Last reviewed: 24 Mar 2025
Last updated: 04 Feb 2022
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Other diagnostic factors
- headache
- transient visual obscurations
- pulse-synchronous tinnitus
- photophobia
- retrobulbar pain
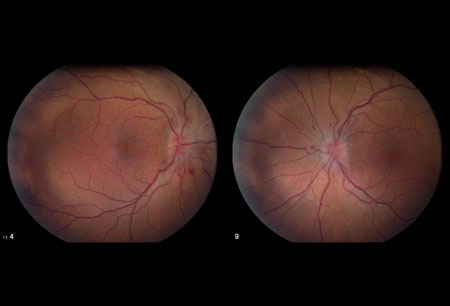
- optical disc swelling
- decreased visual acuity
- ocular motility disturbances
- relative afferent pupillary defect
Risk factors
- female sex
- obesity and weight gain
- certain medication use
- associated causal diseases
- sleep apnoea
- family history
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- visual field testing (perimetry)
- dilated fundoscopy
- visual acuity
- MRI of brain with or without contrast
- lumbar puncture at spinal L3/L4
Investigations to consider
- magnetic resonance venogram of head
- optical coherence tomography
Treatment algorithm
ACUTE
Contributors
Authors
Michael Wall, MD
Professor
Department of Neurology and Department of Ophthalmology & Visual Sciences
University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics and Iowa City VA Health Care System
Iowa City
IA
Disclosures
MW is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Mansoor Mughal, MD
Retina Fellow
Rutgers University
Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital
New Brunswick
NJ
Disclosures
MM declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Paul W. Brazis, MD
Consultant in Neurology and Neuro-Ophthalmology
Mayo Clinic Florida
Jacksonville
FL
Disclosures
PWB declares that he has no competing interests.
Tim D. Matthews, MBBS
Consultant Neuro-ophthalmologist
Birmingham Neuro-ophthalmology Unit
University Hospital Birmingham
Birmingham
UK
Disclosures
TDM declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer