Images and videos
Images
Vitamin B12 deficiency
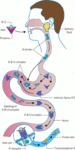
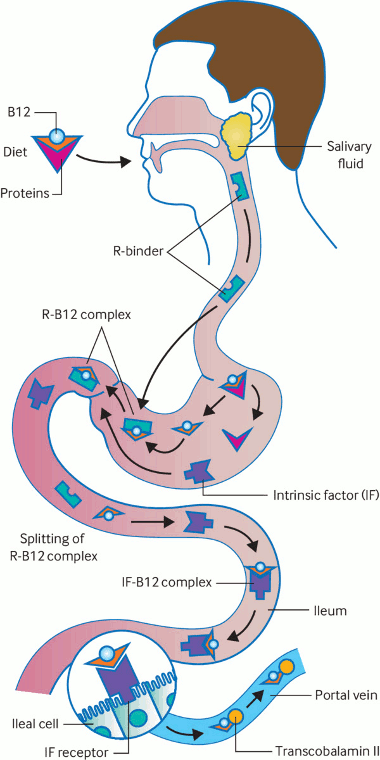
Absorption of vitamin B12. Dietary B12 is released from food in the stomach and binds to R-protein (haptocorrin, this complex is stable in the gastric acidic environment). The R-B12 complex then travels to the duodenum, where B12 binds to intrinsic factor (IF, secreted by gastric parietal cells and therefore lost in pernicious anemia). This B12-IF complex is carried down the small intestine until the terminal ileum, where it attaches to IF receptors and is absorbed into the bloodstream bound to transcobalamin. Over 95% of dietary B12 is absorbed through the IF pathway
Sukumar N et al. Investigating vitamin B12 deficiency. BMJ. 2019 May 10;365:l1865; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Videos
 Venepuncture and phlebotomy: animated demonstration
Venepuncture and phlebotomy: animated demonstrationHow to take a venous blood sample from the antecubital fossa using a vacuum needle.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer