Popliteal cyst
- Overview
- Theory
- Diagnosis
- Management
- Follow up
- Resources
Treatment algorithm
Please note that formulations/routes and doses may differ between drug names and brands, drug formularies, or locations. Treatment recommendations are specific to patient groups: see disclaimer
asymptomatic
no treatment
Asymptomatic patients require no specific treatment.
symptomatic: initial treatment
conservative treatment
Patients with minor signs and symptoms such as fullness or mild discomfort in the popliteal fossa are managed conservatively with physical therapy and simple analgesics (e.g., aspirin or acetaminophen), or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Primary options
aspirin: 325-650 mg orally every 4 hours when required, maximum 4000 mg/day
OR
acetaminophen: 325-1000 mg orally every 4-6 hours when required, maximum 4000 mg/day
OR
ibuprofen: 400 mg orally every 4-6 hours when required, maximum 2400 mg/day
symptomatic: refractory to initial conservative treatment
correction of any underlying joint pathology
Patients with underlying knee joint pathology should undergo orthopedic evaluation for treatment of traumatic, infectious, or arthritic pathology.
If a knee effusion is present, aspiration of the knee joint is usually beneficial. Aspiration of the joint space with or without injection of corticosteroids will decrease intra-articular pressure and decrease inflammatory pathology. This should be done only under ultrasound guidance.
Additional direct aspiration of the cyst may be performed in cases of larger fluid collections, although cysts may recur.[23]Smith MK, Lesniak B, Baraga MG, et al. Treatment of popliteal (Baker) cysts with ultrasound-guided aspiration, fenestration, and injection: long-term follow-up. Sports Health. 2015;7:409-414. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26502415?tool=bestpractice.com
Aspiration should be done with a large-bore needle (i.e., 18 gauge) as the fluid is very viscous.
intra-articular corticosteroid
Treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Intra-articular injection of corticosteroids in patients with underlying knee pathology has been described to produce good symptomatic relief.[9]Handy JR. Popliteal cysts in adults: a review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Oct;31(2):108-18. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11590580?tool=bestpractice.com
Dose may need to be repeated. Adjust doses and frequency according to response. Taper dose gradually after long-term use.
Primary options
betamethasone sodium phosphate/betamethasone acetate: 6-12 mg intra-articularly as a single dose
OR
triamcinolone acetonide: 5-15 mg intra-articularly as a single dose
More triamcinolone acetonideHexacetonide salt may also be used.
OR
methylprednisolone acetate: 4-80 mg intra-articularly as a single dose every 1-5 weeks
supportive therapies
Treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Physical therapy may be used adjunctively.
Simple analgesics (e.g., aspirin or acetaminophen) may be used adjunctively for pain relief, or NSAIDs.
Primary options
aspirin: 325-650 mg orally every 4 hours when required, maximum 4000 mg/day
OR
acetaminophen: 325-1000 mg orally every 4-6 hours when required, maximum 4000 mg/day
OR
ibuprofen: 400 mg orally every 4-6 hours when required, maximum 2400 mg/day
surgery
Surgical treatment is rarely performed, and is only indicated in patients with extensive symptoms who fail conservative and percutaneous treatment.
It is the experience of some surgeons that simple excision of a popliteal cyst results in high incidence of recurrence.
Surgical options have been described, including anterior open synovectomy, arthroscopic synovectomy, radiosynovectomy, capsulectomy, capsuloplasty with pedicle graft, and repair of joint capsule.
Arthroscopic resection facilitates management of the cyst, by arthroscopic decompression, and the associated intra-articular disorder. Surgery involves enlarging the interval between the semimembranosus and medial gastrocnemius, allowing the cyst contents to drain into the joint.
Arthroscopic resection is effective, and is associated with reduced morbidity and recurrence compared with excision.[24]Zhou XN, Li B, Wang JS, et al. Surgical treatment of popliteal cyst: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11:22.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4754995
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26879283?tool=bestpractice.com
[25]Ahn JH, Lee SH, Yoo JC, et al. Arthroscopic treatment of popliteal cysts: clinical and magnetic resonance imaging results. Arthroscopy. 2010;26:1340-1347.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20869836?tool=bestpractice.com
[26]Yang B, Wang F, Lou Y, et al. A comparison of clinical efficacy between different surgical approaches for popliteal cyst. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017 Oct 25;12(1):158.
https://www.doi.org/10.1186/s13018-017-0659-z
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29070055?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Arthroscopic resection of a popliteal cystFrom the collection of Dr John Kelly IV; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Arthroscopic resection of a popliteal cystFrom the collection of Dr John D. Kelly IV; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Arthroscopic resection of a popliteal cystFrom the collection of Dr John D. Kelly IV; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Septae within a popliteal cystFrom the collection of Dr John D. Kelly IV; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Septae within a popliteal cystFrom the collection of Dr John D. Kelly IV; used with permission [Citation ends].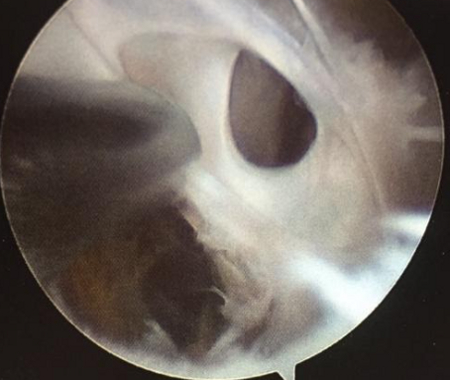
analgesia
Treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Simple analgesics (e.g., aspirin or acetaminophen) may be used adjunctively for pain relief, or NSAIDs.
Primary options
aspirin: 325-650 mg orally every 4 hours when required, maximum 4000 mg/day
OR
acetaminophen: 325-1000 mg orally every 4-6 hours when required, maximum 4000 mg/day
OR
ibuprofen: 400 mg orally every 4-6 hours when required, maximum 2400 mg/day

Choose a patient group to see our recommendations
Please note that formulations/routes and doses may differ between drug names and brands, drug formularies, or locations. Treatment recommendations are specific to patient groups. See disclaimer
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer