Investigations
1st investigations to order
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Test
Screening test. Also used for follow-up.
If TSH is not suppressed, toxic multinodular goitre is ruled out.
Confirms presence of thyroid dysfunction but not its cause.
Result
suppressed
Investigations to consider
free T4 (or total T4 with measure of binding)
Test
If free T4 is not available, total T4 plus a measure of binding should be obtained.
Elevated free T4 confirms hyperthyroidism.
Free T4 may be normal in sub-clinical hyperthyroidism or T3 toxicosis.
If free T4 is normal, elevated T3 should be sought.
Confirms presence of thyroid dysfunction but not its cause.
Result
elevated
total T3 with a measure of binding (or free T3)
Test
Total T3 with a measure of binding is considered to be the more reliable assay.
Elevated free T3 (calculated or assay) confirms hyperthyroidism.
Free T4 may be normal or elevated.
TSH is suppressed and both free T3 and free T4 are normal in subclinical hyperthyroidism.
Confirms presence of thyroid dysfunction but not its cause.
Result
elevated
I-123 thyroid scan and uptake
Test
In the absence of stigmata of Graves’ disease or positive TSH receptor antibodies, thyroid scan and uptake are indicated when biochemical hyperthyroidism is confirmed.
Variegated appearance is typical.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Thyroid scan showing variegated uptake in toxic multinodular goitreCourtesy of Dr Elizabeth Pearce; used with permission [Citation ends].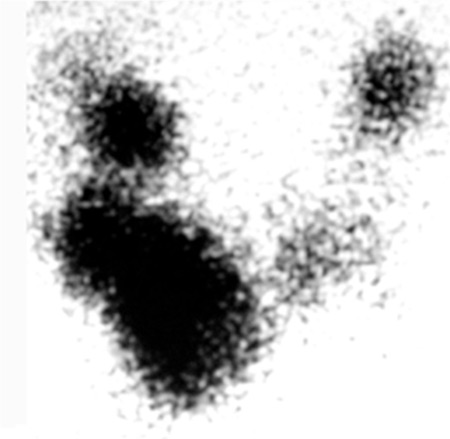 Uptake is often normal.
Uptake is often normal.
Patient may need further work-up of a cold nodule, such as sonogram or fine needle aspiration.
Result
multiple hot and cold areas
Tc-99 pertechnetate scan
thyroid ultrasound
Test
Can be used to define dimensions of cold nodules and detect suspicious features, such as more-tall-than-wide shape, irregular margins, microcalcifications, or marked hypoechogenicity.[1]
The risk of malignancy in a cold nodule in a multinodular goitre is about 5% to 8%, which is similar to that of solitary cold nodules.[31] Cold nodules >1 cm in diameter with suspicious ultrasonographic characteristics should be considered for further evaluation such as fine needle biopsy.[26][27][28]
Result
may help detect suspicious features in a cold nodule
metabolic panel
Test
Non-specific.
Elevated alkaline phosphatase in hyperthyroidism is usually due to increased bone turnover. Most patients with hyperthyroidism will have elevated transaminases prior to initiating treatment and levels typically improve with antithyroid drug therapy.[30]
Result
possible hypercalcaemia or abnormal LFTs
FBC
Test
Non-specific.
Baseline WBC count and differential prior to use of antithyroid drugs (e.g., thiamazole) is advisable. Mild neutropenia should not be regarded as a contraindication to the use of antithyroid drug therapy and hyperthyroidism typically normalises the neutrophil count.[29]
Result
possible anaemia or leukocytosis
thyroid peroxidase antibodies
Test
Sensitive but not specific for Graves' disease.
Result
negative
TSH receptor antibodies
Test
Useful to differentiate toxic multinodular goitre from Graves' disease; third-generation TSH receptor antibody assays are highly sensitive and specific for Graves' disease.
Result
negative
ECG
Test
Older adults may present with apathetic hyperthyroidism, such as atrial fibrillation alone.
Result
may show dysrhythmia
CT neck (non-contrast)
Test
Occasionally indicated for signs or symptoms of neck compression, or as part of pre-operative evaluation before thyroid surgery.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest CT showing marked enlargement of the thyroid gland with an extensive intrathoracic component causing trachea compressionDias T et al. Acute airway obstruction due to benign multinodular goitre. BMJ Case Reports. 2019;12:e228095; used with permission [Citation ends].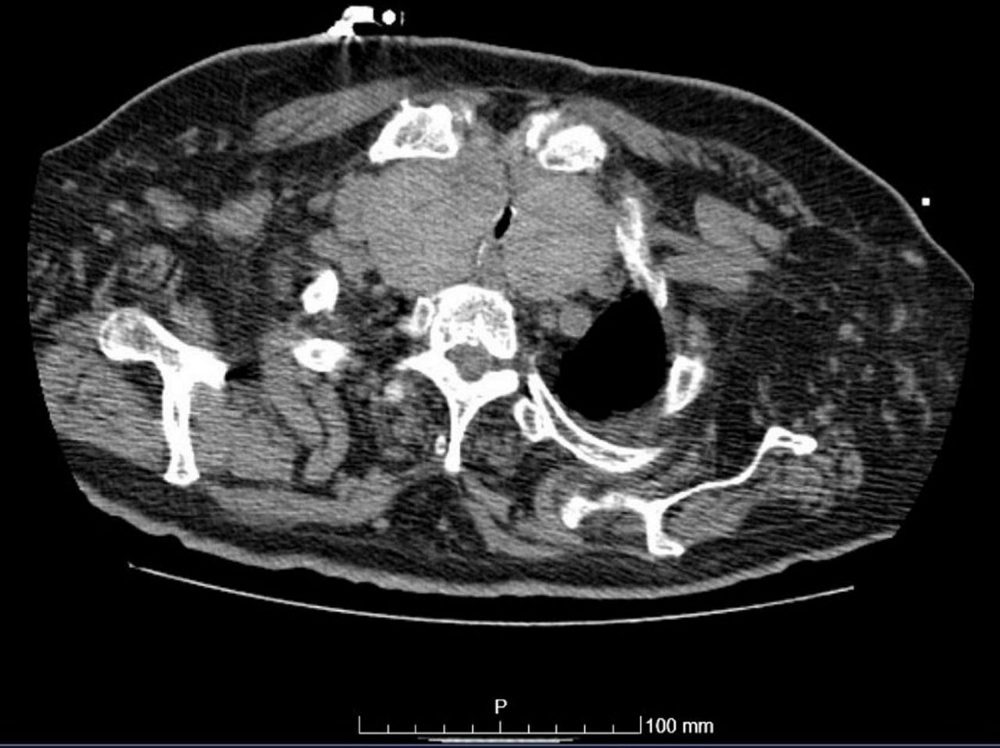
Result
may delineate large goitre
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer