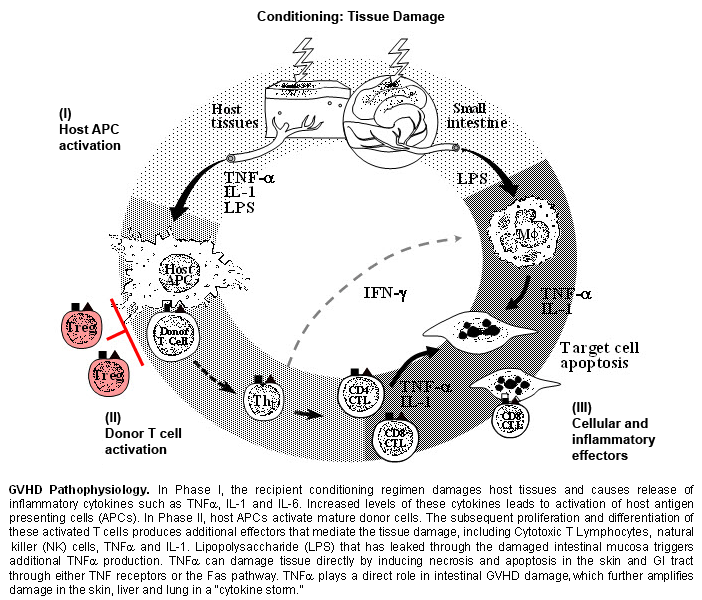
Graft versus host disease (GHVD) is a serious and potentially life-threatening complication following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). GVHD occurs when donor T cells respond to histoincompatible antigens on the host tissues.
Several risk factors determine the development of GVHD, which may be acute or chronic.
Risk factors for the development of acute GVHD include:[18]Wojnar J, Giebel S, Krawczyk-Kulis M, et al. Acute graft-versus-host disease. The incidence and risk factors. Ann Transplant. 2006;11(1):16-23.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17025025?tool=bestpractice.com
[23]Nash RA, Pepe MS, Storb R, et al. Acute graft-versus-host disease: analysis of risk factors after allogeneic marrow transplantation and prophylaxis with cyclosporine and methotrexate. Blood. 1992 Oct 1;80(7):1838-45.
http://bloodjournal.hematologylibrary.org/cgi/reprint/80/7/1838
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1391947?tool=bestpractice.com
[24]Hahn T, McCarthy PL Jr, Zhang MJ, et al. Risk factors for acute graft-versus-host disease after human leukocyte antigen-identical sibling transplants for adults with leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2008 Dec 10;26(35):5728-34.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18981462?tool=bestpractice.com
[25]Storb R, Prentice RL, Buckner CD, et al. Graft-versus-host disease and survival in patients with aplastic anemia treated by marrow grafts from HLA-identical siblings. Beneficial effect of a protective environment. N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 10;308(6):302-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6337323?tool=bestpractice.com
[26]Anasetti C, Beatty PG, Storb R, et al. Effect of HLA incompatibility on graft-versus-host disease, relapse, and survival after marrow transplantation for patients with leukemia or lymphoma. Hum Immunol. 1990 Oct;29(2):79-91.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2249952?tool=bestpractice.com
[27]Weisdorf D, Hakke R, Blazar B, et al. Risk factors for acute graft-versus-host disease in histocompatible donor bone marrow transplantation. Transplant. 1991 Jun;51(6):1197-203.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2048196?tool=bestpractice.com
[28]Hagglund H, Bostrom L, Remberger M, et al. Risk factors for acute graft-versus-host disease in 291 consecutive HLA-identical bone marrow transplant recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995 Dec;16(6):747-53.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8750264?tool=bestpractice.com
[29]Eisner MD, August CS. Impact of donor and recipient characteristics on the development of acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease following pediatric bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995 May;15(5):663-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7670393?tool=bestpractice.com
[30]Young NS, Calado RT, Scheinberg P. Current concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of aplastic anemia. Blood. 2006 Oct 15;108(8):2509-19.
http://bloodjournal.org/content/108/8/2509.full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16778145?tool=bestpractice.com
[31]Martin P, Bleyzac N, Souillet G, et al. Clinical and pharmacological risk factors for acute graft-versus-host disease after paediatric bone marrow transplantation from matched-sibling or unrelated donors. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2003 Nov;32(9):881-7.
https://www.nature.com/articles/1704239
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14561988?tool=bestpractice.com
[32]Gale RP, Bortin MM, van Bekkum DW, et al. Risk factors for acute graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol. 1987 Dec;67(4):397-406.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3322360?tool=bestpractice.com
[33]Atkinson K, Farrell C, Chapman G, et al. Female marrow donors increase the risk of acute graft-versus-host disease: effect of donor age and parity and analysis of cell subpopulations in the donor marrow inoculum. Br J Haematol. 1986 Jun;63(2):231-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3521713?tool=bestpractice.com
[34]Bross DS, Tutschka PJ, Farmer ER, et al. Predictive factors for acute graft-versus-host disease in patients transplanted with HLA-identical bone marrow. Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1265-70.
http://bloodjournal.hematologylibrary.org/cgi/reprint/63/6/1265
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6372895?tool=bestpractice.com
[35]Clift RA, Buckner CD, Appelbaum FR, et al. Allogeneic marrow transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first remission: a randomized trial of 2 irradiation regimens. Blood. 1990 Nov 1;76(9):1867-71.
http://bloodjournal.hematologylibrary.org/cgi/reprint/76/9/1867
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2224134?tool=bestpractice.com
[36]Finke J, Schmoor C, Bethge WA, et al; ATG-Fresenius Trial Group. Prognostic factors affecting outcome after allogeneic transplantation for hematological malignancies from unrelated donors: results from a randomized trial. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012 Nov;18(11):1716-26.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22713691?tool=bestpractice.com
[37]Oh H, Loberiza FR, Zhang MJ, et al. Comparison of graft-versus-host-disease and survival after HLA-identical sibling bone marrow transplantation in ethnic populations. Blood. 2005 Feb 15;105(4):1408-16.
http://bloodjournal.hematologylibrary.org/cgi/content/full/105/4/1408
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15486071?tool=bestpractice.com
[38]Silla L, Fischer GB, Paz A, et al. Patient's socioeconomic status as a prognostic factor for allo-SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009 Apr;43(7):571-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18978820?tool=bestpractice.com
[39]Flowers ME, Inamoto Y, Carpenter PA, et al. Comparative analysis of risk factors for acute graft-versus-host disease and for chronic graft-versus-host disease according to National Institutes of Health consensus criteria. Blood. 2011 Mar 17;117(11):3214-9.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3062319
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21263156?tool=bestpractice.com
[40]Azari M, Barkhordar M, Bahri T, et al. Determining the predictive impact of donor parity on the outcomes of human leukocyte antigen matched hematopoietic stem cell transplants: a retrospective, single-center study. Front Oncol. 2024;14:1339605.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10918844
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38454927?tool=bestpractice.com
[41]Kalhs P, Schwarzinger I, Anderson G, et al. A retrospective analysis of the long-term effect of splenectomy on late infections, graft-versus-host disease, relapse, and survival after allogeneic marrow transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 1995 Sep 1;86(5):2028-32.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7655031?tool=bestpractice.com
Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) mismatch
Oder recipient or donor age
Donor and recipient gender disparity (particularly a female donor with a male recipient)
Parous female donor
Type and stage of the underlying malignant condition
Transplant conditioning regimen intensity
ABO compatibility
Performance score
White/black race
Cytomegalovirus serostatus
Absent or suboptimal GVHD prophylaxis
Splenectomy
Low socioeconomic status
Risk factors for the development of chronic GVHD include:[7]Frey NV, Porter DL. Graft-versus-host disease after donor leukocyte infusions: presentation and management. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2008 Jun;21(2):205-22.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18503987?tool=bestpractice.com
[8]Lee SJ, Vogelsang G, Flowers MED. Chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2003 Apr;9(4):215-33.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12720215?tool=bestpractice.com
[21]Antin JH. Clinical practice. Long-term care after hematopoietic-cell transplantation in adults. N Engl J Med. 2002 Jul 4;347(1):36-42.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12097539?tool=bestpractice.com
[39]Flowers ME, Inamoto Y, Carpenter PA, et al. Comparative analysis of risk factors for acute graft-versus-host disease and for chronic graft-versus-host disease according to National Institutes of Health consensus criteria. Blood. 2011 Mar 17;117(11):3214-9.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3062319
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21263156?tool=bestpractice.com
[42]Anasetti C, Logan BR, Lee SJ, et al; Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network. Peripheral-blood stem cells versus bone marrow from unrelated donors. N Engl J Med. 2012 Oct 18;367(16):1487-96.
http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1203517#t=article
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23075175?tool=bestpractice.com
[43]Cutler C, Giri S, Jeyapalan S, et al. Acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic peripheral-blood stem-cell and bone marrow transplantation: a meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2001 Aug 15;19(16):3685-91.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11504750?tool=bestpractice.com
[44]Loren AW, Bunin GR, Boudreau C, et al. Impact of donor and recipient sex and parity on outcomes of HLA-identical sibling allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006 Jul;12(7):758-69.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16785065?tool=bestpractice.com
[45]Koster EAS, von dem Borne PA, van Balen P, et al. Risk factors for graft-versus-host-disease after donor lymphocyte infusion following T-cell depleted allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1335341.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10966113
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38545096?tool=bestpractice.com
[38]Silla L, Fischer GB, Paz A, et al. Patient's socioeconomic status as a prognostic factor for allo-SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009 Apr;43(7):571-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18978820?tool=bestpractice.com
[46]Lazaryan A, Weisdorf DJ, DeFor T, et al. Risk factors for acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with umbilical cord blood and matched sibling donors. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016 Jan;22(1):134-40.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4787268
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26365153?tool=bestpractice.com
Prior acute GVHD
Older recipient age
Female donor with male recipient
Parous female donor
Mismatched or unrelated donors
Donor lymphocyte infusion (post-HCT)
Use of peripheral blood stem cells
Low socioeconomic status