Investigations
1st investigations to order
maternal blood type
Test
All Rh-negative pregnant women are at potential risk for alloimmunisation and erythroblastosis.
Result
Rh-negative
maternal serum Rh antibody screen
Test
Positive red blood cell antibody screen must prompt further investigation for possible alloimmunisation due to Rh antibodies.[16]
Result
positive screen
Investigations to consider
maternal serum antibody titre
Test
As methods vary between laboratories performing this test, each should report the titre below which severe fetal Rh incompatibility is unlikely and above which further investigations and monitoring are indicated.[38]
The maternal serum antibody titre is a guide to disease severity. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists states that a critical titre (titre associated with a significant risk for severe haemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, and hydrops) is considered to be between 1:8 and 1:32 in most centres.[34] If the initial antibody titre is 1:8 or less, the patient may be monitored with titre assessment every 4 weeks.[34] However, serial titres are not adequate for monitoring fetal status when the mother has had a previously affected fetus or neonate.[34]
Result
critical titre: between 1:8 and 1:32 (may vary among laboratories)
paternal blood type
Test
An Rh-positive partner of an Rh-negative mother creates blood group incompatibility in the fetus.
Result
Rh-positive
paternal zygosity
Test
Heterozygosity denotes a 50% risk of the offspring having an Rh-negative blood type and no risk of Rh incompatibility. Homozygosity denotes a 100% chance of an Rh-positive fetus, at risk of Rh incompatibility. Zygosity is determined by assay of plasma DNA in the case of RhD; serological testing of paternal red cells can be used for analysis of other red cell antigen systems.
Result
homozygous or heterozygous
fetal ultrasound
Test
Fluid in serous cavities of the fetus is easily detected with ultrasonography.[32][37][39][40]
These findings are consistent with severe fetal anaemia in an affected fetus.[39][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Fetal hydrops, with ascites and hepatomegaly (arrow) diagnosed on antenatal ultrasoundThe Ottawa Hospital; used with consent of the patient [Citation ends].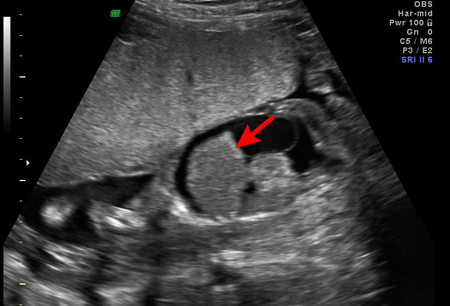
Result
may show subcutaneous oedema, ascites, pleural effusion, or pericardial effusion
Doppler velocimetry of fetal middle cerebral artery (peak systolic velocity)
Test
Measured Doppler sonography with estimation of peak systolic velocity in the fetal middle cerebral artery (MCA) can be used to predict moderate to severe anaemia in the fetus. MCA peak systolic velocity is increased in fetuses with significant anaemia. Elevated blood flow velocity for gestational age should prompt percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (if anaemia is strongly suspected).[37][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Increased velocity in the middle cerebral artery consistent with severe fetal anaemiaThe Ottawa Hospital; used with consent of the patient [Citation ends].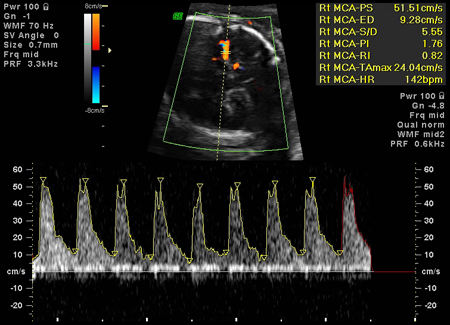
Result
≥1.5 MoM
fetal blood typing (from amniocentesis or maternal circulation)
Test
If the father is heterozygous RhD-positive, or paternity is uncertain, the fetus' RhD type is determined by genetic testing of amniotic fluid cells or it can be estimated using cell-free fetal DNA in the maternal circulation.[35]
Result
Rh type
direct assessment of fetal anaemia
Test
Through umbilical cord venepuncture (cordocentesis) or the intrahepatic vein.
If fetal haemoglobin is within 20 g/L (2 g/dL) (i.e., 2 standard deviations) of gestational age norms and direct antiglobulin test is positive, the fetus is only mildly affected. Haemoglobin deficit of 20-70 g/L (2-7 g/dL) suggests moderate anaemia. Fetal anaemia is severe with haemoglobin deficits >70 g/L (>7 g/dL).
Result
fetal haemoglobin and haematocrit
rosette test
Test
A rosette test can be used to rule out significant fetomaternal haemorrhage.
Result
may be positive
Kleihauer-Betke test/flow cytometry
Test
Can measure the amount of fetal blood in the maternal circulation.
Result
variable
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer