Investigations
1st investigations to order
TSH
Test
Initial test for patients presenting with a thyroid nodule.[1] Usually normal.
A suppressed (lower than normal) thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level suggests hyperthyroidism or the possibility of a hyperfunctioning (hot) nodule. The incidence of carcinoma in hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules is very low.
If TSH is normal or elevated, the next diagnostic step is ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration (FNA) of the thyroid nodule.[1]
Consider asking patients about their biotin (vitamin B7) intake, as a high consumption from dietary supplements may lead to falsely high or low thyroid function test results.[55][56][57]
Result
normal (0.4 to 4.0 mIU/L)
thyroid/neck ultrasound
Test
An ultrasound should be performed in all patients with a thyroid nodule to confirm its presence, and assess size, location, and cystic component(s).[1][29][40][41] Ultrasound evaluation of the cervical lymph nodes should also be performed.[1][41][42]
Thyroid ultrasound and Doppler defines dimensions of nodules and solid/cystic component(s).[1][29][40][41]
Ultrasound-based risk stratification systems can be used to inform decisions on when to perform a fine-needle aspiration (FNA).[11][43][44] The American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging, Reporting, and Data System (ACR TI-RADS) classifies nodules based on ultrasound features as benign, not suspicious, mildly suspicious, moderately suspicious, or highly suspicious for malignancy (TR1 to TR5).[11] See Classification. Each risk stratification system has its own guidance on the threshold for FNA.
Features suspicious for malignancy include micro-calcifications, a more-tall-than-wide shape, marked hypoechogenicity, or irregular margins.[11][47][58]
Ultrasound can be used to guide FNA of suspicious nodules.
Also used to pre-operatively evaluate cervical lymph nodes in patients with medullary cancer.[4]
Result
may show characteristics of a benign, mildly suspicious, moderately suspicious, or highly suspicious thyroid nodule; may show cervical lymphadenopathy
fine-needle aspiration (FNA)
Test
Done if thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is normal or elevated.
FNA of thyroid nodules <1 cm is not recommended unless ultrasound findings are suspicious for malignancy or the patient has a high-risk history.[1][29]
Ultrasound-based risk stratification systems (e.g., American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging, Reporting, and Data System [ACR TI-RADS]) can be used to inform decisions on when to perform an FNA.[11][43][44][59] FNA is recommended for highly suspicious nodules 1 cm or larger.[11] See Classification.
The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (BSRTC) is commonly used to report FNA cytology findings, and is recommended by the American Thyroid Association.[1] The Bethesda system includes six diagnostic categories with an implied cancer risk that recommends the next clinical management step.[8] See Classification.
Cytology may identify the thyroid cancer type.[46] However, for follicular or oncocytic neoplasms, cytology does not distinguish between adenoma (benign) and carcinoma.[47][48] In these cases, molecular testing or surgery (e.g., lobectomy) to look for capsular or vascular invasion is required to confirm a diagnosis.[29][49]
Papillary cancer: intranuclear holes and grooves, 'Orphan Annie' eyes, and psammoma bodies.[29][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histopathology of papillary carcinoma, thyroid: a psammoma body is visible (arrow)CDC Image Library/Dr Edwin P. Ewing, Jr [Citation ends].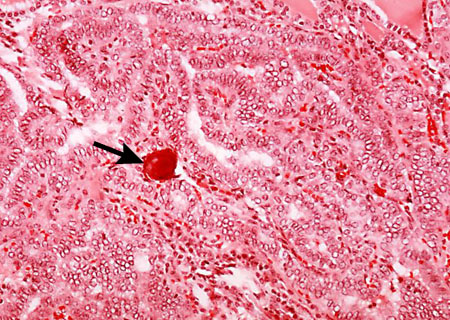
Follicular neoplasms: hypercellularity, microfollicles, and absence of colloid.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histopathology of follicular carcinoma, thyroidCDC Image Library/Dr Edwin P. Ewing, Jr [Citation ends].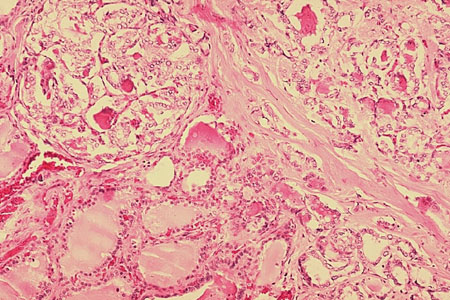
Anaplastic thyroid cancer: wide variations in appearance; subtypes show spindle cell pattern, pleomorphic giant cell pattern, and squamoid pattern; use of special stains or immunohistochemical studies may be required to exclude other treatable entities with better prognoses.[13]
Medullary cancer: eosinophilic cells arranged in nests or sheets separated by amyloid and vascular stroma. Immunohistochemical staining positive for calcitonin.[4][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Medullary thyroid cancer: H&E stain showing nests of tumour cellsMohan V et al. BMJ Case Reports CP 2019;12:e230446; used with permission [Citation ends].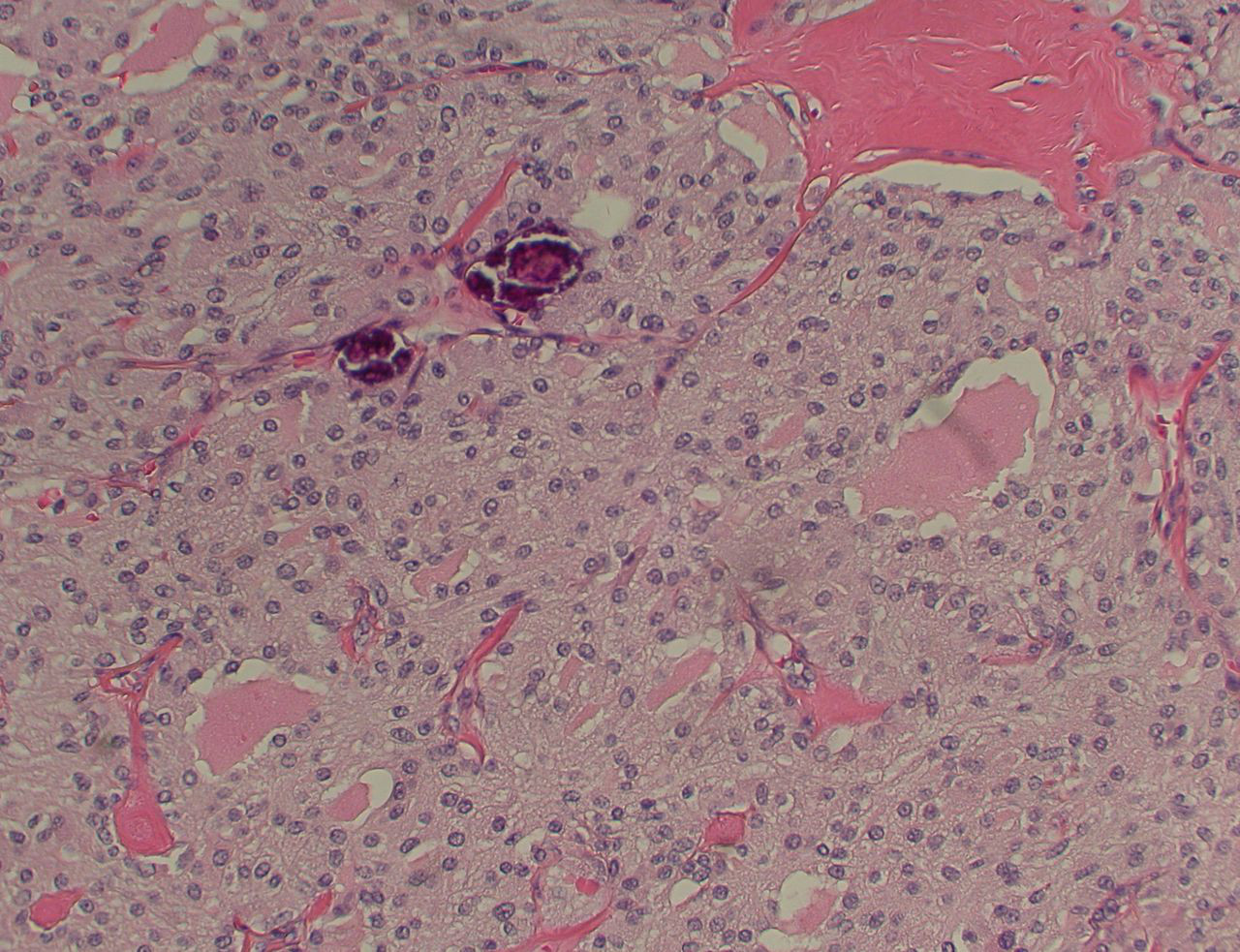
Lymphoma may be identified by flow cytometry and nuclear atypia.[50]
Result
cytology may suggest malignancy
Investigations to consider
molecular testing of cytology specimens
Test
Molecular testing of FNA specimens may be performed to detect genomic mutations/alterations (e.g., BRAF V600, MET, RET/PTC, NTRK, RAS, PAX8::PPARG) to enhance interpretation of indeterminate cytology findings (including follicular or oncocytic neoplasms) and to help guide treatment decisions.[37]
Result
may show genetic alterations associated with malignancy
free T4
Test
Required if thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is abnormal (suppressed). Elevated free T4 suggests hyperthyroidism.
If free T4 is not available, an alternative test is total T4 plus a measure of binding.
Consider asking patients about their biotin (vitamin B7) intake, as a high consumption from dietary supplements may lead to falsely high or low thyroid function test results.[55][56][57]
Result
normal (0.8 to 1.8 nanograms/dL)
free T3
Test
Required if thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is abnormal (suppressed). Elevated free T3 suggests hyperthyroidism.
If free T3 is not available, an alternative test is total T3 plus a measure of binding.
Consider asking patients about their biotin (vitamin B7) intake, as a high consumption from dietary supplements may lead to falsely high or low thyroid function test results.[55][56][57]
Result
normal (2.3 to 4.2 picograms/mL for free T3; 80 to 180 nanograms/dL for total T3).
laryngoscopy
Test
Vocal cord mobility should be examined in patients with voice change/hoarseness.[1]
Laryngoscopy, which may show a paralysed vocal cord, is recommended in patients with pre-operative voice abnormalities and in patients with gross extrathyroidal extension of cancer posteriorly or extensive nodal involvement, even if the voice is normal.[1]
A paralysed vocal cord is highly suggestive of malignancy.
Result
may show ipsilateral paralysed vocal cord
I-123 thyroid scan and uptake
Test
Scan should be ordered for patients with overt or subclinical hyperthyroidism. A hyperfunctioning (hot) nodule is almost always benign.
Most nodules are hypofunctioning (cold). Most of these are benign, but malignant nodules are also cold.
Result
hot or cold nodule
core biopsy
CT neck
Test
Used for preoperative evaluation of cervical lymph nodes in patients with medullary cancer.[4]
Occasionally needed to evaluate large or rapidly expanding neck masses (e.g., suspected lymphomas).
Result
may show cervical lymphadenopathy
serum calcitonin
genetic testing for familial syndromes
Test
Required for patients with a family history of multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) syndromes or a cytologic diagnosis of medullary thyroid cancer.[4][37]
Almost all patients with MEN type 2A (MEN2A), MEN2B, or isolated familial medullary thyroid cancer have germline RET (REarranged during Transfection) mutations, and around 50% of sporadic medullary thyroid cancers have somatic RET mutations.[4]
The RET proto-oncogene codes for a tyrosine kinase receptor, which is expressed in neural crest-derivative tissues.[29]
Different types of RET mutation account for different biological behaviour and may guide future management (such as screening for, and treatment of, pheochromocytoma and hyperparathyroidism).[53]
Result
may detect RET mutations
serum thyroglobulin
Test
Useful for post-treatment monitoring of papillary or follicular (including oncocytic) thyroid cancer, but not for diagnosis of thyroid malignancy.
It is also useful for predicting future disease-free status before post-operative radioiodine therapy for remnant ablation, whereby low pre-ablation thyroglobulin levels may be considered a favourable risk factor in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer.[54]
Result
may be low or elevated
Emerging tests
translaryngeal ultrasound
Test
An emerging modality to evaluate vocal cords pre-operatively. If there is an abnormality seen on vocal cord ultrasonography, this can then be followed by fibre-optic laryngoscopy.
A non-invasive technique that can be performed at the surgery visit.[60]
Result
may show abnormal vocal cord movement
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer