Investigations
1st investigations to order
ECG
Test
This should be done as soon as possible to assess for presence of QRS prolongation.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Classic ECG changesFrom the collection of R.S. Hoffman; used with permission [Citation ends].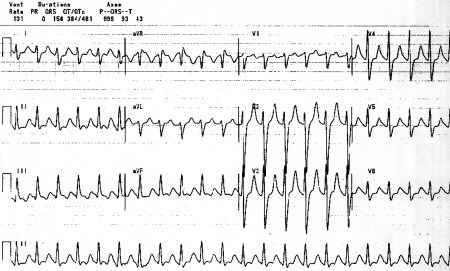
Any QRS duration >100 milliseconds in the setting of overdose, or unknown cause of altered mental status, is suspicious for tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) overdose. However, if no QRS prolongation is found, TCA overdose cannot be excluded.
If QRS prolongation is found on ECG, a cardiac monitor should be attached to the patient and repeat 12-lead ECGs should be performed at least every hour for the first 6 hours.
QRS prolongation >100 milliseconds indicates a 30% likelihood of seizure. When the QRS prolongs to >160 milliseconds, there is a 50% risk of arrhythmia.[19]
The most common ECG abnormality seen in TCA overdose is sinus tachycardia. Other ECG changes that can occur include: prolonged QTc duration, prolonged PR interval, AV block, non-specific ST and T wave changes, downward sloping ST elevation in leads V1 to V3 with right bundle branch block (Brugada wave).[17]
It is useful to look for the presence of a terminal 40 milliseconds rightward axis shift, seen as an R-wave deflection in aVR or an S wave in I or aVL.[18] Although it may be present in any condition that causes right heart strain, such as bronchospasm or large pulmonary embolus, its absence makes the diagnosis of TCA overdose unlikely.
Result
tachycardia; QRS prolongation >100 milliseconds; terminal 40 milliseconds rightward axis deviation
sodium bicarbonate therapeutic trial
Test
Should be administered as soon as QRS prolongation is confirmed. If the QRS narrows after a bolus of sodium bicarbonate, this confirms the presence of a sodium channel blocker, although not specifically a tricyclic antidepressant.
The ECG should be repeated each hour to look for any QRS prolongation >100 milliseconds.
If the QRS fails to narrow after this bolus, then the presence of a sodium channel blocker is unlikely and the QRS prolongation probably has non-toxicological causes (as sodium channel blockade is the only toxicological explanation for QRS prolongation).
Result
narrowing of QRS
ABG
Test
Any acidosis is detrimental since it increases cardiotoxicity. Experimental and clinical studies have shown that both alkalinisation and sodium loading (with either sodium bicarbonate or hypertonic saline, and with or without hyperventilation) are effective at improving ECG abnormalities, consciousness level, and hypotension.[21] The patient’s serum pH should not exceed 7.5 to 7.55.
Result
metabolic acidosis
Investigations to consider
serum TCA concentrations
Test
Serum concentrations >0 nanograms/mL confirm the presence of a tricyclic antidepressant.
Although the test can confirm ingestion, it is not ordered routinely as false-positive results are common and the test has less prognostic value than an ECG.
Levels >1000 nanograms/mL are associated with cardiovascular toxicity.
The test can confirm clinical suspicion, but results rarely return in a clinically useful timeframe.
Result
presence of TCA
serum paracetamol concentrations
Test
Polypharmacy overdose is common.
In patients unable to clearly detail what has been ingested it is important to check for co-ingestants.
Result
may show presence of co-ingestant
serum salicylate concentrations
Test
Polypharmacy overdose is common.
In patients unable to clearly detail what has been ingested it is important to check for co-ingestants.
Result
may show presence of co-ingestant
urine drug screen
Test
Urine tricyclic antidepressant screens are available more rapidly, but their clinical usefulness is limited in the management of an overdose. However, it may assist if there is a strong suspicion of a significant co-ingestion.
Result
presence of TCA; may show presence of co-ingestant
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer