Investigations
1st investigations to order
serum immunofixation electrophoresis
Test
Positive immunofixation (presence of a monoclonal protein in the serum or urine) and/or an abnormal serum immunoglobulin free light chain assay is reported in 99% of patients with AL amyloidosis.[76]
A diagnosis of AL amyloidosis should always be confirmed histologically (e.g., biopsy with amyloid typing) to avoid a misdiagnosis because an incidental monoclonal gammopathy may be present in other types of amyloidosis (e.g., hereditary amyloidosis, wild-type transthyretin [ATTRwt] amyloidosis).[28][29][61][62][77]
A diagnosis of AL amyloidosis is unlikely if immunofixation and serum immunoglobulin free light chain assay are normal.
Result
may be positive for a monoclonal protein
urine immunofixation electrophoresis (using 24-hour urine collection)
Test
Positive immunofixation (presence of a monoclonal protein in the serum or urine) and/or an abnormal serum immunoglobulin free light chain assay is reported in 99% of patients with AL amyloidosis.[76]
The finding of a light chain protein in the urine is suggestive of multiple myeloma and AL amyloidosis.
A diagnosis of AL amyloidosis should always be confirmed histologically (e.g., biopsy with amyloid typing) to avoid a misdiagnosis because an incidental monoclonal gammopathy may be present in other types of amyloidosis (e.g., hereditary amyloidosis, wild-type transthyretin [ATTRwt] amyloidosis).[28][29][61][62][77]
A diagnosis of AL amyloidosis is unlikely if immunofixation and serum immunoglobulin free light chain assay are normal.
Result
may be positive for a monoclonal protein
sreum immunoglobulin free light chain assay
Test
Extremely high sensitivity (>95%) for identifying AL amyloidosis.[98]
Positive immunofixation (presence of a monoclonal protein in the serum or urine) and/or an abnormal serum immunoglobulin free light chain assay is reported in 99% of patients with AL amyloidosis.[76]
A diagnosis of AL amyloidosis should always be confirmed histologically (e.g., biopsy with amyloid typing) to avoid a misdiagnosis because an incidental monoclonal gammopathy may be present in other types of amyloidosis (e.g., hereditary amyloidosis, wild-type transthyretin [ATTRwt] amyloidosis).[28][29][61][62][77]
A diagnosis of AL amyloidosis is unlikely if immunofixation and serum immunoglobulin free light chain assay are normal.
Result
may show abnormal kappa to lambda light chain ratio
FBC with differential
Test
Anaemia is seen generally in those patients with renal insufficiency or gastrointestinal blood loss.
Thrombocythaemia is seen as a consequence of hepatic involvement and hypersplenism.
Result
usually normal
peripheral blood smear
Test
Ordered to assess for a plasma cell disorder.[62]
May show stacked red blood cells (Rouleaux formation) due to elevated immunoglobulins in serum (associated with AL amyloidosis).
Result
may show rouleaux formation
serum quantitative immunoglobulins
Test
Ordered to assess for a plasma cell disorder.[62]
Quantifies the amount of immunoglobulins in the serum, but does not differentiate between polyclonal (normal) and monoclonal (abnormal) immunoglobulins.
Result
may show increased concentration of immunoglobulins
serum protein electrophoresis
Test
Ordered to assess for a plasma cell disorder.[62]
Can identify a monoclonal immunoglobulin in the serum, although sensitivity is low without immunofixation.
Result
may show monoclonal immunoglobulin
comprehensive metabolic profile
Test
Includes serum urea, serum creatinine, electrolytes, serum albumin, serum calcium, serum uric acid, serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), beta-2 microglobulin, and liver function tests (LFTs).[62]
Ordered to assess for renal and liver involvement.[62]
Hepatic amyloid is characterised by elevations of the serum alkaline phosphatase.
Most patients with early renal amyloidosis have preserved clearance of creatinine but can have significant degrees of hypoalbuminaemia due to the urinary protein loss.
Beta-2-microglobulin is predictive of survival in patients with AL amyloidosis.[96][97]
Result
may be normal or abnormal (e.g., hypoalbuminaemia; elevated alkaline phosphatase; low calcium [due to hypoalbuminaemia]; elevated beta-2-microglobulin)
urine protein electrophoresis (using 24-hour urine collection)
Test
Ordered to assess for renal involvement.[62]
May show elevated proteins in the urine (including a monoclonal immunoglobulin, although sensitivity is low without immunofixation)
Result
urine protein may be elevated (proteinuria); may reveal a monoclonal immunoglobulin
24-hour total urine protein
Test
Ordered to assess for renal involvement.[62]
Patients with amyloidosis who have a urinary albumin excretion of >1 g/24 hours are considered to have renal involvement.
A level of >3 g/24 hours defines nephrotic range proteinuria.
Result
may show elevated urinary protein
orthostatic vital sign assessment
Test
Carried out to assess for nerve involvement.[62]
Orthostatic hypotension with syncope can occur if autonomic neuropathy is present (e.g., in AL amyloidosis or ATTRv amyloidosis)
Result
may indicate orthostatic hypotension
tissue biopsy
Test
Histological confirmation of amyloid deposits in tissue is essential for establishing a diagnosis of amyloidosis.
Bone marrow aspirate and biopsy, and subcutaneous fat aspirate (e.g., abdominal fat pad) are recommended in patients with suspected amyloidosis (e.g., if a monoclonal protein is present).[62] Other tissues that can be biopsied include lip (minor salivary gland) and rectum.[62]
Bone marrow aspirate and biopsy can also be used to identify clonal plasma cells and assess for coexistent multiple myeloma. See Multiple myeloma.
If bone marrow and tissue biopsy studies are negative, biopsy of an involved organ (e.g., heart, liver, kidney, nerve) should be performed as clinically indicated.[62]
Multiple tissue or organ biopsies are potentially hazardous and are not recommended.[78] Bone marrow biopsy combined with subcutaneous fat aspirate (e.g., abdominal fat pad) will identify amyloid deposits in most (85%) patients with amyloidosis.[79]
Apple-green birefringence on a Congo red stained aspirate or biopsy specimen is required for diagnosis.[80] Apple-green birefringence after Congo red staining confirms the presence of amyloid deposits but does not differentiate between different types of amyloid.[62] Amyloid typing and/or immunohistochemical studies should be carried out to confirm the type of amyloid.
Amyloid deposits are always extracellular and appear amorphous. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Congo red stain blood vessel in a bone marrow biopsy demonstrating green birefringence pathognomonic of amyloidosisMorie A. Gertz, MD; courtesy of Mayo Clinic [Citation ends].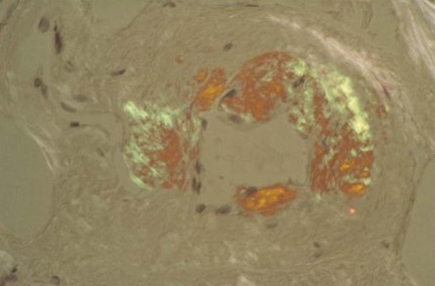 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Renal biopsy demonstrating amyloid deposits as amorphous replacement of the glomerular architectureMorie A. Gertz, MD; courtesy of Mayo Clinic [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Renal biopsy demonstrating amyloid deposits as amorphous replacement of the glomerular architectureMorie A. Gertz, MD; courtesy of Mayo Clinic [Citation ends].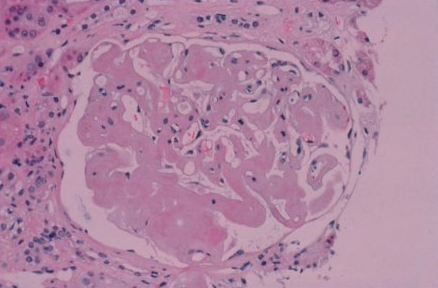
Result
positive apple-green birefringence when aspirate or biopsy specimen is stained with Congo red; may show presence of clonal plasma cells in bone marrow biopsy if multiple myeloma is present
Investigations to consider
mass spectrometry
Test
Used to confirm amyloid type by analysing amyloid protein composition in biopsy tissue. Has high sensitivity (90%). Currently the gold standard for amyloid typing.
Mass spectrometry has higher diagnostic accuracy than immunohistochemistry.[62]
Result
confirms amyloid protein type (e.g., light chain, serum amyloid A, or transthyretin)
immuno-electron microscopy
Test
All forms of amyloid have a fibrillar appearance under the electron microscope and are rigid and non-branching, but all fibrils are not necessarily amyloid.
Immuno-electron microscopy can be used on renal biopsy specimens to clarify the fibrillar nature of the amyloid, but is not part of routine clinical practice for other biopsy material.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Electron micrograph demonstrating classical amyloid fibrilsMorie A. Gertz, MD; courtesy of Mayo Clinic [Citation ends].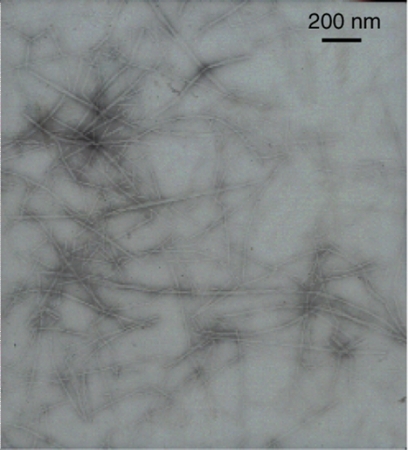
Result
amyloids appear fibrillar, rigid, and non-branching
immunohistochemical studies
Test
Can be attempted to distinguish the various forms of systemic amyloidosis. Commercially available antisera to immunoglobulin light chains, serum amyloid A, and transthyretin are typically used but may lack specificity and sensitivity.
Immunohistochemistry has lower diagnostic accuracy than mass spectrometry.[62]
In most cases, mass spectrometry and immuno-electron microscopy are required to determine the underlying type of amyloid.
Result
may identify immunoglobulin light chains, serum amyloid A, or transthyretin
genetic testing
Test
Patients with clinically suspected amyloidosis with equivocal or normal immunofixation and serum immunoglobulin free light chain assay should undergo genetic testing.
Genetic testing can be used to assess for hereditary amyloidosis (e.g., transthyretin variants [ATTRv], fibrinogen A alpha-chain, apolipoprotein A, lysozyme) and familial periodic fever syndromes associated with secondary (AA) amyloidosis (e.g., familial Mediterranean fever, tumour necrosis factor [TNF] receptor-associated periodic fever syndromes [TRAPS], cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes [CAPS; such as Muckle-Wells syndrome], mevalonate kinase deficiency [formerly known as hyper-IgD syndrome]).[83][84]
Use of genetic testing is important to avoid a misdiagnosis (e.g., AL amyloidosis) in patients with hereditary amyloidosis.[30][62]
Result
may be positive for hereditary amyloidosis or familial periodic fever syndromes
serum amyloid P (SAP) scintigraphy scan
Test
SAP scintigraphy is standard practice in the UK and the Netherlands, but is not available elsewhere.
Result
uptake at sites of amyloid deposition
serum troponin T or I
Test
Used to assess for heart involvement and for prognostication; performed in all patients.[62] Sensitive test of myocardial injury in amyloidosis.
Troponin I can be used if troponin T is unavailable.
Troponin level is incorporated into the staging criteria for AL amyloidosis.[93][94][95] See Criteria.
Patients with a detectable troponin level have a worse prognosis than those with undetectable values.[91]
Result
may be elevated
N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT‐proBNP)
Test
Used to assess for heart involvement and for prognostication; performed in all patients.[62] B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) can be performed if NT-proBNP is unavailable.
A sensitive marker for myocardial stretch and congestive heart failure.[91][92] Has been shown to have important prognostic value in the management of amyloidosis.[92]
NT‐proBNP is incorporated into the staging criteria for AL amyloidosis.[93][94][95] See Criteria.
Levels >300 ng/L (>300 pg/mL) are highly suggestive of myocardial involvement with amyloid.[98]
Patients with <170 ng/L (<170 pg/mL) have a significantly longer survival than patients with >170 ng/L ( >170 pg/mL).
Result
may be elevated
lipid panel
Test
Ordered to assess for heart involvement.[62]
Result
may be abnormal
coagulation studies
Test
Includes prothrombin time (PT), partial thromboplastin time (PTT), and factor X, as clinically indicated.
Ordered to assess for amyloid-related coagulation abnormalities.[62]
Patients with AL amyloidosis may develop acquired factor X deficiency due to adsorption of factor X to amyloid fibrils.[99]
Result
may be abnormal
ECG
Test
Should be performed in all patients (symptomatic or asymptomatic) with suspected or confirmed amyloidosis.[55][71][86] Late diagnosis of cardiac involvement is associated with poor outcomes.[85]
Cardiac involvement is reported in 55% to 76% of patients with AL amyloidosis.[42][43][49][65] Cardiac involvement may also occur in patients with hereditary amyloidosis (e.g., ATTRv amyloidosis) or wild-type transthyretin (ATTRwt) amyloidosis.[54][55]
Result
may show conduction abnormalities; atrial fibrillation
echocardiogram (with tissue Doppler and global longitudinal strain)
Test
Should be performed in all patients (symptomatic or asymptomatic) with suspected (e.g., elevated NT-proBNP) or confirmed amyloidosis.[55][71][86] Late diagnosis of cardiac involvement is associated with poor outcomes.[85]
Cardiac involvement is reported in 55% to 76% of patients with AL amyloidosis.[42][43][49][65] Cardiac involvement may also occur in patients with hereditary amyloidosis (e.g., ATTRv amyloidosis) or wild-type transthyretin (ATTRwt) amyloidosis.[54][55]
Echocardiography with tissue Doppler and global longitudinal strain imaging may identify patterns highly suggestive of cardiac amyloidosis.[55][86]
Myocardial strain is defined as the percentage change in myocardial fiber length per unit length, and the strain rate is the derivative over time of strain.[100][101]
Result
may show diastolic dysfunction (restrictive filling of the ventricular chambers); thickening of the interventricular septum; decreased ejection fraction; increased left ventricular (LV) wall thickness; typical LV longitudinal strain pattern; reduced tissue Doppler velocities
cardiac MRI
Test
Cardiac MRI may be useful if an echocardiogram is suggestive or indeterminate. However, it is not diagnostic and cannot distinguish between AL amyloidosis and TTR amyloidosis.[71][86]
Cardiac MRI parameters should be combined with electrocardiographic, clinical, biomarker, and other imaging findings to maximise diagnostic accuracy.[86]
Myocardial nulling after gadolinium injection is highly specific for cardiac amyloidosis.
Result
may show significantly elevated T1 and T2 relaxation times compared with age-matched controls
cardiac scintigraphy
Test
Cardiac scintigraphy with technetium-labelled bone tracers (99mTc-PYP or 99mTc-DPD) should be performed if transthyretin (TTR) cardiac amyloidosis is suspected.[30] Scintigraphy is sensitive for the detection of TTR cardiac amyloidosis and enables non-invasive clinical diagnosis.[71][86][87][88] However, it lacks specificity; therefore false positives may be seen. A negative monoclonal protein result alongside scintigraphy cardiac uptake (grade 2 or 3) confirms a diagnosis of TTR amyloidosis (without needing biopsy).[62][71] If scintigraphy cardiac uptake is 1 or 0, a biopsy is required (cardiac or non-cardiac, depending on presentation).[62]
In older men with an echocardiogram consistent with cardiac amyloidosis, a cardiac scintigraphy showing uptake of 99mTc-PYP or 99mTc-DPD in myocardial tissue increases the suspicion of wild-type TTR (ATTRwt) amyloidosis.
Result
may show myocardial uptake of 99mTc-PYP or 99mTc-DPD
electromyogram/nerve conduction studies
Test
Ordered to assess for nerve involvement (e.g., if significant peripheral neuropathy is present).[62]
Result
may be abnormal
endocrine tests
Test
Includes thyroid-stimulating hormone and cortisol levels.
Ordered to assess for endocrine involvement.[62]
Result
may be abnormal
pulmonary function tests
Test
Ordered to assess for lung involvement.[62]
Result
may be abnormal
computed tomography (CT) scan
Test
Whole-body low-dose CT (WBLD-CT) can be used to detect osteolytic bone lesions if a monoclonal protein is detected.[62]
Abdominal CT can be used to evaluate liver involvement, as clinically indicated.[62]
Chest CT can be used to evaluate lung involvement, if clinically indicated.[62]
Result
WBLD-CT may detect osteolytic bone lesions; abdominal CT may show liver involvement (hepatomegaly); chest CT may show lung involvement
fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET)/CT
Test
Can be used to detect osteolytic bone lesions if a monoclonal protein is detected.
Result
may detect osteolytic bone lesions
skeletal survey
Test
Can be used to detect osteolytic bone lesions if a monoclonal protein is detected, but only if advanced imaging modalites (CT, FDG-PET/CT) are unavailable.[62]
Sensitivity is significantly lower than CT and FDG-PET/CT.
Result
may detect osteolytic bone lesions
abdominal ultrasound
Test
Ordered to evaluate liver involvement, as clinically indicated.[62]
Result
may show liver involvement (hepatomegaly)
gastric emptying scan
upper and lower endoscopy
Test
Ordered if symptoms suggest gastrointestinal involvement.[62]
Result
may identify features of amyloid deposits (e.g., polypoid protrusions, erosions, ulcerations)
123I-labelled serum amyloid P (SAP) scintigraphy
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer