Investigations
1st investigations to order
brain CT
Test
Essential initial investigation to exclude intracerebral haemorrhage.
Low sensitivity for diagnosing arteriovenous malformation (AVMs). They may be suggested by calcification, hypointensity, and enhancement. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Left posterior frontal intracerebral haematoma secondary to ruptured arteriovenous malformation (axial unenhanced computed tomography scan)From the collection of Mr R. J. Edwards; used with permission [Citation ends].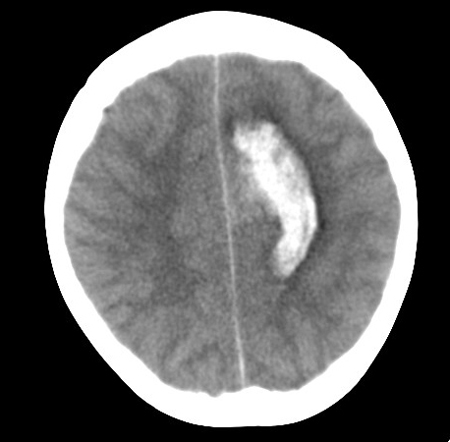
Result
reveals intracerebral haemorrhage; identifies AVM by calcification and isointense or slightly hyperintense vessels
brain MRI
Test
MRI has sensitivity of 89% for detecting cerebral AVMs and offers greater visualisation of surrounding structures than CT.[45][49] Using gadolinium enhancement and sequences to detect blood products increases sensitivity for small AVMs.
AVM vessels appear as flow voids, reflecting high-velocity blood. Areas of gliosis hyperintense on T2. Signal characteristics of any haemorrhage depend on its age.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Unruptured left parieto-occipital arteriovenous malformation (sagittal T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging scan)From the collection of Mr R. J. Edwards; used with permission [Citation ends].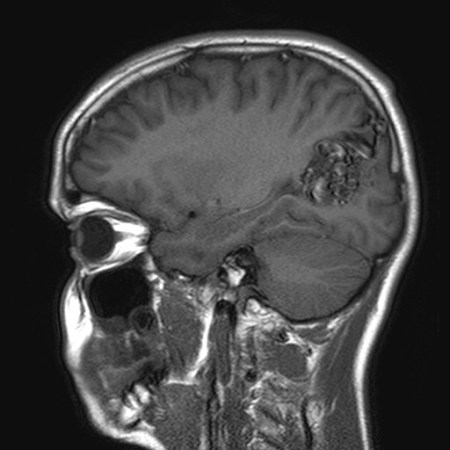 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Unruptured left parieto-occipital arteriovenous malformation (axial T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging scan)From the collection of Mr R. J. Edwards; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Unruptured left parieto-occipital arteriovenous malformation (axial T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging scan)From the collection of Mr R. J. Edwards; used with permission [Citation ends].
Result
detects AVMs ± haemorrhage, and thrombosed vessels
Investigations to consider
brain digital subtraction angiogram
Test
The standard investigation for determining AVM size, location, feeding arteries, associated aneurysms, and venous drainage. Characteristic diagnostic feature is early venous filling (indicating arteriovenous shunting) during arterial phase, but this may also be seen with vascular neoplastic lesions, contusions, and parenchymal infection, and following infarcts.[47] AVM appears as a tangle of tightly packed abnormal vessels with enlarged feeding arteries and dilated, tortuous draining veins. They are often wedge-shaped, pointing toward the ventricle.
Angiograms for AVMs pose a 0.5% risk of permanent stroke,[55] significantly lower than those for transient ischaemic attacks or stroke (3% to 3.7%).[56] Superselective microcatheter angiography can be used to identify micro-AVMs associated with intracerebral haemorrhage that are not detectable on conventional angiographic imaging.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Cerebral angiogram (left carotid artery injection, lateral view) showing posterior frontal arteriovenous malformation fed by pericallosal artery (thin arrow) with arterialised draining vein (thick arrow) draining to superior sagittal sinusFrom the collection of Mr R. J. Edwards; used with permission [Citation ends].
Result
early venous filling (indicating arteriovenous shunting) during arterial phase
brain CT angiogram
Test
High-definition angiographic images can be obtained from CT angiograms without the risks of formal angiography. These can be useful adjuncts to the investigation of a suspected AVM and may be used in follow-up after treatment.
Result
confirms presence of AVM
brain magnetic resonance angiogram
Test
High-definition angiographic images can be obtained by magnetic resonance angiograms without the risks of formal angiography. These can be useful adjuncts to the investigation of a suspected AVM and may be used in follow-up after treatment.
Result
confirms presence of AVM and associated aneurysms
FBC
Test
To rule out low platelet count that may increase bleeding risk, and to assess baseline haemoglobin level if surgery is planned.
Result
excludes coagulopathy
clotting screen and group
Test
Excluding coagulopathies and ensuring that blood can be readily cross-matched is important if the patient presents with haemorrhage, and before surgery.
Result
excludes coagulopathy
electrolyte panel
Test
Hyponatraemia due to syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) or cerebral salt wasting is common in patients with brain injury.
Result
may reveal hyponatraemia
drug toxicology screen
Test
In patients presenting with haemorrhage. Drug abuse is one of the most common causes of stroke in young adults.[38]
Result
may identify cocaine, amphetamine, or ecstasy abuse
functional imaging
Test
Standard imaging techniques (PET, functional MRI, magnetoencephalography) provide excellent anatomical localisation. Functional imaging identifies functionally important cortex that may not correspond with that which would be expected anatomically, as neuronal networks seem to adapt to the presence of AVMs.[52][53]
Result
locates sensori-motor, language, or visual cortex in relation to AVM
superselective Wada
Test
Such testing has revealed the redistribution of cognitive function in response to AVMs.[54] It is a means of assessing function of surrounding cortex before surgery, although functional MRI is more commonly used as it is non-invasive and has fewer complications and adverse effects.
Result
reveals the redistribution of cognitive function in response to AVMs
neuropsychology
Test
In the presence of AVMs, neurocognitive function may be in an unusual cerebral location, some distance from any effects of 'vascular steal'.[54] Eloquent cortical regions (areas of the brain that control speech, motor function, and senses) do not seem to occupy their normal anatomical location; therefore, establishing an individual cortical functional map using neuropsychology and functional imaging before surgery is useful.
Result
locates the site of neurocognitive function
perfusion studies
Test
Numerous imaging techniques (PET, single-photon emission CT, xenon-enhanced CT, perfusion CT, perfusion MRI) have been developed to assess brain haemodynamics. They vary in quantitative accuracy, brain coverage, spatial resolution, and technical requirements. PET is the most accurate method and can also be used to provide functional information.[52]
Result
identifies vascular reserve of local cortex
electroencephalogram
Test
Indicated in patients presenting with seizures.
If the location of the seizure focus is in doubt and surgical resection is being considered, more detailed neurophysiology such as video telemetry and more invasive (e.g., subdural grid) electrode monitoring can be used.
Result
may reveal epileptiform activity
visual fields
Test
If AVM or haemorrhage encroaches on visual pathways.
Result
may reveal visual field defect
Emerging tests
4D CT angiography (CTA)/magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
Test
Adds temporal information to traditional CTA/MRA, so offering some appreciation of AVM flow dynamics. These scans are still in their infancy and are not yet widely available.[57]
Result
confirms presence of AVM
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer