History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
common
presence of risk factors
Risk factors include age 15 to 24 years, inconsistent condom use, multiple or new sexual relationships, previous sexually transmitted infections, bacterial vaginosis, sex worker, or absence of hydrogen peroxide-producing lactobacilli.
purulent vaginal or cervical discharge
Mucopurulent discharge is more characteristic of Neisseria gonorrhoeae or Mycoplasma genitalium. Vaginal discharge is present in up to 70% of patients infected with Trichomonas vaginalis, but its consistency varies from sparse and thin to copious and thick, with 10% to 30% having the classic frothy yellow discharge.[20]
intermenstrual/postcoital bleeding
Should be assessed for sexually transmitted infection and cervical cancer.
dysuria and urinary frequency
If symptoms of cystitis (dysuria and urinary frequency) are associated with a discharge, patients should be assessed for vaginitis/cervicitis because Trichomonas vaginalis can affect the neighboring Skene glands and Chlamydia trachomatis can present as urethritis.
easily induced cervical bleeding
Friable and tender cervix on digital examination or swab use suggests cervicitis.
Other diagnostic factors
uncommon
dyspareunia
Can result from a host of pathological and benign processes, but sexually transmitted infection should be excluded.
vulval and/or vaginal inflammation
May appear erythematous due to inflammatory discharge draining from the vagina or cervix.
Normal-appearing vulva does not exclude cervicitis.
strawberry cervix
Consistent with Trichomonas vaginalis infection.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Strawberry cervix due to trichomoniasisMittal S, et al. Atlas of visual inspection of the cervix with acetic acid for screening, triage, and assessment for treatment: IARC CancerBase No. 16 [Internet]. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; used with permission [Citation ends].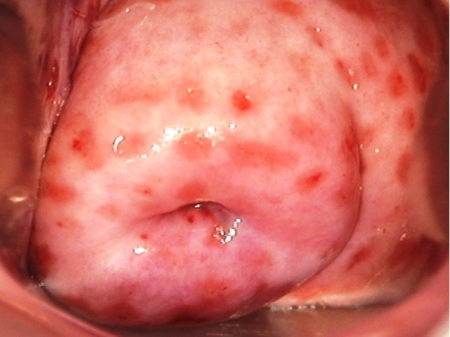
Risk factors
strong
age 15 to 24 years
inconsistent condom use
The failure of condoms to protect against STIs usually results from inconsistent or incorrect use.[1]
multiple sexual relationships
This includes patients with recent new sexual partners.[12]
previous STIs
Patients initially diagnosed with an STI are more likely to be diagnosed with another within a 12-month period.[13]
bacterial vaginosis (BV)
sex worker
absence of hydrogen peroxide-producing lactobacilli
weak
infertility
Infertility patients, particularly those with tubal factor infertility, have a high incidence of prior infection with an STI resulting in undiagnosed pelvic inflammatory disease and subsequent subfertility.
education <12 years
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer