Images and videos
Images
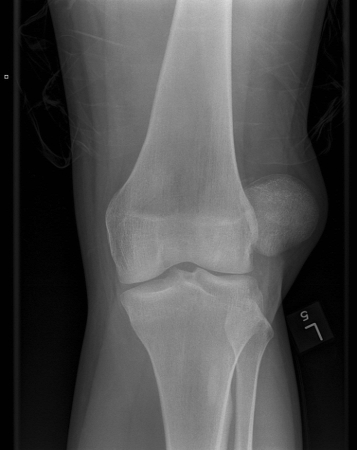
Joint dislocation
Left knee radiograph demonstrating lateral patella dislocation
Yerimah G, et al. BMJ Case Rep. 2013 May 2:2013:bcr2013009832; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
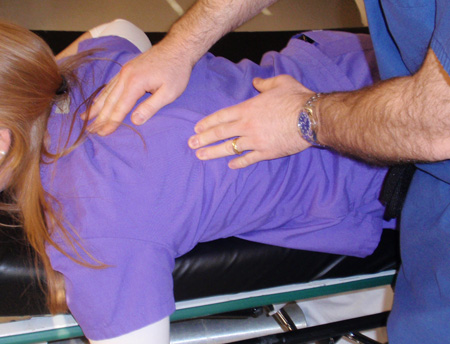
Joint dislocation
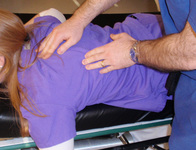
Scapular manipulation technique: one hand is placed on the superolateral border of the scapula with the other hand on the inferomedial border of the scapula, and pressure is applied to rotate the superior border laterally and the inferior border medially
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:
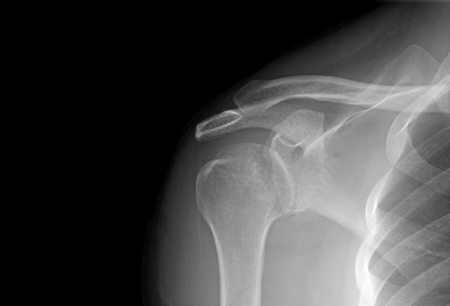
Joint dislocation
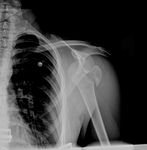
Anteroposterior x-ray view of a shoulder showing a missed posterior dislocation: the glenohumeral joint appears reduced
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:
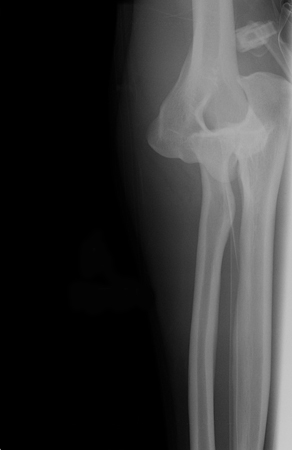
Joint dislocation
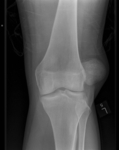
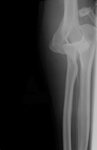
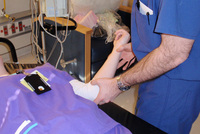
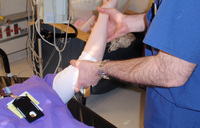
Anteroposterior x-ray view of an elbow dislocation
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:
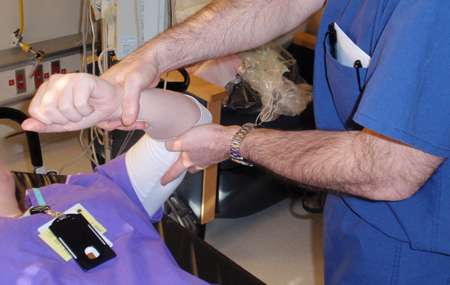
Joint dislocation
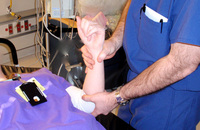
Kocher's method of shoulder reduction, part 2: arm is internally rotated until the patient's hand touches the shoulder
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich.
See this image in context in the following section/s:
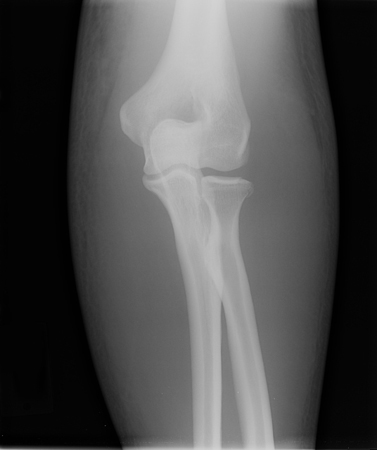
Joint dislocation
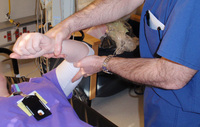
Anteroposterior x-ray view of a reduced elbow dislocation
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:
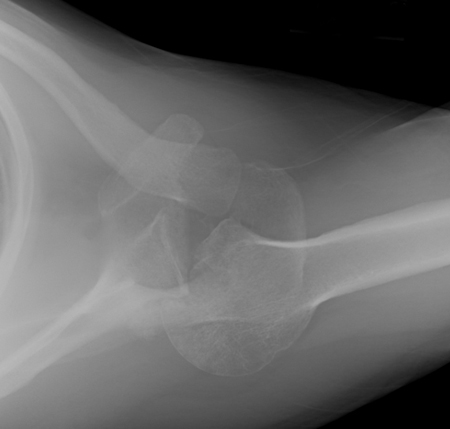
Joint dislocation
Axillary lateral of a shoulder with a missed posterior dislocation: humeral head clearly is not reduced and is locked on the posterior rim of the glenoid
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:
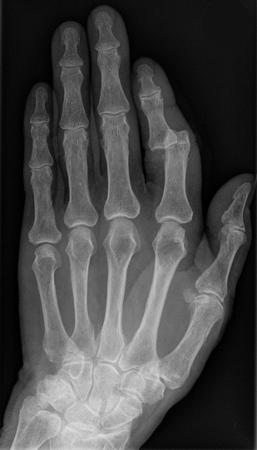
Joint dislocation
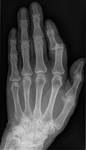
X-ray showing dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint, left index finger
Hellerhoff, CC BY-SA 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons
See this image in context in the following section/s:
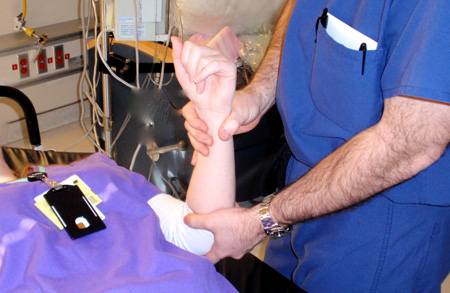
Joint dislocation
External rotation method for shoulder reduction, part 1: patient is positioned supine, and affected extremity is gently adducted until it is parallel to the long axis of the body; elbow is then flexed to 90°
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Joint dislocation
Normal axillary x-ray view of a reduced shoulder dislocation, showing congruency of the glenohumeral joint
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:
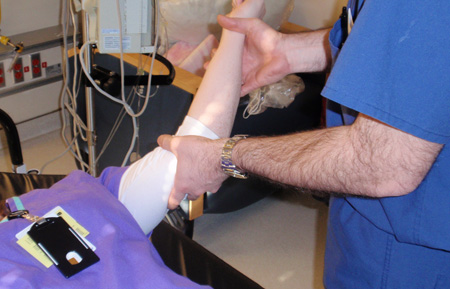
Joint dislocation
Kocher's method of shoulder reduction, part 1: in-line traction of the arm while abducted to 45°; while traction is maintained, arm is externally rotated and elbow is brought across the chest to the mid-line
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:
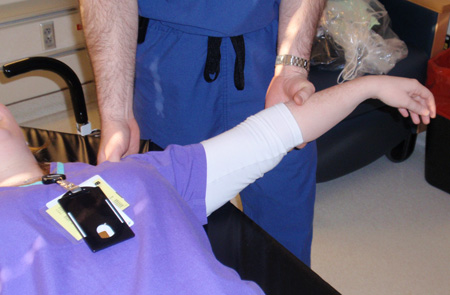
Joint dislocation
Milch's technique for shoulder reduction, part 2: once the arm has reached a position of 90° abduction and 90° external rotation, the shoulder dislocation should spontaneously reduce; if not, the humeral head can be palpated in the axilla and superolateral pressure can then be applied using the thumb and index finger to help guide the humeral head back into the glenoid
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:
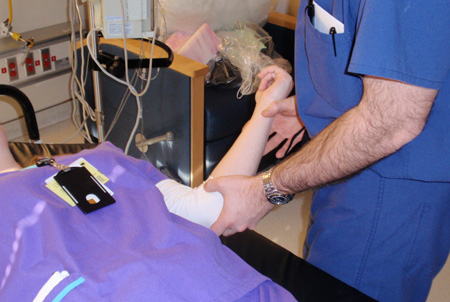
Joint dislocation
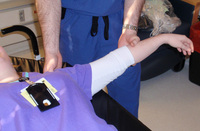
External rotation method for shoulder reduction, part 2: by applying gentle pressure to the wrist, the practitioner slowly externally rotates the arm, taking time to allow spasms and contractions to pass; finally, the arm is externally rotated to 90° (i.e., perpendicular to the long axis of the body); shoulder dislocation should reduce after about 5 minutes
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Joint dislocation
Stimson's method: patient is positioned prone on the stretcher with the affected shoulder slightly off the stretcher; arm is placed perpendicular to the floor (90° forward flexion) with the stretcher high enough to keep the hand from resting on the floor, then weights of 2.3 to 4.5 kg or 1-L bottles of sterile water are wrapped around the wrist using stockinette and hung high enough to not touch the floor
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:
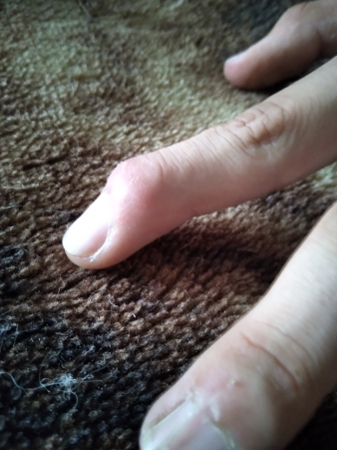
Joint dislocation
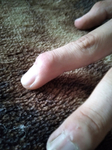
Dislocated distal phalanx, index finger, left hand
Bobjgalindo, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
See this image in context in the following section/s:
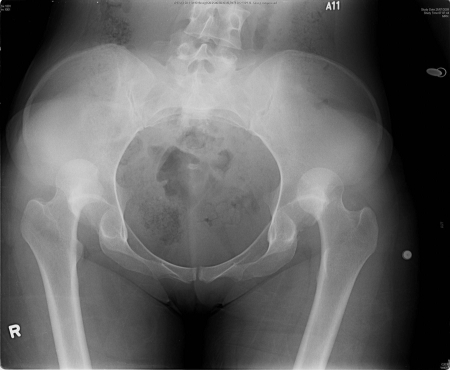
Joint dislocation
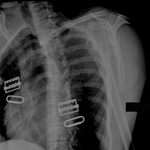
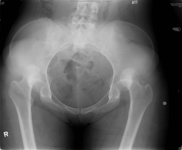
X-ray showing bilateral hip posterior dislocation
Fan KY, et al. BMJ Case Rep. 2015 Mar 25:2015:bcr2014204031; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Joint dislocation
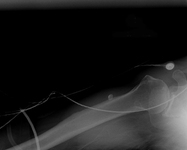
Lateral x-ray view of a posterolateral elbow dislocation
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Joint dislocation
Scapular Y x-ray view showing an anterior dislocation of the shoulder
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Joint dislocation
Traction-countertraction method: with patient supine on the bed, a sheet is looped around the axilla with one free end on the chest and the other underneath the back; the 2 ends should be of even length and are used by an assistant to apply countertraction. The practitioner abducts the arm to 90° and flexes the elbow to 90°; the forearm is used to apply slow longitudinal traction to the affected extremity
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:
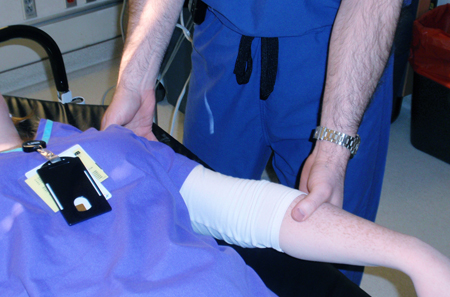
Joint dislocation
Milch's technique for shoulder reduction, part 1: patient is positioned supine on a bed with the head of the bed elevated about 20° to 30°, then the arm is slowly abducted and externally rotated without application of longitudinal traction (in case of pain or resistance, the practitioner pauses)
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Joint dislocation
Scapular Y x-ray view showing an anterior fracture dislocation of the shoulder and fracture of the greater tuberosity
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:
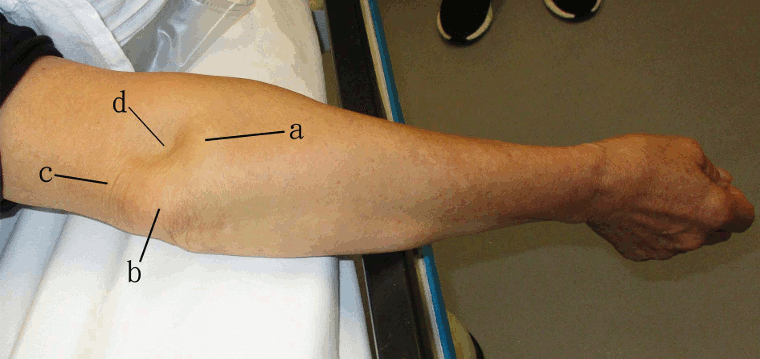
Joint dislocation
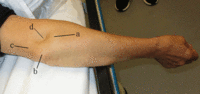
Right elbow dislocation: dislocated radial head (a), olecranon (b), and tensed triceps tendon (c) resulting in a skin depression (d) just proximal to the radial head
Lui TH, et al. BMJ. 2020 Oct 8:371:m3494; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
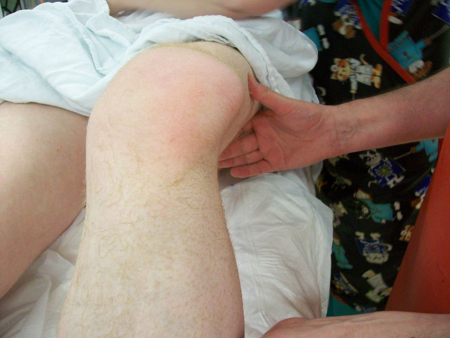
Joint dislocation
Patellar dislocation: knee held in partial flexion with a visible mass lateral to the lateral femoral condyle
Yerimah G et al. BMJ Case Rep. 2013 May 2:2013:bcr2013009832; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
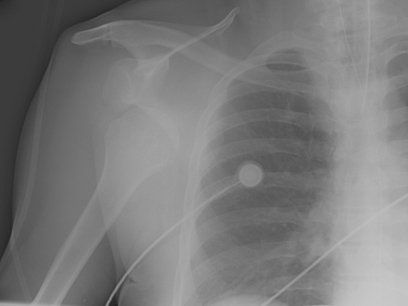
Joint dislocation
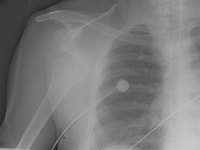
Anteroposterior x-ray view of a shoulder showing an anteroinferior dislocation
Personal collection of Dr Paul Novakovich
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Videos
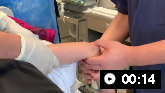 Closed reduction of posterolateral dislocation of the elbow
Closed reduction of posterolateral dislocation of the elbowClosed reduction of posterolateral dislocation of the elbow
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer