Investigations
1st investigations to order
FBC
Test
Order in patients with a non-specific viral illness and a history of exposure to rodent excreta.
During the prodromal phase, thrombocytopenia with a supporting epidemiology is suggestive of hantavirus infection. The degree of thrombocytopenia may be prognostic of poor outcome.[5]
Circulating immunoblast cells constituting >10% of the total lymphocyte count are highly suggestive of hantavirus infection.[49]
Haemoconcentration as indicated by an elevated Hb and haematocrit (Hct) is a marker for capillary leak and may signal the beginning of the cardiopulmonary phase.
Result
platelet count < 150 x 10⁹/L (<150 x 10³/microlitre) is an early clue; leukocytosis with immunoblasts; elevated Hb and Hct
chest x-ray
Test
May be normal or suggestive of early interstitial oedema. It can show diffuse interstitial oedema early in the cardiopulmonary phase progressing to severe diffuse pulmonary oedema with or without effusions.[56][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Bilateral fluffy pulmonary infiltrates in hantavirus pulmonary syndromeCDC Public Health Image Library (PHIL), Loren Ketai, MD [Citation ends].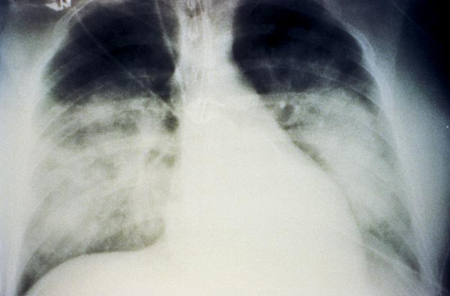
Result
normal in early disease; diffuse interstitial oedema; severe diffuse pulmonary oedema with or without effusions
IgM and IgG serologies for hantavirus
Test
Order if the clinical syndrome and epidemiology are suggestive of hantavirus infection.
Patients uniformly have antiviral antibodies of IgM class, and many have antibodies of IgG class, by the time the symptoms are evident.
These serology tests are available commercially.
Result
positive
reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
Test
This test is able to determine the specific type of hantavirus causing the infection. It is done in reference laboratories and not used as acute diagnostic testing.
Result
positive
Investigations to consider
ABG
Test
May occur during severe cardiopulmonary disease.
Result
cardiopulmonary phase: hypoxia, metabolic acidosis
serum lactate
Test
Serum lactate >4.5 mmol/L is a prognosticator of poor outcome.
Result
>4.5 mmol/L
ECG
Test
As disease progresses, the ECG may show arrhythmias ranging from a sinus bradycardia to ventricular fibrillation.
Result
arrhythmia
echocardiogram
Test
During the cardiopulmonary phase, the patient will have a decreased left ventricular ejection fraction.
Result
decreased left ventricular ejection fraction
flow-directed pulmonary artery catheter (Swan-Ganz catheter)
Test
During the cardiopulmonary phase, a decreased cardiac index and increased peripheral resistance are seen, distinguishing the shock from septic shock, which has a low systemic resistance and high cardiac output. Peripheral resistance and cardiac index are assessed using a flow-directed pulmonary artery catheter. A cardiac index of <2.5 L/minute/m² is one of the criteria for instituting extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.[44][53]
Result
decreased cardiac index, increased peripheral vascular resistance
lung biopsy
Test
May be performed either transbronchially at bronchoscopy or by video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery in patients with unexplained rapidly progressive pulmonary disease.
Immunohistochemical staining for hantavirus RNA shows diffuse endothelial cell staining.[53][54] This is available as a research test through the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Result
intra-alveolar oedema with an interstitial infiltrate of immunoblasts
Emerging tests
serum viral-RNA load
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer