Differentials
Graves disease
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
More common than toxic multinodular goiter (MNG) and occurs in generally younger age group.
Autoimmune features, such as exophthalmos or pretibial myxedema, may be present.
Goiter is diffuse rather than nodular. However, longstanding Graves disease may mimic toxic MNG.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism are generally more marked than for toxic MNG.
INVESTIGATIONS
Thyroid scan shows diffuse rather than variegated appearance. Uptake is high.
Free thyroid hormone levels are usually higher than for toxic MNG.
Often there is evidence of thyroid autoimmunity (i.e., positive thyroid peroxidase antibodies), although this is not diagnostic.
A positive thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor antibody test is diagnostic for Graves disease.
Toxic adenoma
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Patients tend to be younger (<40 to 50 years).
Single, generally large palpable nodule.
INVESTIGATIONS
I-123 or Tc-99 scan shows a single hot area with suppression of extranodular tissue.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Hyperfunctioning thyroid nodule suppressing contralateral gland on thyroid scan (SSN = suprasternal notch)Arem R. Recurrent transient thyrotoxicosis in multinodular goitre. Postgrad Med J. 1990;66:54-56 [Citation ends].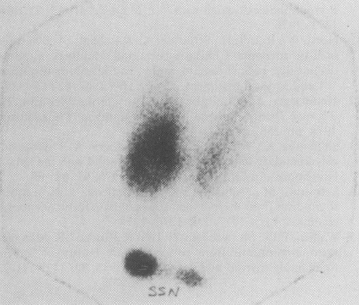
Thyrotoxic phase of painless/lymphocytic thyroiditis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Most often occurs postpartum.
INVESTIGATIONS
Absent or low uptake on I-123 scan, in contrast to generally normal uptake in toxic multinodular goiter.
Often there is evidence of thyroid autoimmunity (i.e., positive thyroid peroxidase antibodies), although this is not diagnostic.
Thyrotoxic phase of subacute thyroiditis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Associated with anterior neck pain and tenderness.
INVESTIGATIONS
Absent or low uptake on I-123 scan, in contrast to generally normal uptake in toxic multinodular goiter. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate is elevated.
Iodine-induced hyperthyroidism
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
History of an iodine load (from iodinated radiographic contrast, amiodarone, or a change in diet) in the setting of autonomous nodular thyroid disease (the Jod-Basedow phenomenon).[13]
INVESTIGATIONS
Low uptake on I-123 scan, in contrast to generally normal uptake in toxic multinodular goiter.
24-hour or spot urine iodine may be high.
Thyroid blood flow on Doppler ultrasound may be increased.[22]
Functional thyroid cancer
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Hyperthyroidism is only very rarely caused by bulky metastatic follicular thyroid cancer.
Thyroid cancer may cause hoarseness, and cervical lymph nodes may be palpable.
INVESTIGATIONS
Total body scan shows radioactive iodine uptake over metastases.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer