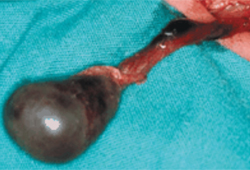
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- testicular pain
- intermittent pain
- no pain relief upon elevation of scrotum
- scrotal swelling or oedema
- scrotal erythema
- reactive hydrocele
- high-riding testicle
- horizontal lie
- absent cremasteric reflex
Risk factors
- age under 25 years
- neonate
- bell clapper deformity
- trauma/exercise
- intermittent testicular pain
- undescended testicle
- cold weather
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- Testicular Workup for Ischaemia and Suspected Torsion (TWIST) score
- ultrasound with Doppler flow imaging
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Hemanshoo Thakkar, MBBS, BSc, FRCS (Paed)
Consultant Paediatric Surgeon
Evelina London Children’s Hospital
Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust
London
UK
Disclosures
HT declares that he has no conflicting interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Hemanshoo Thakkar would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Richard Lee, Dr Caroline Kang, and Dr Jessica Marinaro, Dr George Kaplan, Dr Deborah Dean, and Dr Paul Hamilton, the previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
RL has received funding from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. CK, JM, GK, DD, and PH declared that they had no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Eugene Minevich, MD, FAAP, FACS
Associate Professor
Division of Pediatric Urology
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center
Cincinnati
OH
Disclosures
EM declares that he has no competing interests.
Simon E. Kenny, BSc, ChB (Hons), MD, FRCS (Paed), FAAP
Consultant Pediatric Surgeon/Urologist
Alder Hey Children's NHS Foundation Trust
Liverpool
UK
Disclosures
SEK declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer