Differentials
Superior oblique palsy
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Children with congenital superior oblique palsy, also known as ocular torticollis, tend to tilt their head away from the side of the weak superior oblique muscle to restore binocular vision. On examination, if the head is passively tilted towards the affected side, hypertropia or vertical deviation of the eye may be seen, but this is not always obvious.[3]
INVESTIGATIONS
Ophthalmological examination: hypertropia on contralateral side.
Central nervous system tumour
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Intermittent torticollis associated with neurological symptoms may indicate a posterior fossa or spinal cord tumour.[5]
INVESTIGATIONS
Cranial/cervical spine MRI: posterior fossa or spinal cord tumour.
Vertebral anomaly
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Children with congenital vertebral segmentation anomalies such as hemi-vertebrae or Klippel-Feil syndrome present with a head tilt and can have associated cervico-thoracic scoliosis. There may be more fixed deformities noted on physical examination.
INVESTIGATIONS
Cervical spine x-ray: cervico-thoracic scoliosis.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Cervical spine x-ray showing numerous segmentation anomalies associated with a convex left cervico-thoracic scoliosis. This patient presented with a head tilt. There are segmentation anomalies in the lower thoracic and high cervical region. There is an acute convex left cervico-thoracic scoliosis with a hemi-vertebra at the apex of the curve. Butterfly vertebra is identified rostral to the hemi-vertebra, and segmentation anomalies are also identified caudal to the hemi-vertebraFrom the personal collection of Dr Joyce L. Oleszek; used with permission [Citation ends].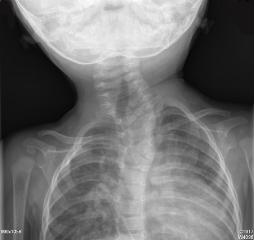
Craniosynostosis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Cranial asymmetry resulting from craniosynostosis is not typical of that seen in CMT with positional plagiocephaly. For example, posterior plagiocephaly produces a parallelogram-shaped head, while unilateral lambdoid synostosis produces a trapezium-shaped head.[28]
INVESTIGATIONS
Skull x-ray or CT: features of craniosynostosis.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer