Summary
Definition
History and exam
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- FBC
- reticulocyte count
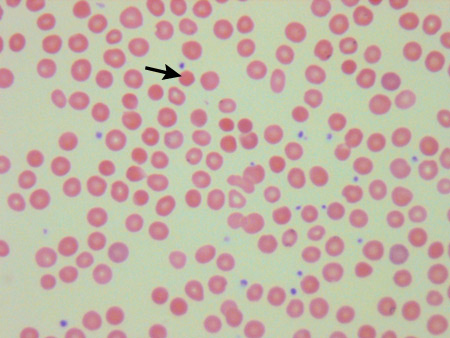
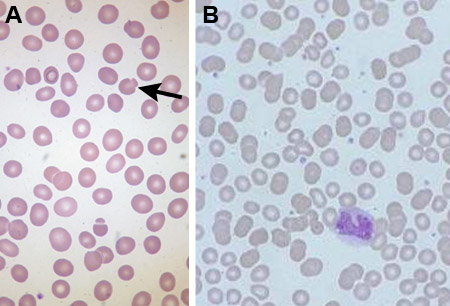
- blood smear
- serum bilirubin
- serum aminotransferases
- direct anti-globulin test (DAT)
Investigations to consider
- eosin-5-maleimide binding test
- acidified glycerol lysis test
- sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Shelley Crary, MD, MSCS
Associate Professor of Pediatrics
University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
Little Rock
AR
Disclosures
SC is reimbursed for membership on a drug and safety monitoring board (Novartis) for a non-related drug.
Acknowledgements
Dr Shelley Crary would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Paula Bolton-Maggs, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
PB-M has received travel and accommodation payments to give a series of lectures on paediatric haematology, one of which was on HS. She also was an expert witness in a legal case concerning a child with HS. PB-M is an author of some references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Robert Schilling, MD
Professor of Medicine Emeritus
School of Medicine and Public Health
University of Wisconsin-Madison
Madison
WI
Disclosures
RS is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer