History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
common
history of thyroid, parathyroid, or laryngeal surgery
Post-surgical hypoparathyroidism is the major aetiology in adults.[1]
chronic alcoholism
malnutrition, malabsorption, diarrhoea
muscle twitches, spasms, cramps
Muscle cramping, stiffness, and tetany may indicate chronic and/or mild hypocalcaemia.
paraesthesias, numbness, tingling
Intermittent or persistent paraesthesia, numbness, or tingling may indicate acute or severe hypocalcaemia. Chronic hypocalcaemia may manifest as perioral and distal hand and foot paraesthesias.
poor memory, slowed thinking
Can manifest with any degree of hypocalcaemia.
uncommon
Chvostek's sign
Ipsilateral contraction of facial muscles when facial nerve is tapped in front of the ear. Chvostek's sign: a video demonstration Opens in new window
convulsions
Usually generalised. May indicate acute or severe hypocalcaemia.
irregular heart beat, tachycardia
Acute or severe hypocalcaemia can cause prolonged QT interval on ECG, irregular heart beat, tachyarrhythmias, hypotension.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ECG demonstrating an atrial arrhythmia most likely to be atrial fibrillation in a patient with hypoparathyroidism and hypocalcaemiaAdapted from Nijjer S, Ghosh AK, Dubrey SW. Hypocalcaemia, long QT interval and atrial arrhythmias. BMJ Case Reports 2010 [doi:10.1136/bcr.08.2009.2216]. Copyright © 2011 by the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd. [Citation ends].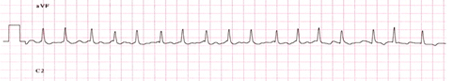
Trousseau's sign
Painful clasping response of fingers and hands when blood pressure cuff is inflated above systolic blood pressure. Trousseau's sign: video clip Opens in new window
Other diagnostic factors
common
anxiety
May be due to hyperventilation, which can worsen symptoms of hypocalcaemia because alkalosis will lower serum fraction of ionised calcium.
dry hair, brittle nails
Chronic hypocalcaemia.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Nail dystrophy due to hypocalcaemiaNijjer S, Ghosh AK, Dubrey SW. Hypocalcaemia, long QT interval and atrial arrhythmias. BMJ Case Reports 2010 [doi:10.1136/bcr.08.2009.2216]. Copyright © 2011 by the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd. [Citation ends].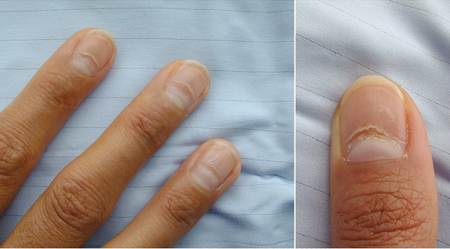
cataracts
Common after long-standing hypocalcaemia in congenital forms of hypoparathyroidism.
uncommon
history of mucocutaneous candidiasis
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 (APS1) presents as mucocutaneous candidiasis in the first few years of life, followed by hypoparathyroidism and/or adrenal insufficiency, typically with onset in childhood.[12]
history of chronic transfusions in patients with thalassaemia
Transfusional iron overload may occur in patients with thalassaemia after many years of transfusions without adequate chelation therapy.
dyspnoea
Can be due to wheezing, congestive heart failure, or laryngeal constriction; requires urgent assessment and treatment.
laryngeal spasm
Can be caused by acute or severe hypocalcaemia. It is a medical emergency that can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Risk factors
strong
thyroid surgery
Extensive surgery, such as total thyroidectomy for cancer, and lymph node dissection; prior surgery in the cervical area; less experienced surgeon.[21]
parathyroid surgery
Prior surgery in the cervical area, especially prior parathyroidectomy; less experienced surgeon.
Risk factors for transient hypoparathyroidism include: extent of parathyroid exploration; moderate hypercalcaemia as an indication for parathyroid surgery (with the possibility of suppression of remaining normal gland[s] by prevailing hypercalcaemia).[22]
hypomagnesaemia
moderate and chronic maternal hypercalcaemia (neonatal hypocalcaemia)
Strong propensity to suppress neonatal parathyroid function.
weak
hereditary haemochromatosis
Hypoparathyroidism is a late manifestation after extensive iron deposition in tissues has occurred (e.g., liver, heart, pituitary gland).
transfusional iron overload in thalassaemia
Seen after many years of transfusions without adequate chelation therapy.
Wilson's disease
Copper deposition is a rare cause of hypoparathyroidism.
metastatic cancer
Hypoparathyroidism due to tumour infiltration or radiotherapy is a very rare manifestation.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer