Last reviewed: 16 Mar 2025
Last updated: 10 Apr 2024
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- hearing loss
- ear discharge resistant to antibiotic therapy
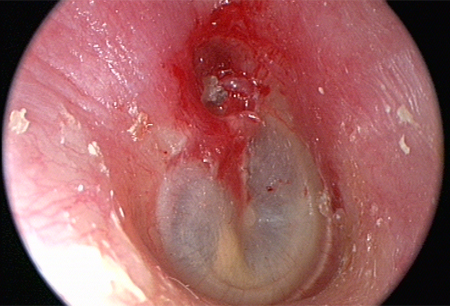
- attic crust in retraction pocket
- white mass behind intact tympanic membrane
Risk factors
- middle ear disease
- eustachian tube dysfunction
- otological surgery
- traumatic blast injury to ear
- congenital anomalies
- family history
Diagnostic investigations
Investigations to consider
- fistula test
- MRI scan of the head and petrous temporal bones
- bacterial culture
Treatment algorithm
ACUTE
Contributors
Authors
Susan A. Douglas, MBBS (Hons) UWI, FRCSEd, FRCS (ORL-HNS)
Consultant Otolaryngologist and Otologist
Rotherham NHS Foundation Trust
Rotherham
UK
Disclosures
SAD declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Cliff Megerian, MD
Professor and Vice Chairman of Otolaryngology
Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine
Cleveland
OH
Disclosures
CM is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Iain Swan, MD, FRCS
Senior Lecturer in Otolaryngology
Honorary Consultant Otolaryngologist
Glasgow Royal Infirmary
Glasgow
UK
Disclosures
IS declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer