Differentials
Appendicitis (uncommon in this age group)
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
In appendicitis, rectal bleeding is not present.
Patients with appendicitis may describe abdominal pain that has migrated from a periumbilical position to the right lower quadrant.
The abdominal pain of intussusception is more colicky than the abdominal pain that is commonly described in appendicitis.
INVESTIGATIONS
The findings of an intussusception mass and target sign (variants according to appearance or imaging modality include bull’s eye sign, doughnut sign, crescent-in-doughnut sign, and multiple concentric ring sign) will be absent on ultrasound examination if appendicitis is present.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Transverse sonogram of the abdomen showing the doughnut sign (concentric rings within the lumen of a distended loop of bowel)Adapted from the Student BMJ. 2008;16:76. Copyright 2010 by the BMJ Publishing Group; used with permission [Citation ends].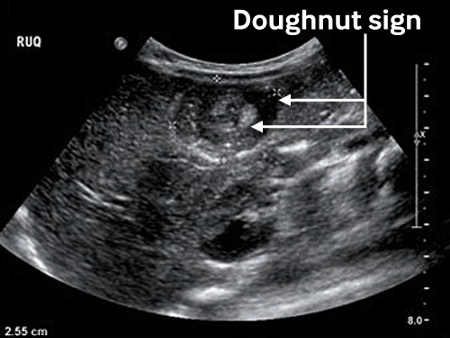
Ultrasound has value in the detection of appendicitis, although clinical experience dictates that the use of ultrasound is highly operator-dependent.
CT may be helpful in identifying appendicitis; although, it carries an additional risk of radiation.
Gastroenteritis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Gastroenteritis involves episodes of vomiting that are typically non-bilious, often in association with anorexia, fever, lethargy, and diarrhoea.
Rectal bleeding is absent in gastroenteritis, except in the presence of invasive organisms such as Salmonella or Shigella.
INVESTIGATIONS
The findings of an intussusception mass and characteristic signs will be absent on ultrasound examination if an infant presents with gastroenteritis.
Plain abdominal films may show dilated small- and large-bowel loops.
Urinary tract infection
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Urinary tract infection may present with fever, foul-smelling urine, lethargy, frequent urination, painful urination, anorexia, and vomiting.
INVESTIGATIONS
Urinalysis and culture establish the diagnosis.
Plain films may reveal an ileus pattern; ultrasound or CT may show evidence of urologic abnormality, or pyelonephritis in advanced cases.
Pyloric stenosis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Typically develops in a 3- to 6-week-old infant, but may be seen between 2 and 12 weeks.
Presents with projectile non-bilious vomiting after feeding.
An upper abdominal mass (olive) may be detected by palpation.
INVESTIGATIONS
Abdominal ultrasound shows a pyloric channel length >17 mm and pyloric muscle thickness >4 mm.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer