Investigations
1st investigations to order
serum calcium
Test
Reported as calcium adjusted for albumin or ionised calcium. Normal range of ionised calcium is 1.1 to 1.3 mmol/L (4.4 to 5.3 mg/dL).
Formulae used to calculate corrected calcium only provide an approximation, and this measurement may not be reliable for critically ill patients.[28] Measurement of ionised calcium is preferred.
Symptoms may be seen at slightly higher values if there had been a precipitous drop from elevated values, or if exacerbated by low magnesium or respiratory alkalosis.
If a normal serum calcium is found despite symptoms of hypocalcaemia, an arterial blood gas for carbon dioxide can be performed to determine whether hyperventilation is present.
Result
low; severe hypocalcaemia if <1.88 mmol/L (<7.5 mg/dL); moderate 1.88 to 2.00 mmol/L (7.5 to 8.0 mg/dL); and mild 2.00 to 2.13 mmol/L (8.0 to 8.5 mg/dL)
plasma intact PTH
Test
Intact PTH is measured using a second- or third-generation PTH assay.[1][29]
Measure simultaneously with calcium, if calcium level is low.
PTH levels may fall within minutes of resection of parathyroid tissue.
PTH may be elevated in the rare patient with pseudohypoparathyroidism with PTH resistance.
Result
low or normal
serum albumin
Test
Low albumin will give falsely low total serum calcium; ionised calcium will accurately reflect physiological calcium.
Result
normal; a low value affects total serum calcium
serum magnesium
Test
Magnesium deficiency exacerbates hypocalcaemia and impairs PTH secretion.
Result
may be low
serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D
Test
Vitamin D deficiency is common in the general population and in patients with hypoparathyroidism; it may make the management of hypoparathyroidism challenging.
Levels of 50 nanomol/L (20 nanograms/mL) are generally considered sufficient. If supplements are being taken, levels up to 250 nanomol/L (100 nanograms/mL) or higher may be seen: these higher levels may be needed to maintain calcium balance in hypoparathyroidism if the patient is not taking activated vitamin D or its analogues.
Result
may be low
serum phosphorus
Test
Most commonly associated with increased levels.
Result
usually elevated
serum creatinine
Test
Renal impairment complicates electrolyte replacement, and renal failure requires different treatment.
Result
normal
ECG
Test
Prolonged QT interval indicates severe life-threatening hypocalcaemia.
Arrhythmias may occur.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ECG demonstrating an atrial arrhythmia most likely to be atrial fibrillation in a patient with hypoparathyroidism and hypocalcaemiaAdapted from Nijjer S, Ghosh AK, Dubrey SW. Hypocalcaemia, long QT interval and atrial arrhythmias. BMJ Case Reports 2010 [doi:10.1136/bcr.08.2009.2216]. Copyright © 2011 by the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd. [Citation ends].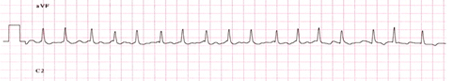
Result
prolonged QT interval
Investigations to consider
24-hour urine calcium, creatinine
Test
An elevated urinary calcium excretion, if hypocalcaemia is present and before treatment is started, suggests autosomal dominant hypocalcaemia type 1.
Result
normal, or elevated urine calcium
24-hour magnesium, creatinine
Test
In conditions of renal magnesium wasting due to renal tubular transport defects or medications (e.g., cisplatin, diuretics), urinary levels of magnesium will be normal or elevated.
If gastrointestinal losses of magnesium cause hypomagnesaemia, then the kidney will conserve magnesium, and urinary magnesium levels will be low normal or frankly low.
Result
low, normal, or elevated
liver function tests
Test
Consider possible haemochromatosis, Wilson's disease, or chronic alcohol abuse if elevated.
Result
normal
arterial blood gases (ABGs)
Test
Low serum ionised calcium levels in patients who are hyperventilating will not be detected because the sample is corrected to normal pH. If a normal serum calcium is found despite symptoms of hypocalcaemia, an ABG should be performed to determine whether hyperventilation is present.
Result
high pH, low PaCO₂ (with hyperventilation)
serum free thyroxine, thyrotropin
Test
Thyroid dysfunction should be excluded.
Result
normal
morning cortisol and adrenocorticotrophin (ACTH) stimulation testing
Test
Random cortisol levels and ACTH stimulation testing can be done to detect autoimmune adrenal insufficiency, a key component of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 (APS1). If levels and/or responses are subnormal, then adrenal insufficiency should be considered.
Result
normal
full blood count
Test
Anaemia is present in patients with thalassaemia, or if an untreated hormone deficiency state is present (e.g., adrenal insufficiency).
Result
normal
serum iron, transferrin, ferritin
Test
Iron studies show iron overload if haemochromatosis or transfusional haemosiderosis is present.
Result
normal
serum copper
Test
If elevated, Wilson's disease should be considered.
Result
normal
ophthalmological examination
Test
Chronic, long-standing hypoparathyroidism of any aetiology may produce early cataracts.
Result
normal
audiology
Test
If hearing deficit is present, consider GATA3 mutation
Result
normal
renal imaging
Test
If renal anatomical anomalies are present on ultrasound or computed tomography, consider GATA3 mutation as possible aetiology for hypoparathyroidism.
If kidneys, ureter, bladder (KUB) radiography or CT suggest nephrocalcinosis, consider CASR mutation or autosomal dominant hypocalcaemia type 1 as possible cause for hypoparathyroidism.
Result
normal
autoantibodies to type 1 interferon or 21-hydroxylase
Test
Positive antibodies to type 1 interferon (accompanied by at least one major feature [mucocutaneous candidiasis, hypoparathyroidism, or adrenal insufficiency]) suggest autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 (APS1).[1] Antibodies to 21-hydroxylase are commonly positive in autoimmune adrenal insufficiency.
Antibodies to type 1 interferons (alpha, omega) are present before endocrine deficiency occurs.[12]
Result
positive in APS1
gene sequencing
Test
Specific genetic testing can also be considered in patients who have a positive family history of non-surgical hypoparathyroidism, present with syndromic features, or are younger than 40 years.[1]
Result
variable
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer