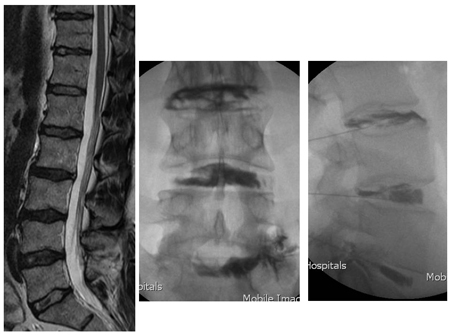
Result
reproduction of the pain (concordant pain) by increasing the intradiscal pressure when injecting the affected disk with a contrast material
MRI with gadolinium (contrast)
Test
Alternative to discography in patients with symptomatic degenerative disk disease who have contraindications to discography. Provides differentiation of the presence of scarring tissue that forms within a healing full-thickness annular tear.
Result
enhancement of the edematous, scarring structures on T1-weighted images
Emerging tests
genetic testing
Test
Testing is currently under development and not available for routine clinical use.
Result
genes that code for collagen I (COL9A2), collagen IX (COL9A3), collagen XI (COL11A2), interleukin 1 (IL-1), interleukin 6 (IL-6), aggrecan (AGC1), vitamin D receptor (VDR), metalloproteinases (MMP-3), and cartilage intermediate layer protein (CILP)
functional spinal imaging
Test
Testing is currently under development and not available for routine clinical use.
Result
includes magnetic resonance spectroscopy; MRI with mapping T2 relaxation time; mapping T1 rho; dynamic MRI; and diffusion imaging
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer