Tests
1st tests to order
high-resolution chest CT
Test
High-resolution CT scan is the best diagnostic tool for bronchiectasis in adults. In children and adolescents, high-resolution multidetector CT (MDCT) scans and a lower diagnostic threshold (broncho-arterial dilatation >0.8 vs. the adult cutoff of >1 to 1.5) are recommended due to the importance of early diagnosis on improving prognosis.[9]
Shows dilatation of bronchi with or without airway thickening.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Severe cystic and varicose bronchiectasis in a 49-year-old man with idiopathic bronchiectasis and scoliosisFrom Pamela J. McShane, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].
In cross-sectional appearance, the bronchi are larger than their adjacent pulmonary artery (signet ring sign).[62][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest computed tomography scan with presence of signet ring on leftFrom archives of Dr Sangeeta M. Bhorade; used with permission [Citation ends].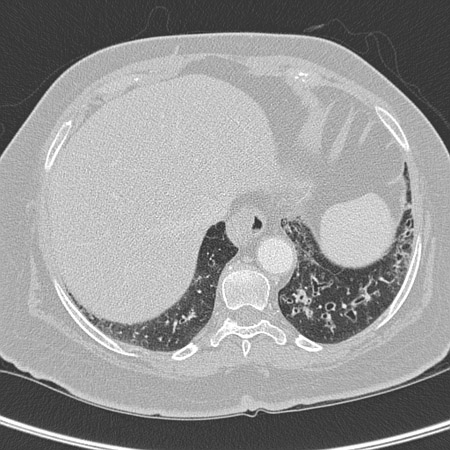 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Signet ring signs in a 20-year-old woman with bronchiectasisFrom Pamela J. McShane, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Signet ring signs in a 20-year-old woman with bronchiectasisFrom Pamela J. McShane, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].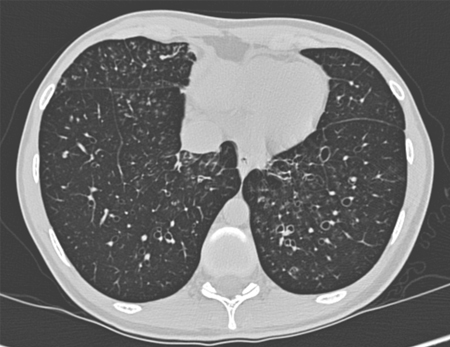
Abnormal bronchial dilation is recognized as the lack of normal tapering of bronchi, producing a tram line or flared appearance in the periphery of the lung; more prominent when the bronchial walls are thickened.
Affected small airways plugged by mucus appear as small, irregular, V- and Y-shaped markings 2 mm in size in the periphery of the lung (tree-in-bud pattern).[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest computed tomography scan with dilated and thickened airways and peripheral tree-in-bud patternFrom archives of Dr Sangeeta M. Bhorade; used with permission [Citation ends].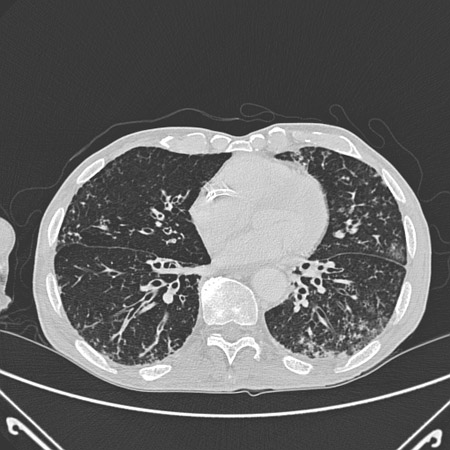
May show fluid-filled cysts; these represent superimposed infection and warrant a course of systemic antibiotics.
Result
thickened, dilated airways with or without air fluid levels; varicose constrictions along airways; cysts and/or tree-in-bud pattern
CXR
Test
Findings are nonspecific and often nondiagnostic, but may show characteristic volume loss obscuring the underlying hemidiaphragm, tram lines, and tubular or ovoid opacities.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray with dilated and thickened airwaysFrom archives of Dr Sangeeta M. Bhorade; used with permission [Citation ends].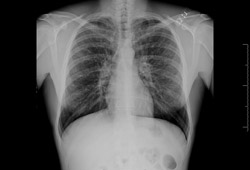 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray with lack of normal tapering producing a tram lineFrom archives of Dr Sangeeta M. Bhorade; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray with lack of normal tapering producing a tram lineFrom archives of Dr Sangeeta M. Bhorade; used with permission [Citation ends].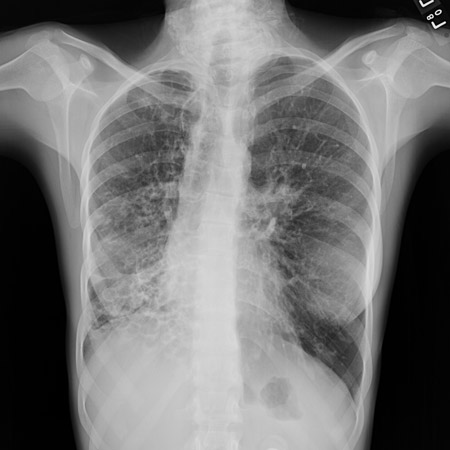
Thin-walled ring shadows with or without fluid levels may also be present.
Although chest CT scan is the diagnostic procedure of choice, a baseline CXR may provide a useful comparator if there is subsequent clinical deterioration.[45]
In a child with a chronic wet cough, a chest x-ray can be used to exclude other causes, such as a foreign body or pneumonia.[59]
Result
may be normal or show obscured hemidiaphragm, thin-walled ring shadows with or without fluid levels, tram lines, tubular or ovoid opacities
CBC
Test
The WBC count will aid in determining the presence of a superimposed infection or exacerbation.
If the eosinophil count is high, an underlying allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis is possible.
Result
WBC differential may reveal high eosinophil count in bronchopulmonary aspergillosis; neutrophilia suggests superimposed infection or exacerbation
sputum culture and sensitivity
Test
Specimens for bacterial, fungal, and acid-fast bacilli cultures are recommended for all patients. Single or multiple pathogens may be present. Aids in guiding antibiotic selection.
Frequently, a pathogenic organism can be recovered in the sputum. There may be single or multiple pathogens present. The most common gram-negative organism is Pseudomonas aeruginosa, present in about 25% of patients; it may be in mucoid form. Mucoid P aeruginosa has been shown to correlate with lower pulmonary function and is a marker for severe lung damage.[49][50] It requires special attention because it is more likely to be resistant to antibiotics than nonmucoid Pseudomonas species.[51]
Specimens for bacterial culture may be requested as "cystic fibrosis bacterial culture" in patients who are at high risk for Pseudomonas or who have had Pseudomonas growth in sputum cultures in the past. This will allow for special vigilance for mucoid-type Pseudomonas, which has been shown to correlate with lower pulmonary function. A cystic fibrosis bacterial culture employs separate agars to select for gram-negative bacterial growth, as well as Burkholderia cepacia. Sensitivities for these cultures are done by manual disk diffusion because mucoid Pseudomonas does not grow well by automated methods.
Gram-positive cocci (Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, or beta-hemolytic streptococci) represent about 18% of positive sputum cultures.
Other common gram-negative organisms are Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella pneumonia, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Serratia marcescen. Mycobacteria are commonly isolated as well.
Infectious disease consultation may be needed if nontuberculous mycobacteria is present in sputum cultures.[47]
Other organisms that may be cultured include fungi (especially Aspergillus) and Nocardia. These may not initially be of clinical significance but may require treatment if they are repeatedly cultured from an individual patient.[52][53]
Result
gram-positive bacteria; gram-negative bacteria; nontuberculous mycobacteria; fungi
serum alpha-1 antitrypsin phenotype and level
Test
Recommended to identify alpha-1 antitrypsin disease as underlying etiology in patients with coexisting basal panacinar emphysema.[45]
Referral for consideration of replacement therapy is suggested if abnormal phenotype or level.
The MM phenotype indicates patient is homozygous for the normal M allele.[55]
Result
may be abnormal phenotype or level
serum immunoglobulins
Test
Immunoglobulin levels (serum total IgG, IgM, and IgA), IgG subclasses (IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4), and response to Pneumovax vaccine with Strep pneumo 23 serotype titers are recommended to identify individual immunoglobulin deficiencies as underlying etiology.[45][56] Immunoglobulin replacement reduces the frequency of infectious episodes and prevents further destruction of the airways.
Result
decreased IgG, IgM, and/or IgA with inappropriate titers to Pneumovax
sweat chloride test
Test
Recommended for all children and for adults in whom there is a high index of suspicion for cystic fibrosis because patients may present with variant forms of cystic fibrosis in adulthood.
Minimum testing for a diagnosis of cystic fibrosis to be made should include two measurements of sweat chloride and then cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR) mutation analysis.[54]
Result
≥60 mEq/L cystic fibrosis is likely; 30 to 59 mEq/L cystic fibrosis is possible; <30 mEq/L cystic fibrosis is unlikely
rheumatoid factor
Test
The prevalence of bronchiectasis is increased in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with the general population.
The symptoms of bronchiectasis may precede other systemic findings in rheumatoid arthritis.[37]
Result
positive rheumatoid factor may be detected
specific IgE or skin prick test to Aspergillus fumigatus
Test
Recommended in all patients, in conjunction with CBC and serum total IgE, to investigate for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis.[45]
A diagnosis of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis warrants referral to a pulmonary specialist.
Result
immediate cutaneous reactivity to antigen in bronchopulmonary aspergillosis; increased IgE
serum HIV antibody
Test
Recommended in all patients.
Patients with HIV infection are predisposed to developing recurrent sinopulmonary infections and bronchiectasis, which is likely due to abnormal B-lymphocyte function.[57]
Result
positive in HIV infection
nasal nitric oxide (NNO)
Test
Recommended for the diagnosis of primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) in cooperative patients 5 years or older with a clinical phenotype consistent with PCD and with cystic fibrosis excluded.[34] It is recommended over transmission electron microscopy and/or genetic testing in this group of patients.[34][58]
Sensitivity of 97% and specificity of 90% for PCD.
A low NNO should be followed up with confirmatory testing because other conditions such as cystic fibrosis may present with low NNO.
A high NNO virtually excludes PCD.
This test is not available in all centers.
Result
low (<100 parts per billion) NNO level in primary ciliary dyskinesia, if cystic fibrosis is excluded; high NNO level excludes a diagnosis of PCD
pulmonary function tests
Test
Spirometry is recommended with most office visits for those patients old enough to cooperate with the test. Obstructive airways disease may be evidenced by reduced forced expiratory volume in the first second of expiration (FEV₁) or an FEV₁/forced vital capacity (FVC) ratio of <70%.[47] Reduction of the FEV₁ suggests the presence of infection or worsening bronchiectasis.
Diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) may be reduced in severe disease.
Result
reduced FEV₁, elevated residual volume (RV)/total lung capacity (TLC)
Tests to consider
primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) testing
Test
Extended genetic panel testing or microscopy of ciliary structure can be used to confirm a diagnosis of primary ciliary dyskinesia.
Nasal or bronchial tissue is analyzed by video microscopy to evaluate ciliary beat motion and, under electron microscopy, to evaluate ciliary ultrastructure.[34]
Lipid-laden macrophages seen in bronchial biopsy specimens suggest aspiration.
Extended genetic panel testing (>12 genes) can be used as a diagnostic test in patients with a high probability of having PCD.[34]
Result
abnormal ciliary beat motion and/or morphology in primary ciliary dyskinesia; discovery of PCD-causing genes
cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR) protein gene mutation testing
Test
Minimum testing for a diagnosis of cystic fibrosis to be made should include two measurements of sweat chloride and then CFTR mutation analysis.[54]
Result
positive in cystic fibrosis
swallow study
Test
Suggested to evaluate for chronic aspiration.
If a swallow study suggests the presence of aspiration, referral to a gastroenterologist and/or otolaryngologist is recommended.
Result
may be abnormal in presence of chronic aspiration
pH monitoring of esophagus
Test
Suggested to evaluate for chronic aspiration. May be done by a gastroenterologist in some centers.
If pH monitoring suggests the presence of aspiration, referral to a gastroenterologist is recommended.
Result
low pH in patients with chronic aspiration
6-minute walk test
Test
Should be considered for patients at risk for desaturation with exercise. Can be used to assess serial changes in functional capacity.
Result
reduced in those with significantly reduced lung function
tuberculosis testing
Test
Consider for children in high-prevalence settings or with a history of close contract with tuberculosis.[9]
Result
positive in tuberculosis infection
diagnostic bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage
Test
May be used to exclude a foreign body and to obtain microbiologic samples.[9]
Result
foreign body excluded; also, used to obtain microbiologic samples
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer