Investigations
1st investigations to order
x-ray of a long bone
Test
X-rays of knees and wrists are taken when rickets is suspected.[4][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Right wrist of a patient with vitamin D deficient rickets before treatment. His right wrist x-ray showed sclerotic and widened end plates of the radius and ulna (arrows)Seerat I, Greenberg M. Hypocalcaemic fit in an adolescent boy with undiagnosed rickets. BMJ Case Reports 2010; doi:10.1136/bcr.10.1136/bcr10.2008.1153 [Citation ends].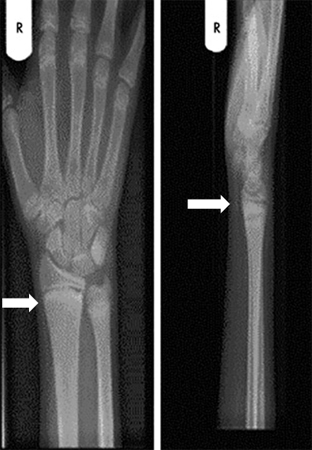
Result
widening of the epiphyseal plate, loss of definition of the zone of provisional calcification at the epiphyseal/metaphyseal interface, cupping, splaying, and fraying of the metaphysis; Looser's zone (pseudofracture)
serum calcium
serum inorganic phosphorus
serum parathyroid hormone level
25-hydroxyvitamin D levels (calcidiol)
Test
Calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D) is the active form of vitamin D, but calcidiol (25-hydroxyvitamin D) is preferred for testing as it has a longer half-life and is found at much higher levels in the serum.
Normal values >25 nanomoles/L (>10.0 nanograms/mL).[3]
Result
low in vitamin D-deficient rickets, usually <25 nanomoles/L (<10 nanograms/mL); normal in genetic forms of hypocalcaemic rickets and in hypophosphataemic rickets
alkaline phosphatase and liver function tests
serum creatinine and urea
Test
Kidney disease causes abnormal calcium and phosphorus regulation and impaired synthesis of calcitriol.[4]
Result
raised in rickets caused by kidney disease
urinary calcium and phosphorus
Test
Serum and urine values are used to calculate percent tubular reabsorption of phosphate (TRP). Low TRP is diagnostic of hypophosphataemic rickets in the absence of vitamin D deficiency.[25] TRP is normally >80%.[24]
Result
urinary calcium is decreased and urinary phosphorus is increased in hypocalcaemic rickets; urinary calcium is normal and urinary phosphorus is high in hypophosphataemic rickets
Investigations to consider
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels (calcitriol)
Test
Normal values 43 to 139 picomoles/L; up to 250 picomoles/L in pre-term babies.[3][5]
Calcitriol may be normal, low, or high in relation to the reference range. Serum calcitriol concentration is inappropriately low for the prevailing phosphate level in patients with X-linked hypophosphataemic rickets (hypophosphataemia typically stimulates calcitriol synthesis), and very low in type I vitamin D-dependent rickets (pseudovitamin D-deficient rickets). In patients with type II vitamin D-dependent rickets (end-organ resistance to calcitriol), serum calcitriol concentration is usually very high.
Result
typically normal or elevated in hypocalcaemic rickets as a result of parathyroid hormone action; usually normal in hypophosphataemic forms of rickets
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer