Tests
1st tests to order
CBC
Test
Pronounced leukocytosis (usually >15,000 WBC/microliter) is often present. Anemia of chronic disease is found with chronic abscesses.
Result
leukocytosis, anemia
chest x-ray
Test
Usually reveals classical segmental or lobar consolidation with central cavitation, an air-fluid level, and thick and irregular cavity wall.
Aspiration-related lung abscesses are usually found in the right lung and dependent lung areas (i.e., posterior segment of the right upper lobe and superior segments of both lower lobes).
Multilobar involvement with multiple peripheral abscesses suggests hematogenous dissemination from extrapulmonary sepsis (e.g., septic embolism). Chest x-ray in the supine or semi-recumbent position (e.g., in ICU or emergency departments) is often insensitive for diagnosing lung abscess.[9][27][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray showing a left upper lobe lung abscessFrom the collection of Dr Ioannis P. Kioumis [Citation ends].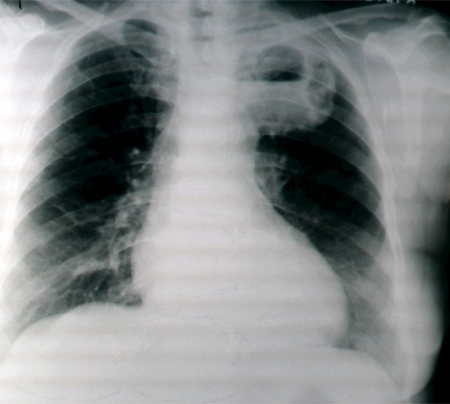 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray showing a left-sided lung abscess with surrounding infiltrationFrom the collection of Dr Ioannis P. Kioumis [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray showing a left-sided lung abscess with surrounding infiltrationFrom the collection of Dr Ioannis P. Kioumis [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray showing a left-sided cavitating lesion with an air-fluid levelFrom the collection of Dr Ioannis P. Kioumis [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray showing a left-sided cavitating lesion with an air-fluid levelFrom the collection of Dr Ioannis P. Kioumis [Citation ends].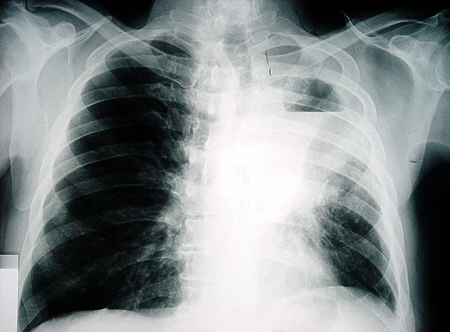 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray showing a right-sided lung abscess with surrounding infiltrationFrom the collection of Dr Ioannis P. Kioumis [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray showing a right-sided lung abscess with surrounding infiltrationFrom the collection of Dr Ioannis P. Kioumis [Citation ends].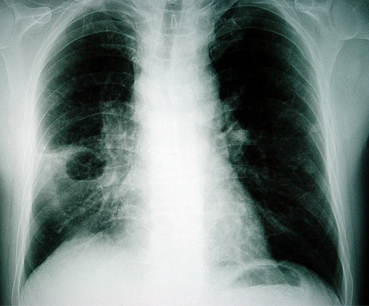
Result
consolidation with central cavitation and air-fluid level, cavity wall thick and irregular
sputum Gram stain
Test
Gram staining is a simple and useful tool for establishing a quick diagnosis. Specimens are usually contaminated by the normal anaerobic flora of the mouth.
Result
One predominant gram-positive or -negative organism and neutrophils in aerobic infections, mixed flora with many neutrophils in anaerobic infections
sputum culture
Test
Expectorated sputum cultures are of limited value because they are usually contaminated by the normal flora of the mouth and respiratory tract. However, despite the low diagnostic yield in lung abscess, sputum should be cultured in all patients.
Result
growth of normal respiratory flora in polymicrobial anaerobic infections, growth of infecting organism in aerobic infections
blood culture
Test
All patients should undergo routine blood cultures.
Result
positive for infecting organism in aerobic infections, bacteremia, and septic embolism; seldom positive in anaerobic infections
empyema fluid culture
Test
Thoracocentesis with culture of the empyema fluid.
Result
cultures may be negative in polymicrobial anaerobic infections; growth of infecting organism in aerobic infections
Tests to consider
CT chest
Test
Contrast-enhanced CT can identify proximal endobronchial obstruction and distinguish between lung abscess and empyema that may be missed by chest x-ray.[9][31][32]
Empyema appears lenticular in shape, has a thin wall with smooth luminal margins, has a smooth exterior wall, forms obtuse angles with the chest wall, and may compress the uninvolved lung; it may also show separate pleural layers (the split pleura’ sign).[9][31]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT of thorax showing a lung abscessFrom the collection of Dr Ioannis P. Kioumis [Citation ends].
Result
thick-walled, usually round cavity with irregular margins forming an acute angle with chest wall, no signs of compression of surrounding lung
bronchoscopy
Test
Indicated when an underlying carcinoma or foreign body obstruction is suspected, treatment response is poor, or sputum analysis is inconclusive. Underlying malignancy is clinically suspected in cases with a low-grade fever, leukocyte count <11,000/microliter, minimal systemic complaints, no factors predisposing to aspiration, nonresponse to antibiotics by day 10, and a deteriorating course.[26] Can be used to collect specimens from protected specimen brushing or bronchoalveolar lavage.[33][34]
Result
proximal airway obstruction by a tumor or foreign body
quantitative cultures of protected specimen brushings
Test
Samples obtained bronchoscopically. Although useful in selected patients, they are seldom required in routine clinical practice.
Result
>1000 colony-forming units/mL of fluid
quantitative cultures of protected bronchoalveolar lavage samples
Test
Samples obtained bronchoscopically. Although useful in selected patients, they are seldom required in routine clinical practice.
Result
>10,000 or 100,000 colony-forming units/mL of fluid
percutaneous needle aspiration and culture
Test
Ultrasound- or CT-guided percutaneous needle aspiration has a significantly higher yield than sputum, blood, or bronchoalveolar lavage and can establish a bacteriologic diagnosis when cultures from these other sources are inconclusive.[29][30] The complications and limitations of the method mean that a careful risk-benefit analysis is always required.
Result
growth of infecting organism
sputum cytology
Test
Indicated in patients who do not respond to antibiotics or who present with hemoptysis to rule out an underlying malignancy.
Result
malignant cells in underlying malignancy
lung ultrasound
Test
Used as an imaging technique to guide percutaneous needle aspiration or as a useful tool for bedside diagnosis in critically ill patients.[29]
Result
hypoechoic lesion with irregular outer wall and cavity appearing as a hyperechoic ring
echocardiogram
Test
Performed for patients with lung abscess suspected to be secondary to septic embolism from right-sided (e.g., tricuspid valve) bacterial endocarditis.
Result
vegetations on affected valve in bacterial endocarditis
rapid enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for D-dimer
Test
Performed for patients with lung abscess suspected to be secondary to infection of pulmonary embolism.
Care should be taken when interpreting the result, as several conditions, including acute infection, may raise the D-dimer.
Result
elevated in pulmonary embolism
multidetector CT thorax
Test
Undertaken in patients with lung abscess suspected to be secondary to infection of infarct related to a pulmonary embolism. Contrast is required.
Result
intraluminal filling defects in pulmonary embolism
ventilation-perfusion scan
Test
Undertaken in patients with lung abscess suspected to be secondary to infection of infarct related to a pulmonary embolism.
Result
perfusion defects in areas with normal ventilation in pulmonary embolism
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer