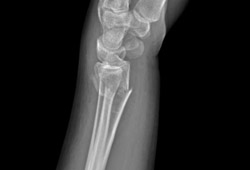
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- wrist pain
- tenderness over the distal radius
- swelling
Other diagnostic factors
- deformity
- tenderness in the anatomic snuff-box
- numbness in the fingers
- hypo-aesthesia
- open wound
Diagnostic investigations
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Expert advisers
Michael Barrett, MBChB, FRCS (Tr & Orth), PG Cert Med Ed
Consultant Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgeon
Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
Cambridge
UK
Disclosures
MB is a director of Orthohub.xyz, an online education platform for orthopaedic surgeons. Orthohub.xyz receives sponsorship from the healthcare industry.
Acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice would like to gratefully acknowledge the previous expert contributor, whose work has been retained in parts of the content:
Niels W.L. Schep, MD
Trauma, Hand, and Wrist Surgeon
Department of Trauma and Hand Surgery
Maasstad Hospital
Rotterdam
Netherlands
Disclosures
NWLS is an author of several references cited in this topic. He is a consultant for Synthes, Medartis, and Arthrex, and has received honoraria from The AO Foundation for teaching courses.
Peer reviewers
Ramon Tahmassebi, MBBS, BSc (Hons), FRCS (Tr & Orth)
Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon
Clinical Director Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery
King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
London
UK
Disclosures
RT declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer