Investigations
1st investigations to order
FBC
Test
FBC, serum creatinine, and liver function tests (LFTs) are recommended for all patients presenting with clinical features of cytomegalovirus (CMV).
Can be used at baseline and for monitoring while on treatment. Bone marrow involvement with CMV leads to suppression of all cell lines. Treatment with ganciclovir/valganciclovir can also cause bone marrow suppression.
Result
immunocompetent: atypical lymphocytosis; transplant or immunocompromised patients: anaemia, leukopenia, or thrombocytopenia; newborns: thrombocytopenia
serum creatinine
Test
FBC, serum creatinine, and liver function tests (LFTs) are recommended for all patients presenting with clinical features of cytomegalovirus (CMV).
Symptoms and signs of tissue-invasive CMV infection in solid organ or bone marrow recipients may mimic acute allograft rejection (rise in serum creatinine and aminotransferases).
Serum creatinine measurement is also recommended during treatment with antiviral drugs.
Result
normal; may be elevated in patients with solid organ and haematopoietic stem cell transplant patients with tissue-invasive CMV infection
serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
Test
FBC, serum creatinine, and liver function tests (LFTs) are recommended for all patients presenting with clinical features of cytomegalovirus.
Abnormal LFTs often suggest tissue-invasive disease in immunocompromised patients. Can also be elevated at initial presentation in a healthy person.
Result
both immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients: elevated
serum alkaline phosphatase
Test
FBC, serum creatinine, and liver function tests (LFTs) are recommended for all patients presenting with clinical features of cytomegalovirus (CMV).
Elevated levels are often one of the initial manifestations of CMV hepatitis and cholangitis in immunocompromised patients, such as those with AIDS.
Result
hepatobiliary system involvement: elevated
serology
Test
The test is done using ELISA. The utility of CMV-IgM is modest for the diagnosis of acute cytomegalovirus (CMV) disease in immunocompromised patients.[42]
Result
CMV-IgM titre is indicative of acute infection; CMV-IgG titre suggests past infection; antibody avidity is low in recent infection
pp65 antigenaemia
Test
Can be used in initial testing and subsequent disease monitoring, but has largely been replaced by nucleic acid testing. Slide method is used to demonstrate the presence and the number of leukocytes containing cytomegalovirus pp65 antigen. More sensitive than viral culture.
Limited utility in patients with severe leukopenia, such as haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients.
The quantitative and semi-quantitative property of this test may guide therapeutic response.[42]
Result
number of pp65-positive cells per 150,000 to 200,000 cells
nucleic acid detection
Test
Used in initial testing and subsequent disease monitoring. Nucleic acid testing (NAT) is the most sensitive method for the detection of cytomegalovirus in blood/plasma and tissue specimens.
The clinical significance of the number of genomic copies depends on the testing platform, the specimen used (plasma vs. whole blood) and the patient population. In most cases, however, a positive test suggests infection.
The quantitative property of the test is used for predicting the risk of disease, to guide pre-emptive therapy, to monitor response to treatment, and to indicate the presence of drug-resistant virus.[42]
Result
number of genomic copies per volume of specimen
CD4 count
Test
Used initially to assess the risk of cytomegalovirus disease in transplant patients. Also used to guide when to discontinue treatment in AIDS patients who have undergone immune reconstitution following use of antiretroviral therapy.[2]
Result
severe immunosuppression in AIDS: <50 cells/microlitre
chest x-ray
Test
Chest x-ray should be performed in any immunocompromised patient with pulmonary symptoms suggestive of cytomegalovirus (CMV) disease. It may also be used in subsequent monitoring for improvement. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray showing diffuse pulmonary infiltrates in an immunocompromised patient with severe CMV pneumonitisFrom the collection of Dr Raymund Razonable; used with permission [Citation ends].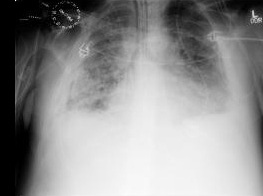
Result
CMV pneumonitis: presence of interstitial infiltrates; nodules may occasionally be seen
Investigations to consider
chest CT scan
Test
Chest CT scan will assist in demonstrating diffuse interstitial and parenchymal changes as a result of cytomegalovirus pneumonitis in a lung transplant recipient. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest CT scan of a lung transplant recipient with diffuse interstitial and parenchymal changes as a result of primary CMV pneumonitisFrom the collection of Dr Raymund Razonable; used with permission [Citation ends].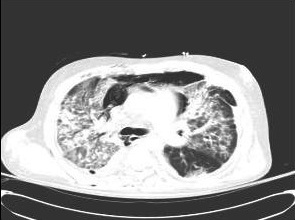
Result
diffuse interstitial and parenchymal changes
histopathology of biopsy
Test
In patients with clinical illness suggestive of tissue-invasive cytomegalovirus (CMV) disease, biopsy of tissue specimens (liver, intestinal mucosa, lung) is recommended. However, in solid organ transplant recipients biopsy may be recommended only in case of non-response to initial antiviral therapy.[42][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Active cytomegalovirus infection of lung in AIDSCenters for Disease Control and Prevention: Dr Edwin P. Ewing, Jr [Citation ends].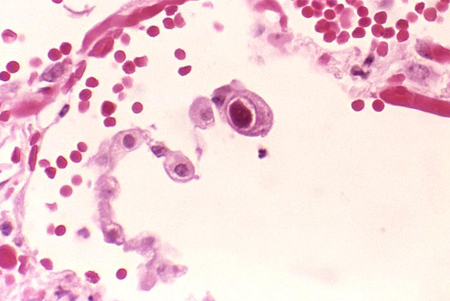
Result
demonstration of CMV-specific cytoplasmic and intra-nuclear inclusions
upper gastrointestinal endoscopy and colonoscopy
Test
Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy and colonoscopy can be performed in patients with suspected cytomegalovirus (CMV) disease and gastrointestinal symptoms. This can be useful for confirming the diagnosis, particularly in patients with negative blood nucleic acid tests for CMV. Repeat colonoscopy is suggested by some experts where symptoms persist despite appropriate therapy, or in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, to document clearance of disease prior to discontinuation of treatment.
Result
spectrum of endoscopic lesions is variable and ranges from patchy erythema, exudates, and micro-erosions to diffusely oedematous mucosa, to multiple mucosal erosions, to deep ulcers and pseudo-tumours
serial fetal ultrasound examinations (congenital CMV infection)
Test
Should be performed every 2-4 weeks after a diagnosis of congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection in order to detect sonographic abnormalities.
May aid in determining fetal prognosis, although the absence of sonographic findings does not guarantee a normal outcome.[29]
Result
features suggestive of congenital CMV infection include: intrauterine fetal growth restriction; enlargement of the cerebral ventricles; intracranial calcification; microcephaly; increase or decrease in the volume of amniotic fluid; enlargement of the liver, spleen, or heart; hyperechogenicity of the bowel
amniocentesis or fetal blood sampling (congenital CMV infection)
Test
These antenatal investigations enable testing for cytomegalovirus (CMV).[29][30]
Important factors to consider in antenatal diagnosis are: confirmation of primary CMV infection in the mother and subsequent determination of the time at which the mother was infected, as well as the most appropriate timing for viral detection (usually after 21 weeks of gestational age). There is an increased risk of false-negative results if fetal sampling is performed before 21 weeks of gestation or too close to the onset of infection in the mother.
Mothers should be counselled about the risks of fetal transmission, risks associated with diagnostic procedures, and risks involved in fetal infection, in order to make a decision on further testing and how to continue with pregnancy.[10]
Fetal blood specimens and amniotic fluid are tested for CMV using nucleic acid testing. IgM antibody measurement, pp65 antigenaemia, and viral culture are not commonly used.[30]
Result
detection of CMV from amniotic fluid or fetal blood specimen by at least two different assays
brain ultrasound/brain MRI: newborns
Test
Brain ultrasound and MRI are part of the systematic screening of any newborn with congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Audiological testing and an ophthalmologic examination are also part of routine neonatal screening, as are regular developmental assessments.
Result
intra-cranial calcifications; microcephaly; cerebral ventricular enlargement
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer