Tests
1st tests to order
enzyme assay
Test
It is important to check with the laboratory before sending the sample. It may be appropriate to request assay of a single enzyme (e.g., glucocerebrosidase if Gaucher disease is suspected), or of a group of enzymes (e.g., requesting leukocyte enzyme assay as a screen for mucopolysaccharidosis [MPS] disorders). Specimens are subject to decay.
Plasma and leukocyte activity may need to be tested in some conditions: for example, Fabry disease.
Cultured fibroblasts are a good source of enzyme to assay; DNA will also be available.
Result
reduced activity of deficient enzyme; increased activity of some other enzymes in metabolic pathway; in the X-linked lysosomal storage diseases (e.g., Fabry, MPS II), heterozygous females can often have values that are borderline, as about half of their cells will be normal
substrate assay
Test
Urinary glycosaminoglycans will be elevated in the mucopolysaccharidosis disorders.[61] Urinary levels of globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) are elevated in Fabry disease. Urinary glucose tetrasaccharide (Glc4) and plasma glucose tetrasaccharide (Hex4) levels are increased in patients with Pompe disease.[62] Plasma levels of glucosylceramide are elevated in Gaucher disease.
Result
elevated substrate related to deficient enzyme
DNA analysis
Test
It is important to check with the laboratory before sending the sample. The result needs to be considered in light of detailed clinical information and data on enzyme activity.
Some mutations are polymorphisms and may not be associated with disease. Many polymerase chain reaction tests only screen for common mutations; "private" mutations are only detected by sequence analysis in research laboratories.
Denaturing high-pressure liquid chromatography is a method for rapid screening for single-base mutations.
Carrier detection in X-linked disorders can only be reliably achieved by DNA analysis.
If there are existing genetic test results, do not perform repeat testing unless there is uncertainty about the existing result, e.g., the result is inconsistent with the patient’s clinical presentation or the test methodology has changed.[65]
Not all mutations have been analyzed and some disorders will only be diagnosed in specialist laboratories; it is essential that specialist centers are consulted in the design and implementation of the diagnostic strategy for these rare diseases.
Result
mutation in gene of interest
CBC
Test
Anemia may be multifactorial due to chronic disease, renal impairment, feeding difficulties, marrow replacement.[30]
Leukopenia typically due to splenomegaly.
Abnormal inclusions in leukocytes: for example, periodic acid-Schiff-positive lymphocytes in Pompe disease; abnormal leukocyte appearances in blood/marrow in Tay-Sachs.[66][86]
Thrombocytopenia typically due to splenomegaly; disturbed platelet function in, for example, Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome.[67]
Result
anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
Tests to consider
ECG
echocardiogram
pulmonary function tests
Test
Critical in Niemann-Pick types A and B. Useful in assessing severity.
Result
abnormal lung function: airway obstruction, deficient gas transfer
bone marrow biopsy
Test
Bone marrow biopsy is often undertaken in the investigation of hepatosplenomegaly and may reveal characteristic storage cells such as substrate-laden macrophages in Gaucher disease.[71][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Bone marrow aspirate showing a typical Gaucher cell. This is a macrophage that has ingested cellular material; the undegraded substrate (glucosyl ceramide) accumulates within lysosomesFrom the personal collection of Professor Atul B. Mehta [Citation ends].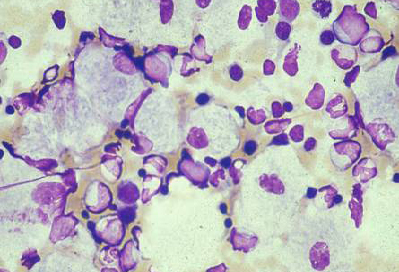
Result
characteristic storage cells
muscle biopsy
Test
Muscle biopsy is of diagnostic utility in many lysosomal storage diseases (e.g., late-onset Pompe; however, appearances may be normal).[72]
Result
abnormal
CT/MRI of enlarged organ (Gaucher)
Test
CT and MRI can measure organ volumes and assess the skeleton in Gaucher disease.[42][75][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Skeletal magnetic resonance imaging in type 1 Gaucher disease showing widespread skeletal deposition of substrate with associated necrosis and bony infarction. There is avascular necrosis of the head of the femur (arrow)From the personal collection of Professor Atul B. Mehta [Citation ends].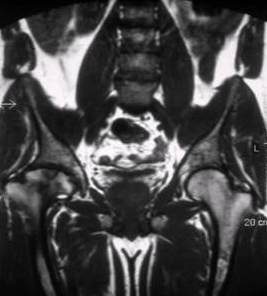
Result
enlarged
ultrasound/MRI (Fabry)
CT/x-ray (mucopolysaccharidosis)
Test
CT and x-ray can assess communicating hydrocephalus, atlanto-axial dysplasia, and spinal/vertebral anomalies in mucopolysaccharidosis disorders.[78]
Result
abnormal
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer