Complications
Diabetes is common in Turner syndrome, and thus baseline screening of fasting glucose is advised. Diabetes is typically mild and may be controlled by diet alone or with metformin. Patients are generally sensitive to insulin treatment despite obesity.
Metabolic abnormalities and hypertension should be managed aggressively, because these women are at an increased risk of premature ischaemic heart disease.[53]
Dyslipidaemia is common in Turner syndrome, and thus baseline screening of fasting lipids is advised.
Elevations in lipids are responsive to statin treatment.
Metabolic abnormalities and HTN should be managed aggressively, because these women are at an increased risk of premature ischaemic heart disease.[53]
Most girls and women with Turner syndrome are infertile due to premature ovarian insufficiency. Spontaneous menses and pregnancy may occur in 2% to 3%. Assisted reproduction may be possible for some women with Turner syndrome, but pregnancy exacerbates underlying metabolic, hypertensive, and cardiovascular problems and may be catastrophic. Very stringent pre-pregnancy screening and patient education as to risks are imperative prior to attempting assisted reproduction.[44]
A hearing screen should be performed in all patients with Turner syndrome. Otitis media is common in girls, owing to short and badly angled eustachian tubes. This is often associated with significant conductive hearing loss and formation of cholesteatoma, and should thus be treated aggressively. Initial evaluation by an otolaryngologist with audiometry will determine the frequency of follow-up. Adults suffer early onset of sensorineural hearing loss and need regular audiometry.[55]
Osteoporosis is more likely in patients with a late diagnosis or if oestrogen treatment was not started until adult years. Bone density evaluation with DXA is recommended in these patients. If the patient is very small, densitometry with DXA will give artificially low scores that need to be corrected for small bone size.[56]
Women who have been treated with adequate oestrogen since at least the age of 16 years have near-normal trabecular bone density.[57][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Importance of oestrogen therapy in young adults with Turner syndrome (TS): X-ray figure A shows near collapse of T11, diffuse osteoporosis, and dorsal kyphosis in a woman with TS who discontinued HRT at age 18 years. Figure B shows normal spinal architecture and bone health in another woman with TS, age 30 years, who has taken HRT consistently since age 12.8 yearsFrom the personal collection of Carolyn Bondy, MS, MD (NIH study) [Citation ends].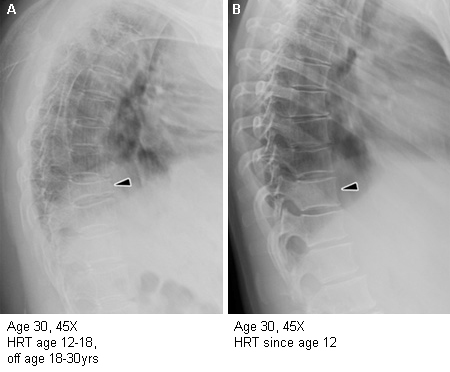
Cortical bone is thin in many girls and women with Turner syndrome, and this is intrinsic to the genetic defect.[58][59] It responds poorly to bisphosphonate or oestrogen treatment.[59]
Aortic dimensions should be measured at the sinuses of Valsalva, at the ascending aorta at the level of the right pulmonary artery and at the descending aorta diameter at the same level. These dimensions must be assessed relative to body surface area to determine dilation and risk of dissection.[60][61] This cardiovascular screening is given highest priority, because complications of congenital heart disease and coronary disease are leading causes of premature morbidity and mortality in women with Turner syndrome.[53][62]
Essential hypertension (HTN) is common in girls and women with Turner syndrome, affecting 30% to 40%.[52] At diagnosis, BP needs to be checked in all 4 extremities to assess possible aortic coarctation as a cause of HTN. BP needs to be evaluated with respect to height, because girls with Turner syndrome are small for age.
The International Turner Syndrome Consensus Group and American Heart Association recommend treatment with angiotensin receptor blockers, beta-blockers, or both because of their potential salutary effects on aortic wall stress.[5][27]
Metabolic abnormalities and HTN should be managed aggressively because of the increased risk of premature ischaemic heart disease.[53]
Haplo-insufficiency for genes located on Xp results in distinctive neurocognitive traits, such as variably poor social skills, higher verbal versus visual-spatial performance scores, and difficulties in recognition of facial expressions.[22] Full scale IQ is usually normal.
Autoimmune thyroid disease, consisting primarily of Hashimoto's thyroiditis but also less commonly Graves' disease, is found in 30% to 50% of girls and women with Turner syndrome. Therefore, thyroid function tests should be measured at the time of diagnosis and annually thereafter.
Autoimmune thyroid disease, consisting primarily of Hashimoto's thyroiditis but also less commonly Graves' disease, is found in 30% to 50% of girls and women with Turner syndrome. Therefore, thyroid function tests should be measured at the time of diagnosis and annually thereafter.
Between 30% and 40% of patients have 'Turner hepatitis', with elevated ALT, AST, and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GT). Some of the enzymes may be elevated 2- to 10-fold. There is no specific treatment other than avoidance of hepatotoxic agents and surveillance. Adequate oestrogen replacement and healthy lifestyle with weight loss may decrease liver enzymes. A liver ultrasound is done if fatty liver is suspected. If liver enzymes remain significantly elevated over several measurements, for 1 year or more, a liver biopsy may be considered.[54]
Women with a clear Y chromosome have an increased risk of gonadoblastoma, a benign tumour. There is no reliable way of monitoring disease progression, so patients with a Y chromosome need bilateral gonadectomy. However, this is extremely stressful to the patient and her family and should be undertaken in a sensitive manner in a specialised unit with multi-disciplinary support.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer