Last reviewed: 18 Mar 2025
Last updated: 15 Feb 2024
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- painful and tender joints
- osteoarthritis-like involvement of joints (wrists, shoulders)
- sudden worsening of osteoarthritis
Other diagnostic factors
- red and swollen joints
- joint effusion and fluctuance
- fever and malaise
Risk factors
- advanced age
- injury
- hyperparathyroidism
- haemochromatosis
- family history of CPPD
- hypomagnesaemia
- hypophosphatasia
- gout
- other metabolic conditions
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- arthrocentesis with synovial fluid analysis
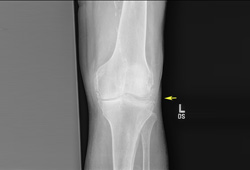
- x-rays of affected joints
- serum calcium
- serum parathyroid hormone
- iron studies
- serum magnesium
- serum alkaline phosphatase
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Ann K. Rosenthal, MD

Professor of Medicine
Medical College of Wisconsin
Milwaukee
WI
Disclosures
AKR is the author of several articles cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Priyanka Iyer, MD
Clinical Assistant Professor
University of California, Irvine
Irvine
CA
Disclosures
PI declares that she has no competing interests.
Ade Adebajo, MBBS, MSc, FRCP (Glasgow), FACP
Consultant Rheumatologist
Rheumatology
University of Sheffield Medical School
Sheffield
UK
Disclosures
AA declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer