Images and videos
Images
Common hereditary lysosomal storage diseases
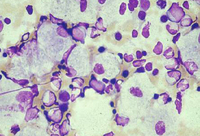
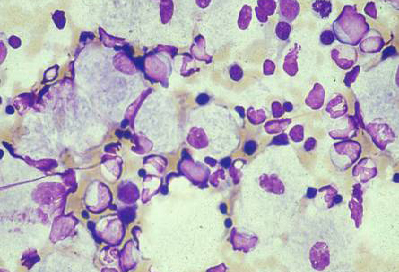
Bone marrow aspirate showing a typical Gaucher cell. This is a macrophage that has ingested cellular material; the undegraded substrate (glucosyl ceramide) accumulates within lysosomes
From the personal collection of Professor Atul B. Mehta
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Common hereditary lysosomal storage diseases
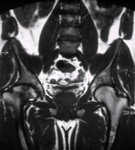
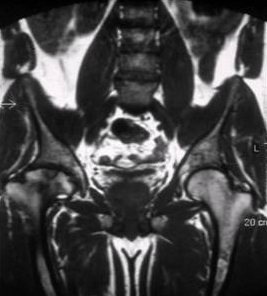
Skeletal magnetic resonance imaging in type 1 Gaucher disease showing widespread skeletal deposition of substrate with associated necrosis and bony infarction. There is avascular necrosis of the head of the femur (arrow)
From the personal collection of Professor Atul B. Mehta
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Common hereditary lysosomal storage diseases
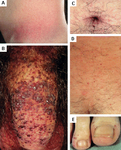
Cutaneous lesions in Fabry disease: (A) flank, (B) genitals, (C) umbilicus, (D) lower back, (E) toes
Orteu CH, Jansen T, Lidove O, et al. Fabry disease and the skin: data from FOS, the Fabry Outcome Survey. Br J Dermatol. 2007 Aug;157(2):331-7; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Common hereditary lysosomal storage diseases
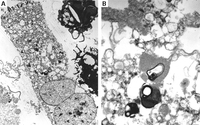
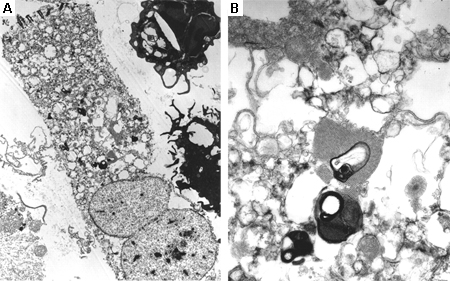
Electron microscope image of biopsy of pulmonary epithelial cells in Fabry disease showing the characteristic deposits of substrate in lysosomes, forming "zebra bodies": (A) magnification x8000, (B) magnification x62,500
Kelly MM, Leigh R, McKenzie R, et al. Induced sputum examination: diagnosis of pulmonary involvement in Fabry's disease. Thorax. 2000 Aug;55(8):720-1; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Common hereditary lysosomal storage diseases
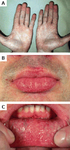
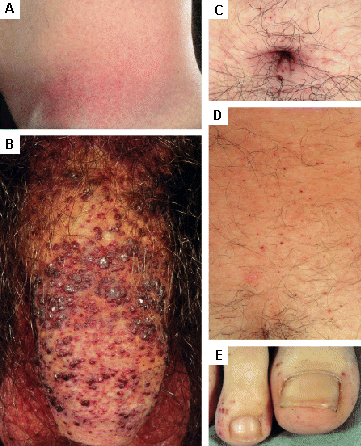
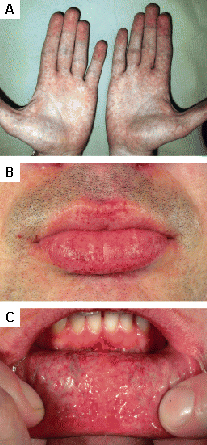
Cutaneous lesions in Fabry disease: (A) palms, (B) lips, (C) labial mucosa
Orteu CH, Jansen T, Lidove O, et al. Fabry disease and the skin: data from FOS, the Fabry Outcome Survey. Br J Dermatol. 2007 Aug;157(2):331-7; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer