Differentials
Common
Alcohol induced
History
history of alcohol use or misuse
Exam
splenomegaly, spider telangiectasias, ascites, palmar erythema, jaundice, encephalopathy
1st investigation
- FBC with differential and peripheral smear:
anaemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, target red blood cells, spur cells
- comprehensive metabolic panel:
elevated aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase; direct hyperbilirubinaemia
More - coagulation tests:
prolonged prothrombin time and PTT; low fibrinogen
Other investigations
- abdominal CT scan:
shrunken nodular liver; enlarged homogeneous spleen; ascites
- upper endoscopy:
oesophageal varices
- liver biopsy:
bridging fibrosis between portal triads
More
Hepatic steatosis
History
absence of significant alcohol use; obesity, insulin resistance or diabetes, hyperlipidaemia and/or hypertension (metabolic syndrome); rapid weight loss; total parenteral nutrition; early disease: pruritus, fatigue, malaise, right upper quadrant discomfort; late disease: increasing abdominal girth, haematemesis
Exam
early disease: mild hepatomegaly; late/advanced disease: sequelae of portal hypertension such as splenomegaly, ascites, variceal bleeding, jaundice
1st investigation
- comprehensive metabolic panel:
mildly elevated aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase; elevated total bilirubin
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)
History
age between 45 and 60 years, female sex, autoimmune disease (personal or family history); early disease: fatigue, pruritus; late/advanced disease: steatorrhoea, metabolic changes (weight loss, muscle mass loss, and skin thinning)
Exam
early disease: xanthelasma; late/advanced disease: sequelae of portal hypertension (splenomegaly, ascites, variceal bleeding, jaundice)
1st investigation
- liver function tests:
markedly elevated alkaline phosphatase and/or gamma glutamyl transpeptidase concentrations; elevated bilirubin; hypercholesterolaemia
- antimitochondrial antibodies:
elevated in 95% of patients with PBC
- serum cholesterol:
hypercholesterolaemia
- serum immunoglobulin:
increased levels of IgM
Other investigations
- FBC with reticulocyte count and peripheral smear:
possible thrombocytopenia
- anti-nuclear antibodies:
nearly all anti-mitochondrial antibody-negative patients have PBC-specific anti-nuclear antibodies
More - liver biopsy:
florid bile duct lesion with granuloma formation
More - transient elastography:
identifies and quantifies liver fibrosis
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
History
age between 40 and 50 years, male sex, history of inflammatory bowel disease (typically ulcerative colitis but possibly Crohn's colitis); early disease: fatigue, upper abdominal pain, pruritus; late/advanced disease: steatorrhoea, weight loss
Exam
late/advanced disease: jaundice, splenomegaly, ascites, encephalopathy, oesophageal variceal bleeding, and/or fever (from episodic bacterial cholangitis)
1st investigation
- liver function tests:
usually cholestatic pattern
More
Other investigations
- serum immunoglobulins:
elevated polyclonal IgG and IgM
- magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP):
strictures and dilation of intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts[66]
- liver biopsy:
obliteration of bile ducts by fibrous tissue
- FBC with reticulocyte count and peripheral smear:
normal or thrombocytopenia, anaemia, and/or leukopenia
Haemochromatosis
History
family history of haemochromatosis; arthralgias, diabetes mellitus; lethargy, fatigue, loss of libido
Exam
splenomegaly, skin bronzing, small testes, amenorrhoea, cardiomyopathies, arrhythmias, heart failure
1st investigation
- serum iron level, serum ferritin, transferrin-iron saturation:
elevated ferritin level, increased transferrin saturation (homozygotes >45%)
- unsaturated iron binding capacity:
<26 micromol/L has a sensitivity of 90% and specificity of 90% for detecting C282Y homozygosity
More - HFE genetic testing:
C282Y mutation homozygosity (p.Cys282Tyr)
- CRP:
normal
More - liver function tests:
increased aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase
- fasting blood sugar:
may be elevated
Other investigations
- serum alpha-fetoprotein:
increased in advanced stage
- liver MRI:
loss of signal intensity in the liver suggests iron overload, splenic iron deposition suggests secondary iron overload
- liver biopsy:
excess tissue iron
- ECG:
decreased QRS amplitude and T-wave flattening or inversion
- echocardiogram:
restrictive cardiomyopathy
Hodgkin's lymphoma
History
may be asymptomatic; or B symptoms such as fever (especially afternoon or evening), night sweats, weight loss, several months' history of persistent adenopathy; rarely, generalised pruritus and alcohol-induced pain in the spleen area or in pathologically enlarged nodes; uncommonly, enlarged lymph nodes may cause shortness of breath, cough, chest pain, abdominal pain, superior vena cava syndrome
Exam
splenomegaly (age >60 years), cervical and/or supraclavicular lymphadenopathy (young adults); bruising or petechiae (suggesting thrombocytopenia)
1st investigation
- FBC with differential and peripheral smear:
elevated white blood cell count with circulating malignant cells; lymphocytosis on peripheral smear
- CT with contrast: neck, chest, and abdomen/pelvis:
may show enlarged lymph nodes and other sites of disease
- PET scan:
involved sites appear fluorodeoxyglucose avid (bright)
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL)
History
clinical history depends on the type of lymphoma and the stage at presentation; low-grade NHL: often minimally symptomatic or asymptomatic; high-grade NHL: B symptoms (fever, drenching night sweats, weight loss), pallor (anaemia), purpura (thrombocytopenia), jaundice (liver failure), left upper quadrant pain; T-cell NHL: can present with B symptoms similar to B-cell NHL, pruritus may also occur
Exam
lymphadenopathy, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, skin nodules, abnormal neurological examination
1st investigation
- FBC with differential:
elevated white blood cell count with circulating malignant cells; anaemia, leukopenia, or thrombocytopenia
- peripheral smear:
lymphocytosis
- serum lactate dehydrogenase:
elevated
- lymph node biopsy:
positive
- bone marrow biopsy:
positive
More
Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia or lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma
History
family history of Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia; often asymptomatic, but non-specific symptoms may be reported (weakness and fatigue, anorexia and weight loss, abdominal pain); skin and mucosal bleeding; visual disturbances; neurological symptoms such as headache and dizziness
Exam
splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, lymphadenopathy, retinopathy
1st investigation
- FBC with differential:
anaemia; other cytopenias are less common
- basic metabolic panel:
derangements may be present and should raise suspicion of lymphoblastic lymphoma
- high-resolution serum electrophoresis with immunofixation:
positive for kappa or lambda IgM monoclonal component; kappa IgM is more common in Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia
More - serum free light chains:
elevated in proportion to tumour burden
More
Other investigations
- bone marrow examination:
intertrabecular monoclonal lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, ranging from predominantly lymphocytic to lymphoplasmacytic to overt plasma cells
More
Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML)
History
prior history of haematological disease; chemotherapy; genetic disorders (chromosomal fragility and/or bone marrow failure disorders; chromosomal trisomies); exposure to radiation or benzene; fatigue, fevers, bleeding gums or nose, menorrhagia in females, bone pain, skin rash, or masses
Exam
pallor, ecchymoses, petechiae, extramedullary infiltration (hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, skin and testicular masses), infection (dental abscess, nasopharyngeal, chest, or perianal), cutis infiltration, cutaneous ulcers (Sweet's syndrome or pyoderma gangrenosum); rarely, acute abdomen
1st investigation
- FBC with differential:
anaemia, neutropenia, and/or thrombocytopenia
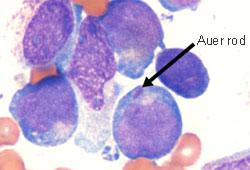
More - peripheral blood smear:
myeloid blasts characterised by Auer rods or phi bodies
More - coagulation profile:
prothrombin time, PTT may be prolonged, D-dimer elevated, fibrinogen decreased
More - serum lactate dehydrogenase:
may be elevated
More
Other investigations
- bone marrow examination:
abundance of myeloblasts
Chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML)
History
fever, chills, malaise, weight loss, night sweats, abdominal fullness or left upper quadrant pain, excessive bruising
Exam
splenomegaly; hepatomegaly may be present with a soft, ill-defined lower edge; pallor of mucous membranes
1st investigation
- FBC with differential:
elevated white blood cell count, anaemia, thrombocytopenia
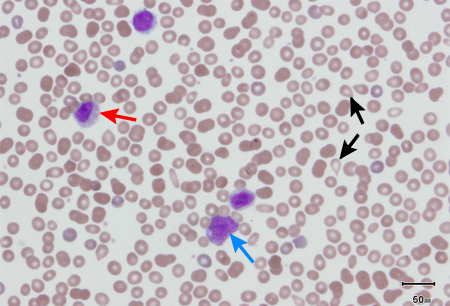
More - peripheral blood smear:
myeloid maturing cells, elevated basophils, eosinophils, and granulocyte precursors
More - BCR-ABL gene rearrangement analysis:
positive
- bone marrow biopsy:
granulocytic hyperplasia
More - cytogenetics:
positive for Philadelphia chromosome t(9,22)
More
Other investigations
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL)
History
fatigue, dyspnoea, dizziness, bleeding, easy bruising; recurrent infections with fever, abdominal pain, bone pain; history of malignancy, chemotherapy, exposure to radiation or environmental toxins and pollutants, smoking
Exam
pallor, ecchymoses, petechiae, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, abdominal or testicular masses, renal enlargement, skin infiltrations
1st investigation
Other investigations
- bone marrow biopsy or aspiration:
bone marrow hypercellularity and infiltration by lymphoblasts
More - immunophenotyping and HLA typing:
presence of surface antigens and molecular markers helps to identify ALL-specific lineage; HLA typing results are variable
More - chest x-ray:
exclusion of mediastinal mass, pleural effusion, or lower respiratory tract infections
Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL)
History
asymptomatic in 20% to 40% of cases; constitutional symptoms (fever, night sweats, and weight loss), abdominal fullness, and pain in the left upper quadrant; excessive bruising
Exam
lymphocytosis or lymph node enlargement, splenomegaly in 75% of cases, hepatomegaly may also be present
1st investigation
Other investigations
- flow cytometry:
presence of B cells or T cells
More
Hairy cell leukaemia
History
asymptomatic or fatigue, abdominal pain, fever, weight loss
Exam
palpable massive splenomegaly; less often, hepatomegaly and lymphadenopathy
1st investigation
- FBC with differential:
pancytopenia
- peripheral blood smear:
presence of hairy cells
- bone marrow trephine biopsy and aspiration (morphology assessment):
presence of hairy cells in the bone marrow
More
Other investigations
- immunophenotyping (immunohistochemistry or flow cytometry):
positive
More
Myelofibrosis
History
gradual onset of fatigue and left upper quadrant pain
Exam
massive splenomegaly (pain and early satiety); spleen infarction: acute exacerbation of pain, fever; signs of spontaneous spleen rupture (abdominal and/or left shoulder pain, hypotension, tachycardia)
1st investigation
- peripheral smear:
nucleated red cells, teardrop cells, leukoerythroblastic changes
More - bone marrow biopsy:
fibrosis (fibroblasts, collagen, and reticulin)
Other investigations
- abdominal CT scan:
enlarged spleen; perisplenic fluid collection (if splenic infarction has occurred)
Polycythaemia vera
History
age >40 years; frequently asymptomatic; aquagenic pruritus, bleeding; patients evolving to a 'spent phase' may have weight loss, fever, night sweats
Exam
splenomegaly or hepatosplenomegaly; plethora
1st investigation
- FBC with differential:
elevated red blood cells and Hb/haematocrit; white blood cell count and platelets often elevated
- peripheral smear:
densely packed erythrocytes
Other investigations
- JAK2 mutation (V617F):
present in most cases (90%)
- serum erythropoietin:
low
Essential thrombocytosis
History
headache, painful burning in palms or soles
Exam
splenomegaly or hepatosplenomegaly; digital ischaemia, gangrene, thrombosis, bleeding, infection, malignancy
1st investigation
Other investigations
- JAK2 mutation (V617F):
present in about 60% of cases
- bone marrow biopsy:
megakaryocytic hyperplasia
More
Splenic metastases
History
weight loss, cough, change in bowel habits (suggests colon cancer), pain in the left upper quadrant
Exam
breast lump, signs of lung consolidation or effusion, faecal occult blood
1st investigation
- abdominal CT scan:
may show multiple tumours in the spleen that have metastasised from primary tumour sites, particularly colon or breast
More
Other investigations
- FBC with reticulocyte count and peripheral smear:
normal or anaemia
Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia
History
gradual onset of fatigue
Exam
mild splenomegaly, jaundice, anaemia
1st investigation
Other investigations
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
History
joint deformities; history of bilateral, symmetrical pain and swelling of the small joints of the hands and feet (>6 weeks); morning stiffness
Exam
mild-to-moderate splenomegaly, synovial effusions, decreased joint mobility
1st investigation
Other investigations
- FBC with reticulocyte count and peripheral smear:
variable; possible anaemia, leukocytosis or leukopenia, thrombocytosis or thrombocytopenia
Felty syndrome
History
white ancestry, previous history of rheumatoid arthritis (>10 years), family history of rheumatoid arthritis
Exam
splenomegaly, joint deformities
1st investigation
Other investigations
- bone marrow aspiration and biopsy:
typically myeloid hyperplasia with maturation arrest of granulocyte lineage
More
Systemic lupus erythematosus
History
fatigue, fever, weight loss, arthralgias, sun sensitivity, Raynaud's phenomenon, alopecia, fluid retention
Exam
mild-to-moderate splenomegaly, synovial effusions, decreased joint mobility
1st investigation
- FBC with differential:
anaemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia; rarely, pancytopenia
- activated partial thromboplastin time:
may be prolonged in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies
- serum urea and creatinine:
may be high
- serum anti-nuclear antibodies:
positive
Other investigations
- bone marrow biopsy:
presence of reticulin fibrosis
More
Sarcoidosis
History
family history of sarcoidosis, chronic fatigue, weight loss, low-grade fever, cough, dyspnoea, arthralgia (knees, ankles, elbows, and wrists)
Exam
enlarged and non-tender lymph nodes, enlarged spleen (causing pain and inanition), hepatomegaly, erythema nodosum, and lupus pernio
1st investigation
- FBC with differential:
mild leukopenia, lymphopenia, anaemia
More - serum urea and creatinine:
may be elevated
- serum liver enzymes:
aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase may be elevated
- serum calcium:
elevated
- chest x-ray:
hilar and/or paratracheal adenopathy with predominantly upper lobe bilateral infiltrates
- ECG:
conduction abnormalities
More - serum ACE:
elevated
Malaria
History
recent travel to endemic areas; chronic malarial parasite exposure leading to hyper-reactive malarial splenomegaly (HMS); fever, chills, headache, loss of appetite, epigastric pain, body aches
Exam
splenomegaly; may be absent in non-immune falciparum malaria
1st investigation
- FBC with differential:
usually normocytic, normochromic anaemia; sometimes monocytosis, leukopenia, and thrombocytopenia
- peripheral blood smear:
detection of the asexual forms of parasites inside erythrocytes
More
Other investigations
- antimalarial antibodies and IgM titre:
elevated in HMS
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
History
fevers, sore throat
Exam
posterior cervical lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly; prominent hepatosplenomegaly with generalised adenopathy in immunocompromised patients
1st investigation
Other investigations
- LFTs:
raised transaminases
Endocarditis
History
recent dental work, intravenous drug abuse, constitutional symptoms (fevers, night sweats, weight loss)
Exam
splenomegaly, new cardiac murmurs, Janeway lesions, Roth spots
1st investigation
- FBC with differential, reticulocytes, and peripheral smear:
leukocytosis
- blood cultures:
positive for bacteria or fungus
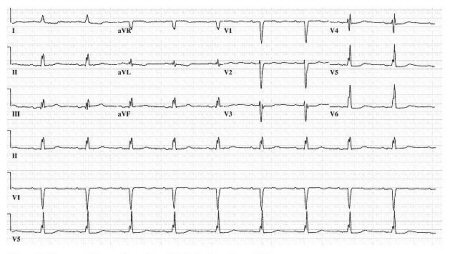
- ECG:
prolonged PR interval; non-specific ST-T wave abnormalities; AV block
More - echocardiogram:
valvular vegetations
Other investigations
- CT scan abdomen:
splenic abscess
- trans-oesophageal echocardiogram:
splenomegaly, hypoechoic splenic infarcts or haematoma
Sepsis-related splenic abscesses
History
history or symptoms referable to urinary, pulmonary, soft-tissue, or intravenous line source of septicaemia; fever and chills
Exam
mild-to-moderate splenomegaly, tachypnoea, tachycardia, hypotension
1st investigation
- FBC with differential, reticulocytes, and peripheral smear:
leukocytosis
- blood, urine, and sputum cultures:
positive for aetiological organism
Other investigations
- CT scan abdomen:
splenic abscess
Chronic hepatitis C
History
frequently asymptomatic; history of intravenous drug abuse or transfusions
Exam
end-stage: splenomegaly without hepatomegaly; ascites, jaundice, spider telangiectasias, palmar erythema, signs of encephalopathy
1st investigation
- hepatitis C antibody:
positive
More
Other investigations
- quantification of hepatitis C by polymerase chain reaction:
quantifies viral burden
- FBC with reticulocyte count and peripheral smear:
possible anaemia or thrombocytopenia
- abdominal CT scan:
shrunken nodular liver with enlarged spleen
Chronic hepatitis B
History
frequently asymptomatic; history of intravenous drug use or living in an endemic area
Exam
end-stage: splenomegaly without hepatomegaly; ascites, jaundice, spider telangiectasias, palmar erythema, signs of encephalopathy
1st investigation
- serum HBsAg:
positive
More
Other investigations
- quantification of hepatitis B by polymerase chain reaction:
quantifies viral burden
- FBC with reticulocyte count and peripheral smear:
possible anaemia or thrombocytopenia
- abdominal CT scan:
shrunken nodular liver with enlarged spleen
Sickle cell anaemia
History
African ancestry, positive family history of sickle cell disease, lifelong jaundice, bone pain
Exam
signs of haemolysis (jaundice, pallor, or tachycardia) or splenic sequestration crisis (pallor, tachycardia or shock, purpura, and petechiae); splenomegaly
1st investigation
- FBC with differential:
anaemia, leukocytosis, thrombocytosis
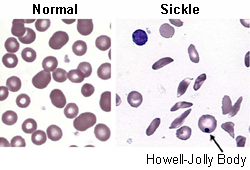
- peripheral blood smear:
presence of nucleated red blood cells, sickle-shaped cells, and Howell-Jolly bodies
More - reticulocyte count:
decreased
Other investigations
- haemoglobin electrophoresis:
migration of haemoglobin S
More
Cytoskeletal defects
History
positive family history, lifelong jaundice, recurrent bouts of symptomatic anaemia/fatigue after viral infections (hereditary spherocytosis)
Exam
splenomegaly, jaundice
1st investigation
- FBC with differential:
anaemia
More - peripheral blood smear:
hereditary elliptocytosis: elliptocytes
- reticulocyte count:
elevated
Other investigations
- Coombs test:
negative
- serum fractionated bilirubin:
indirect hyperbilirubinaemia
- osmotic fragility tests:
increased osmotic fragility in hereditary spherocytosis
Thalassaemias
History
Mediterranean or Southeast Asian ancestry, positive family history, lifelong jaundice
Exam
frontal bossing maxillary expansion, short stature, jaundice, splenomegaly, and hepatomegaly
1st investigation
- FBC with differential:
alpha-thalassaemia: normal-to-low Hb, low MCV, low MCH; beta-thalassaemia: microcytic anaemia, normal-to-elevated leukocyte and platelet counts
- peripheral smear:
thalassaemia major: severe anaemia with mild anisocytosis and poikilocytosis and severe microcytosis
Other investigations
- haemoglobin electrophoresis:
elevated Hb A2 in beta-thalassaemia
- alpha-globin gene deletion analysis:
abnormal in alpha-thalassaemia
Uncommon
Benign splenic tumours
History
often asymptomatic, no unusual history of pain or abdominal swelling
Exam
isolated splenomegaly
1st investigation
- CT scan upper abdomen:
splenomegaly
More
Other investigations
- FBC with differential:
may show low platelet count
- bone marrow biopsy or aspiration:
normal
- splenectomy:
histology: benign lesion such as splenic hamartoma; littoral cell angioma (lesions that are benign growths of endothelial cells and may recur in other organs over time); haemangioma; or cysts
More
Portal vein thrombosis
History
generalised abdominal pain, history of myeloproliferative disorders (polycythaemia vera, especially in young women), history of paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria, history of antiphospholipid antibody syndrome, prior or current treatment with oral contraceptives
Exam
mild-to-severe splenomegaly, epigastric tenderness
1st investigation
Other investigations
- FBC with reticulocyte count and peripheral smear:
leukopenia and/or thrombocytopenia
Splenic vein thrombosis
History
left upper quadrant, generalised abdominal or epigastric pain; history of acute pancreatitis
Exam
rapid-onset tender splenomegaly
1st investigation
- Doppler venous study of portal vein:
occlusion
More - MRI of abdomen:
occlusion of splenic vein
Other investigations
- serum lipase and amylase:
elevated in pancreatitis
More - FBC with reticulocyte count and peripheral smear:
leukopenia and/or thrombocytopenia
Budd-Chiari syndrome
History
personal or family history of thrombophilia, high-dose chemotherapy, history of paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria or myeloproliferative disorders; abdominal pain
Exam
splenomegaly; classic triad of abdominal tenderness (specifically right upper quadrant tenderness), ascites (bulging flank as fluid accumulates), and hepatomegaly; jaundice
1st investigation
- colour and pulsed Doppler ultrasonography:
thrombosis, stenosis, fibrotic cord, or insufficient recanalisation of hepatic and/or caval veins; caudate lobe hypertrophy
- JAK2 mutation (V617F):
positive with underlying myeloproliferative disorder
- LFTs:
elevated aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin; decreased albumin
- urea and creatinine:
elevated in fulminant presentations
- coagulation profile:
prolonged prothrombin time in fulminant presentations
More
Other investigations
- FBC with reticulocyte count and peripheral smear:
leukopenia and/or thrombocytopenia
Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH)
History
acutely ill, fever, may have symptoms and signs of multi-organ failure
Exam
splenomegaly, hepatomegaly may be present
1st investigation
- diagnostic criteria:
criteria satisfied according to HLH-2004 or HScore
More - FBC:
cytopenias affecting ≥2 out of 3 cell lines
More - ferritin:
elevated
More - fibrinogen:
decreased
More - triglycerides:
elevated
More - liver function tests:
increased ALT, AST, bilirubin
- C-reactive protein:
increased
- D-dimer:
increased
Other investigations
- abdominal CT:
imaging to detect splenomegaly
- abdominal ultrasound:
imaging to detect splenomegaly
- bone marrow biopsy:
haemophagocytosis
- natural killer cell activity:
low or absent
- soluble CD25:
elevated
Amyloidosis
History
diarrhoea, weight loss, paresthaesias, dyspnoea, fatigue
Exam
mild-to-severe splenomegaly, lower extremity oedema, macroglossia or periorbital purpura, jugular venous distension
1st investigation
- serum immunofixation:
monoclonal protein
- urine immunofixation:
monoclonal protein
- serum immunoglobulin free light chain assay:
abnormal kappa to lambda ratio
Gaucher's or Niemann-Pick disease
History
Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry, bone pain, infections, oculomotor disturbances, epilepsy, motor disturbances, kyphosis
Exam
hepatosplenomegaly
1st investigation
- glucocerebrosidase assay:
low in Gaucher's disease
Severe dengue
History
resident in or visitor to endemic area, incubation period 4-10 days; abrupt-onset very high fever 39.4°C to 40.5°C (103°F to 105°F) for 5 to 7 days; frontal headache; skin flushing or maculopapular/rubelliform rash, malaise; lethargy/restlessness; anorexia; nausea/vomiting; epigastric discomfort/pain; dizziness; collapse
Exam
hepatomegaly; splenomegaly; ascites; postural dizziness; pleural effusion; haemorrhagic signs include petechiae, purpura, or a positive tourniquet test (inflate a blood pressure cuff to midway between systolic and diastolic blood pressures for 5 minutes; positive if ≥10 petechiae per square inch appear on the forearm); haemorrhagic signs (epistaxis; gingival bleeding; haematemesis; melaena; vaginal bleeding; bleeding from a venipuncture site); hypotension; shock
1st investigation
- FBC:
leukopenia and thrombocytopenia
- reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) in the first 5 days:
positive
More - IgM enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and IgG ELISA after the first 5 days:
positive IgM and IgG in a single serum sample is highly suggestive of dengue infection, while IgM or IgG seroconversion in paired sera or a fourfold IgG titre increase in paired sera confirms the diagnosis
More
Other investigations
- non-structural protein 1 (NS1) day 1-9:
positive
- coagulation studies:
variable
- serum ferritin:
elevated ≥500 nanograms/mL
- LDH:
elevated
- ultrasound:
splenomegaly
More
Splenic rupture
History
recent left-sided abdominal trauma such as motor vehicle accident
Exam
left upper quadrant tenderness; tachypnoea, tachycardia, hypotension
1st investigation
- abdominal CT:
enlarged spleen and large amount of dense fluid consistent with abdominal haemorrhage
Other investigations
- FBC with reticulocyte count and peripheral smear:
low Hb/haematocrit
Subcapsular haemorrhage
History
recent abdominal trauma, especially left-sided
Exam
left upper quadrant tenderness
1st investigation
- abdominal CT:
subcapsular haemorrhage along outer splenic margin
More
Other investigations
- FBC with reticulocyte count and peripheral smear:
low Hb/haematocrit
Secondary to granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)
History
history of receiving G-CSF therapy for neutropenia
Exam
splenomegaly, signs of splenic rupture (rare)
1st investigation
- abdominal CT:
enlarged spleen
Other investigations
- FBC with reticulocyte count and peripheral smear:
leukocytosis; low Hb if splenic rupture
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer