Tests
1st tests to order
chest x-ray
Test
Radiologic stage by chest radiography at presentation inversely correlates with likelihood of spontaneous resolution.
Stage 0: normal
Stage I: bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy
Stage II: bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy plus pulmonary infiltrates
Stage III: pulmonary infiltrates without hilar lymphadenopathy
Stage IV: extensive fibrosis with distortion.[30][56]
Typically shows bilateral hilar adenopathy. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Bilateral hilar adenopathyFrom the collection of Dr M.P. Muthiah; used with permission [Citation ends].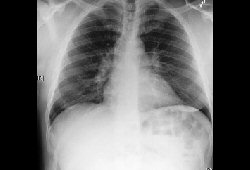
Result
bilateral hilar and right paratracheal adenopathy, although isolated bilateral hilar adenopathy more frequent; bilateral pulmonary infiltrates, predominantly in the upper lobes; pleural effusions (rare) and egg shell calcifications (very rare) may be seen
CBC
serum BUN
Test
To screen for renal involvement.
Result
may be elevated
serum creatinine
Test
To screen for renal involvement.
Result
may be elevated
liver enzymes
Test
To screen for hepatic sarcoidosis.
US guidelines recommend baseline serum alkaline phosphatase testing.[31]
Asymptomatic aminotransferase (AST and ALT) elevation possible.
Result
elevated
serum calcium
Test
To screen for abnormal calcium metabolism.
Hypercalcemia occurs due to dysregulated production of calcitriol by activated macrophages and granulomas.
Result
may be elevated
PFTs
Test
Including spirometry and gas transfer analysis to monitor disease.
Often normal in nonfibrotic sarcoidosis; may not reflect disease activity or symptom burden.[30]
Obstructive pattern with bronchodilator response may mimic asthma.
Persistent decline in forced vital capacity indicates disease progression.[14]
Result
restrictive or obstructive or mixed pattern
ECG
Test
To exclude or confirm cardiac involvement.
About half of patients with cardiac sarcoidosis have abnormalities of rhythm, conduction, or repolarization.[57]
Result
conduction defects
eye exam
Test
To exclude or confirm ocular involvement.
Some patients present with uveitis as their initial clinical manifestation.
Annual eye exams should be considered.
Result
uveitis, retinal vascular changes, conjunctival nodules, lacrimal gland enlargement
interferon gamma release assay
Test
Tuberculosis and atypical mycobacterial infections can mimic sarcoidosis.
Interferon gamma release assay is used for screening, and preferable to tuberculin skin testing due to anergy.
Interferon gamma release assays cannot distinguish between latent infection and active disease.
Result
negative
Tests to consider
serum ACE
CT scan of chest
Test
Not necessary in the routine evaluation or management of sarcoidosis.
Ground-glass appearance may indicate a potentially reversible condition.
Cystic architectural distortion suggests irreversible disease.[60]
Result
hilar and/or paratracheal adenopathy with upper lobe predominance, bilateral infiltrates in a bronchovascular and/or a perilymphatic distribution; calcified hilar or mediastinal lymph nodes in patients with longstanding disease
endobronchial ultrasound-transbronchial needle aspiration
Test
Most patients with pulmonary symptoms, with no histologic diagnosis of sarcoidosis from extrathoracic sites, require bronchoscopy.
In patients with suspected pulmonary sarcoidosis, diagnostic yield is superior with endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS)-guided transbronchial node aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) compared with conventional transbronchial lung biopsy.[43][44] EBUS-TBNA is standard of care and routine practice for the diagnosis of mediastinal lymphadenopathy, with high sensitivity (88%) and specificity (100%).[45][46][47]
Endobronchial biopsy and transbronchial biopsy can be performed.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Photomicrograph showing well-formed granulomas typical for sarcoidosisFrom the collection of Dr M.P. Muthiah; used with permission [Citation ends].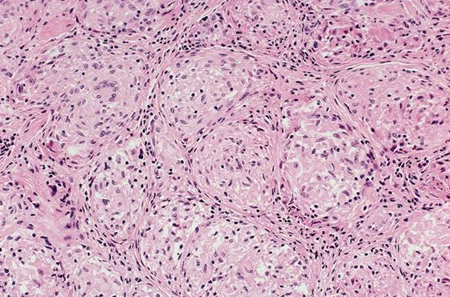
Result
noncaseating granulomas, with negative acid-fast and fungal stains
bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)
Test
Specificity of 94%. Sensitivity of 53%.[14]
Result
BAL lymphocytosis, with CD4-to-CD8 ratio >3.5
skin biopsy
Test
Skin biopsy of lesion suspicious for sarcoidosis may histologically confirm diagnosis.
Result
noncaseating granulomas
24-hour urine calcium
Test
May be ordered in patients with a history of renal calculi to rule out hypercalciuria, which, when present, can cause nephrocalcinosis with progressive renal insufficiency.
Hypercalciuria due to abnormal calcium and vitamin D regulation from macrophages inside granulomas.[61]
Result
may be elevated
gallium-67 scan
Test
Typical patterns include panda sign: lacrimal and parotid gland uptake; lambda sign: parahilar, infrahilar, and right paratracheal or azygos node uptake.[48]
Lacks specificity. Serial images sometimes require 48 hours to complete.
The clinical value of this test remains controversial.[30]
Result
may show typical uptake patterns
vitamin D
Test
If assessment of vitamin D metabolism is deemed necessary (e.g., to determine whether vitamin D replacement is indicated) measure both 25- and 1,25-OH vitamin D levels.[31]
Potential benefits of vitamin D supplementation need to be weighed against risk of hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria.
Result
25-OH vitamin D may be depleted, while 1,25-OH vitamin D may be elevated
MRI
Test
May be useful in identifying areas of sarcoidosis involvement including the heart and the brain.[48][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: A) Gadolinium-enhanced MRI scan of the heart (short axis) showing delayed enhancement in the anteroseptal myocardiumAdapted from https://casereports.bmj.com/content/2009/bcr.2006.070805.full [Citation ends].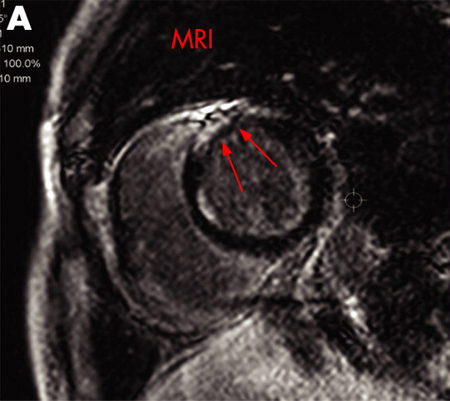
Result
heart findings include nodular lesions and/or focal myocardial thickening; brain findings are varied and nonspecific and include meningeal enhancement with or without periventricular white matter lesions
(18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET scan
Test
PET scanning has been shown to have a characteristic pattern of uptake in sarcoidosis and may aid in the diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis.[38][49][50] This test is much less invasive than endomyocardial biopsy, with minimal to no complications from the procedure.[51][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: B) 18F-FDG PET scan of the heart (short axis) showing focal uptake in the anteroseptal wall corresponding to granulomatous inflammation. (C) 18F-FDG PET scan of the heart (short axis) from the base to the apex (from left to the right) showing focal uptake in the anteroseptal wall at baseline (upper series) and disappearance of the uptake after treatment (lower series)Adapted from https://casereports.bmj.com/content/2009/bcr.2006.070805.full [Citation ends].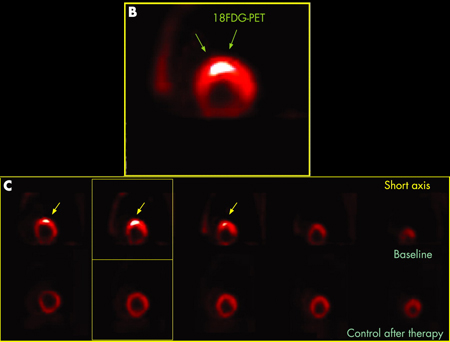
May also be used when there is diagnostic/monitoring uncertainty in the assessment of activity and distribution of disease at baseline as well as assessment of disease response.[50]
Result
heterogeneous myocardial FDG uptake
Emerging tests
3'-deoxy-3'-[18F]-fluorothymidine (FLT) PET scan
Test
Uptake of FLT determined by cellular proliferation, including sarcoidosis granulomas; does not require extensive patient preparation.[52]
Result
uptake correlates with myocardial lesions
4'-[methyl-11C]-thiothymidine PET/CT scan
Test
May be useful in identifying active cardiac lesions, as well as in the assessment of treatment response; does not require extensive patient preparation.[62]
Result
uptake correlates with myocardial lesions
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer