Testicular torsion should be diagnosed clinically. A high index of suspicion is important to ensure timely diagnosis and management. Training of primary care and accident and emergency department staff should include early recognition, atypical or warning presentations, urgent referral pathways, and the importance of timely surgery.[12]National Confidential Enquiry into Patient Outcome and Death. Testicular torsion. Feb 2024 [internet publication].
https://www.ncepod.org.uk/2024testiculartorsion.html
[21]NHS England. GIRFT children and young people: testicular torsion pathway. Feb 2024 [internet publication].
https://gettingitrightfirsttime.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Paediatric-testicular-torsion-pathway-guide-FINAL-V1-February-2024.pdf
A history and physical examination consistent with testicular torsion mandates an immediate surgical consultation for scrotal exploration, without delay for additional diagnostic tests.[12]National Confidential Enquiry into Patient Outcome and Death. Testicular torsion. Feb 2024 [internet publication].
https://www.ncepod.org.uk/2024testiculartorsion.html
[21]NHS England. GIRFT children and young people: testicular torsion pathway. Feb 2024 [internet publication].
https://gettingitrightfirsttime.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Paediatric-testicular-torsion-pathway-guide-FINAL-V1-February-2024.pdf
[22]Royal College of Surgeons of England. Commissioning guide topics: management of paediatric torsion. Oct 2016 [internet publication].
https://www.rcseng.ac.uk/standards-and-research/commissioning/commissioning-guides/topics/#:~:text=Management%20of%20paediatric%20torsion
If diagnosis is unclear, immediate referral is required; however, additional diagnostic tests may help avoid unnecessary surgery.[12]National Confidential Enquiry into Patient Outcome and Death. Testicular torsion. Feb 2024 [internet publication].
https://www.ncepod.org.uk/2024testiculartorsion.html
[20]Leslie JA, Cain MP. Pediatric urologic emergencies and urgencies. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2006 Jun;53(3):513-27.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16716794?tool=bestpractice.com
History
Testicular torsion can affect males at any age but boys aged between 12 and 18 years are usually at greatest risk.[3]Kapoor S. Testicular torsion: a race against time. Int J Clin Pract. 2008 May;62(5):821-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18412935?tool=bestpractice.com
[19]Turgut AT, Bhatt S, Dogra VS. Acute painful scrotum. Ultrasound Clin. 2008;3:93-107.[20]Leslie JA, Cain MP. Pediatric urologic emergencies and urgencies. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2006 Jun;53(3):513-27.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16716794?tool=bestpractice.com
Neonates are at risk for extra-vaginal torsion during the perinatal period although this is a rare event.
There is usually a history of sudden-onset severe scrotal pain, often with associated nausea and vomiting.[22]Royal College of Surgeons of England. Commissioning guide topics: management of paediatric torsion. Oct 2016 [internet publication].
https://www.rcseng.ac.uk/standards-and-research/commissioning/commissioning-guides/topics/#:~:text=Management%20of%20paediatric%20torsion
There is typically no relief of pain upon elevation of the scrotum. A history of intermittent or acute on-and-off pain may indicate periods of torsion and spontaneous de-torsion. Fever, dysuria, and penile discharge are not typically associated with torsion and would be more suggestive of an infectious or inflammatory process. Trauma is believed to account for only 4% to 10% of cases of torsion.[5]Ringdahl E, Teague L. Testicular torsion. Am Fam Physician. 2006 Nov 15;74(10):1739-43.
https://www.aafp.org/afp/2006/1115/p1739.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17137004?tool=bestpractice.com
[14]Zhong H, Bi Y. Pediatric trauma-induced testicular torsion: A surgical emergency. Urol Int. 2021;105(3-4):221-224.
https://www.doi.org/10.1159/000511747
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33378756?tool=bestpractice.com
Any patient with a history of undescended testes who presents with sudden abdominal pain should always be evaluated for possible torsion.[3]Kapoor S. Testicular torsion: a race against time. Int J Clin Pract. 2008 May;62(5):821-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18412935?tool=bestpractice.com
Urinary frequency is not usually associated with testicular torsion and may suggest alternative diagnoses such as epididymitis or orchitis.
Patients presenting with a symptom duration of <4 to 6 hours have a greater likelihood of testicular viability. Testicular salvage rates decline as the duration of symptoms increases, with greatly reduced testicular salvage at 24 hours and consistently poor results beyond 48 hours.[20]Leslie JA, Cain MP. Pediatric urologic emergencies and urgencies. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2006 Jun;53(3):513-27.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16716794?tool=bestpractice.com
[23]Morin OA, Carr MG, Holcombe JM, et al. Optimal predictor of gonadal viability in testicular torsion: Time to treat versus duration of symptoms. J Surg Res. 2019 Dec;244:574-578.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2019.06.033
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31357158?tool=bestpractice.com
Physical examination
General abdominal examination
Genital examination
There is usually severe tenderness to palpation of the affected testicle. The testis may have a transverse lie and may be in a higher position ('high-riding') than the unaffected testis. A cremasteric reflex, which normally elicits ipsilateral testicular rise when the inner thigh is stroked, may be absent in cases of torsion.[20]Leslie JA, Cain MP. Pediatric urologic emergencies and urgencies. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2006 Jun;53(3):513-27.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16716794?tool=bestpractice.com
A more delayed presentation may reveal a worsening of the scrotal erythema and oedema, and a reactive hydrocele may develop.[20]Leslie JA, Cain MP. Pediatric urologic emergencies and urgencies. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2006 Jun;53(3):513-27.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16716794?tool=bestpractice.com
Elevation of the testis does not result in any pain relief (negative Prehn’s sign) as compared to that seen in acute epididymitis.[24]European Association of Urology. Paediatric urology. Apr 2024 [internet publication].
https://uroweb.org/guidelines/paediatric-urology
Not all patients present with all of these findings. Testicular tenderness alone may exist without other signs suggestive of torsion.
Clinical relief or improvement after manual de-torsion is highly suggestive of the diagnosis of torsion.
Testicular Workup for Ischaemia and Suspected Torsion (TWIST) score
The TWIST score is a clinical risk score that can be used to support the assessment of a child or young person with testicular pain. It is a 7-point score generated from five parameters:[25]Barbosa JA, Tiseo BC, Barayan GA, et al. Development and initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children. J Urol. 2013 May;189(5):1859-64.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23103800?tool=bestpractice.com
[26]Sheth KR, Keays M, Grimsby GM, et al. Diagnosing testicular torsion before urological consultation and imaging: validation of the TWIST score. J Urol. 2016 Jun;195(6):1870-6.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26835833?tool=bestpractice.com
Testicular swelling (2 points)
Hard testis (2 points)
High-riding testis (1 point)
Nausea or vomiting (1 point)
Absent cremasteric reflex (1 point)
Patients are categorised into low risk (score 0 to 2), intermediate risk (3 to 4), and high risk (5 to 7). These categories are useful for clinical decision-making as the sensitivity is 98.4% in low-risk patients and the specificity is 97.5% in high-risk patients.[27]Qin KR, Qu LG. Diagnosing with a TWIST: systematic review and meta-analysis of a testicular torsion risk score. J Urol. 2022 Jul;208(1):62-70.
https://www.auajournals.org/doi/10.1097/JU.0000000000002496
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35238603?tool=bestpractice.com
Emergency scrotal exploration is recommended if the TWIST score ≥5 in a child or young person with <48 hours of pain, unless there is a strong suspicion of an alternative diagnosis that would significantly change management.[21]NHS England. GIRFT children and young people: testicular torsion pathway. Feb 2024 [internet publication].
https://gettingitrightfirsttime.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Paediatric-testicular-torsion-pathway-guide-FINAL-V1-February-2024.pdf
However, a score ≤4 does not completely exclude testicular torsion.
The TWIST score has also been validated for the diagnosis of testicular torsion in adults.[28]Barbosa JABA, de Freitas PFS, Carvalho SAD, et al. Validation of the TWIST score for testicular torsion in adults. Int Urol Nephrol. 2021 Jan;53(1):7-11.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32844355?tool=bestpractice.com
Investigations
Advances in imaging modalities have improved the ability to identify cases of torsion; however, if history and physical examination suggest testicular torsion, immediate surgical exploration should take precedence over diagnostic tests.[21]NHS England. GIRFT children and young people: testicular torsion pathway. Feb 2024 [internet publication].
https://gettingitrightfirsttime.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Paediatric-testicular-torsion-pathway-guide-FINAL-V1-February-2024.pdf
[22]Royal College of Surgeons of England. Commissioning guide topics: management of paediatric torsion. Oct 2016 [internet publication].
https://www.rcseng.ac.uk/standards-and-research/commissioning/commissioning-guides/topics/#:~:text=Management%20of%20paediatric%20torsion
If the diagnosis is unclear, additional diagnostic tests may help avoid unnecessary surgery.[12]National Confidential Enquiry into Patient Outcome and Death. Testicular torsion. Feb 2024 [internet publication].
https://www.ncepod.org.uk/2024testiculartorsion.html
However, the primary goal is to determine the need for immediate surgical intervention as soon as possible.
Ultrasound assessment
Ultrasound assessment can rapidly and accurately determine the presence of testicular torsion or identify other aetiologies for testicular pain.[29]Sparano A, Acampora C, Scaglione M, et al. Using color power Doppler ultrasound imaging to diagnose the acute scrotum. A pictorial essay. Emerg Radiol. 2008 Sep;15(5):289-94.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18351406?tool=bestpractice.com
[30]Ota K, Fukui K, Oba K, et al. The role of ultrasound imaging in adult patients with testicular torsion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2019 Jul;46(3):325-34.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30847624?tool=bestpractice.com
Although not usually required, it may be indicated in the following scenarios:[21]NHS England. GIRFT children and young people: testicular torsion pathway. Feb 2024 [internet publication].
https://gettingitrightfirsttime.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Paediatric-testicular-torsion-pathway-guide-FINAL-V1-February-2024.pdf
Pain present for ≥48 hours, or
Strong suspicion of an alternative diagnosis that would significantly change management, or
Newborns with a suspected antenatal torsion (to exclude alternative diagnoses).
If ultrasound can be performed without delaying treatment, it may be considered to confirm diagnosis of torsion in children and young people with pain for <48 hours.[21]NHS England. GIRFT children and young people: testicular torsion pathway. Feb 2024 [internet publication].
https://gettingitrightfirsttime.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Paediatric-testicular-torsion-pathway-guide-FINAL-V1-February-2024.pdf
Grey-scale ultrasound can identify the whirlpool sign (swirling appearance of the spermatic cord), which is specific to partial or complete testicular torsion.[31]Vijayaraghavan SB. Sonographic differential diagnosis of acute scrotum: real-time whirlpool sign, a key sign of torsion. J Ultrasound Med. 2006 May;25(5):563-74.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16632779?tool=bestpractice.com
[32]Expert Panel on Urological Imaging, Gerena M, Allen BC, et al. ACR appropriateness criteria® acute onset of scrotal pain-without trauma, without antecedent mass: 2024 update. J Am Coll Radiol. 2024 Nov;21(11s):S364-71.
https://www.jacr.org/article/S1546-1440(24)00706-3/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/39488348?tool=bestpractice.com
[33]Kim DJ, Bell CR, Sheppard G. Genitourinary ultrasound. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2024 Nov;42(4):819-38.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/39326990?tool=bestpractice.com
However, the whirlpool sign is of limited utility in neonates, and the sensitivity of detection varies with ultrasonographer experience.[34]McDowall J, Ahmed A, Gerber L. The ultrasonographic "whirlpool sign" in testicular torsion: valuable tool or waste of valuable time? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Emerg Radiol. 2018 Jun;25(3):281-92.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29335899?tool=bestpractice.com
Colour Doppler and/or power Doppler studies are also needed to establish the presence or absence of blood flow to the testicles.[29]Sparano A, Acampora C, Scaglione M, et al. Using color power Doppler ultrasound imaging to diagnose the acute scrotum. A pictorial essay. Emerg Radiol. 2008 Sep;15(5):289-94.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18351406?tool=bestpractice.com
[32]Expert Panel on Urological Imaging, Gerena M, Allen BC, et al. ACR appropriateness criteria® acute onset of scrotal pain-without trauma, without antecedent mass: 2024 update. J Am Coll Radiol. 2024 Nov;21(11s):S364-71.
https://www.jacr.org/article/S1546-1440(24)00706-3/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/39488348?tool=bestpractice.com
Power Doppler is more sensitive to low blood flow than regular colour Doppler.[32]Expert Panel on Urological Imaging, Gerena M, Allen BC, et al. ACR appropriateness criteria® acute onset of scrotal pain-without trauma, without antecedent mass: 2024 update. J Am Coll Radiol. 2024 Nov;21(11s):S364-71.
https://www.jacr.org/article/S1546-1440(24)00706-3/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/39488348?tool=bestpractice.com
Spectral analysis can be used in combination with colour and power Doppler ultrasound to determine pulsatile flow, arterial or venous.[32]Expert Panel on Urological Imaging, Gerena M, Allen BC, et al. ACR appropriateness criteria® acute onset of scrotal pain-without trauma, without antecedent mass: 2024 update. J Am Coll Radiol. 2024 Nov;21(11s):S364-71.
https://www.jacr.org/article/S1546-1440(24)00706-3/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/39488348?tool=bestpractice.com
[33]Kim DJ, Bell CR, Sheppard G. Genitourinary ultrasound. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2024 Nov;42(4):819-38.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/39326990?tool=bestpractice.com
Normal or increased intra-testicular blood flow (i.e., hyperaemia) may suggest an inflammatory diagnosis or successful de-torsion.[29]Sparano A, Acampora C, Scaglione M, et al. Using color power Doppler ultrasound imaging to diagnose the acute scrotum. A pictorial essay. Emerg Radiol. 2008 Sep;15(5):289-94.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18351406?tool=bestpractice.com
However, blood flow does not exclude a diagnosis of testicular torsion because arterial flow may be present in early phases of torsion, or in partial or intermittent torsion. Comparison with the contralateral testicle should be carried out to identify differences in flow.[24]European Association of Urology. Paediatric urology. Apr 2024 [internet publication].
https://uroweb.org/guidelines/paediatric-urology
[33]Kim DJ, Bell CR, Sheppard G. Genitourinary ultrasound. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2024 Nov;42(4):819-38.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/39326990?tool=bestpractice.com
Spectral analysis may also be helpful in these cases.[33]Kim DJ, Bell CR, Sheppard G. Genitourinary ultrasound. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2024 Nov;42(4):819-38.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/39326990?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Bilateral transverse colour Doppler images in a 12-year-old boy with right-sided scrotal pain of sudden onset, showing no colour flow signals in the right testis, which is enlarged and has heterogeneous echogenicity; reactive hydrocele (h) and thickening of the scrotal wall (*) are also seen; testicular torsion and bell clapper deformity were confirmed at surgeryAso C, et al. RadioGraphics. 2005;25:1197-1214. Used with permission [Citation ends].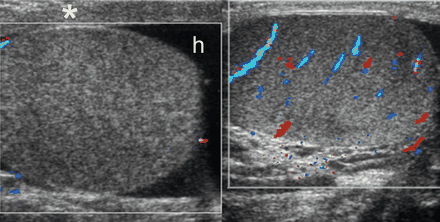
Urinalysis
If urinalysis is abnormal this usually suggests an alternate diagnosis (e.g., epididymitis or orchitis). However, it is important to note that the urinalysis may be negative in cases of epididymitis or orchitis and positive in the setting of testicular torsion.[35]Blaivas M, Brannam L. Testicular ultrasound. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2004 Aug;22(3):723-48.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15301848?tool=bestpractice.com
Scintigraphy
Further testing to rule out testicular torsion can be done with scintigraphy (nuclear scanning), which has almost 100% sensitivity for identifying patients with torsion; however, it takes longer and is less readily available than Doppler ultrasound.[5]Ringdahl E, Teague L. Testicular torsion. Am Fam Physician. 2006 Nov 15;74(10):1739-43.
https://www.aafp.org/afp/2006/1115/p1739.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17137004?tool=bestpractice.com
[36]Hod N, Maizlin Z, Strauss S, et al. The relative merits of Doppler sonography in the evaluation of patients with clinically and scintigraphically suspected testicular torsion. Isr Med Assoc J. 2004 Jan;6(1):13-5.
http://www.ima.org.il/IMAJ/ViewArticle.aspx?year=2004&month=01&page=13
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14740502?tool=bestpractice.com
Scintigraphy provides information about anatomy and vascular perfusion that can be used to distinguish testicular torsion from other non-surgical causes of an acute scrotum, preventing unnecessary surgery.
