Differentials
Psoriasis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
A common inflammatory dermatosis. Typically presents with well-defined erythematous plaques with silvery scales that are symmetrically distributed and favor extensor surfaces of elbows, knees, lower back, and scalp. May also present with guttate, pustular, and erythrodermic lesions. Nails and joints may be involved.
Typically diagnosed on clinical features alone. Family history of psoriasis common.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Plaque psoriasis on kneeFrom the collection of Dr. Tsu-Yi Chuang [Citation ends].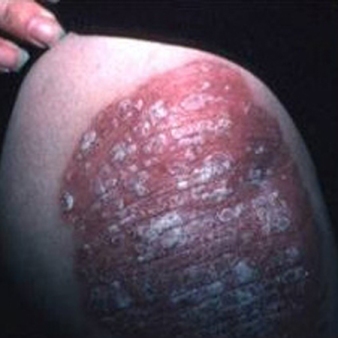
INVESTIGATIONS
Histology on skin biopsy specimen shows epidermal acanthosis, parakeratosis, absence of granular layer, and neutrophil microabscesses with dermal vascular dilation.
Eczema
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
A heterogeneous group of inflammatory dermatoses characterized by intensely itchy, erythematous papulovesicles, patches, and thickened lichenified plaques. In the most common variant, atopic eczema, these are symmetrically distributed and favor flexural surfaces of elbows, knees, hands, and face. Weeping, crusting, excoriation, and signs of secondary infection are frequently present. May present with erythrodermic eczema. Other clinical variants include irritant and allergic contact eczema, discoid (nummular) eczema, pompholyx eczema, and photosensitive eczema.
Typically diagnosed on clinical features alone. Positive family history is usually present in atopic eczema and associated with other atopic manifestations, such as asthma and hay fever. Pruritus is usually the predominant symptom.
INVESTIGATIONS
Histology depends on eczema subtype, but typically shows spongiosis of the epidermis with a mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate and secondary epidermal changes due to scratching.
Dermatophyte infection
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Common infectious dermatosis of skin, scalp, and nails. Typically affects web spaces of toes (athlete's foot) and groins (jock itch). When it affects other body sites, typically presents with asymmetrical, erythematous, annular lesions, with scaling at the leading edges of lesions. Topical corticosteroids may induce pustular changes and lead to deterioration.
INVESTIGATIONS
Diagnosis confirmed by microscopy (KOH preparation) and culture of skin scrapings. If skin biopsy taken, no evidence of atypical lymphocytes in epidermis. Periodic acid-Schiff stain positive.
Parapsoriasis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
A group of inflammatory skin conditions characterized by scaly patches or slightly elevated papules and/or plaques that resemble those of psoriasis. There is no uniformly accepted definition, but the group generally includes small plaque parapsoriasis (digitate dermatoses, chronic superficial dermatoses), a benign condition, and large plaque parapsoriasis, which may be a precursor of CTCL in a proportion of cases.
Pityriasis lichenoides (acuta and chronica), a benign lymphoproliferative disorder of unknown cause, is sometimes included in this category.
INVESTIGATIONS
No specific diagnostic finding on histology to define parapsoriasis, which is a clinicopathologic correlation.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer