Differentials
Common
Benign positional paroxysmal vertigo (BPPV)
History
vertigo on rolling over in bed or looking up, which lasts for seconds
Exam
Dix-Hallpike test: diagnostic of BPPV, typically demonstrating nystagmus and symptoms that are delayed by about 15 seconds, peak in 20-30 seconds, and then decay with complete resolution of the episode of vertigo; supine lateral head turns: similar to the Dix-Hallpike maneuver, a positive test is noted when the patient experiences vertigo with nystagmus.
1st investigation
- none:
diagnosis usually made clinically with Dix-Hallpike test and supine lateral head turns
Other investigations
- pure-tone audiogram:
normal pattern
- brain MRI:
normal
More
Meniere disease
History
spontaneous vertigo attacks (each lasting 20 minutes to 12 hours) with documented low- to mid-frequency sensorineural hearing loss in the affected ear before, during, or after one of the episodes of vertigo, with fluctuating aural symptoms (hearing loss, tinnitus, or ear fullness) in the affected ear
Exam
usually normal, Romberg’s test may be positive, may have horizontal and/or rotatory nystagmus which is suppressed by fixation
1st investigation
- pure-tone audiogram:
sensorineural hearing-loss pattern usually at low frequencies
Vestibular neuritis
History
acute onset of vertigo with nausea and vomiting, lasting days but without hearing loss; single episodes frequently recur; symptoms exacerbated by changes in head position
Exam
acute episode: may be nystagmus to the affected side, head impulse test will be abnormal (due to loss of the vestibulo-ocular reflex); loss of balance; between episodes of vertigo exam may be normal
1st investigation
- pure-tone audiogram:
normal pattern
More
Other investigations
- MRI brain:
normal
More
Labyrinthitis
History
acute onset of vertigo with nausea and vomiting lasting days; associated hearing loss with or without tinnitus; may be a preceding history of acute otitis media
Exam
nystagmus is usually horizontal, and severity improves as the illness resolves; patients may have difficulty walking; unilateral sensorineural hearing loss demonstrated with Rinne and Weber tuning fork tests; ear exam may demonstrate evidence of acute otitis media (bulging, erythematous, or opaque tympanic membrane); postaural redness or swelling may occur if mastoiditis complicates the infection
1st investigation
- pure-tone audiogram:
unilateral sensorineural hearing-loss pattern; a conductive loss pattern may occur if acute otitis media is present
Vestibular migraine
History
personal history or family history of migraine; vertigo with or without headaches; symptoms variable including true episodic vertigo, movement-provoked disequilibrium, lightheadedness, symptoms similar to benign positional paroxysmal vertigo, photophobia, phonophobia, or other auras, or symptoms similar to Meniere disease; associated symptoms of nausea and fatigue; symptoms might last minutes to days
Exam
usually normal, may have positional nystagmus and positive Romberg test in acute attack[118]
1st investigation
- pure-tone audiogram:
normal pattern
Other investigations
- MRI brain:
normal
More
Presyncope
History
variable depending on specific cause but may include generalized weakness, giddiness, headache, blurred vision, and diaphoresis; may be paresthesia, nausea, and vomiting; patients have a sensation of an impending loss of consciousness
Exam
vasovagal attack: hypotension and bradycardia during attack; cardiopulmonary disease: altered cardiac rhythm, murmurs, evidence of cardiac failure
1st investigation
- ECG:
may demonstrate arrhythmia, ischemic changes or signs of structural heart disease
Other investigations
- echocardiogram:
may be evidence of structural heart disease
- cardiac or event monitoring:
arrhythmia may be detected associated with symptomatic episodes
- tilt-table testing:
may demonstrate evidence of autonomic neuropathy if symptoms are provoked
Orthostatic hypotension
History
dizziness on standing from a lying or sitting position, episodes are usually transient, may be a history of hypotension, antihypertensive medication use, dehydration, autonomic dysfunction (e.g., with Parkinson disease, multiple system atrophy, diabetic autonomic neuropathy); if associated with autonomic dysfunction may also have dizziness when standing upright for prolonged periods, swimming, or running and may complain of feeling "spacey" or "foggy" without vertigo during exertion; may be a history of bariatric surgery
Exam
drop in systolic BP by 20 mmHg or diastolic BP by 10 mmHg within three minutes of standing from a lying position
1st investigation
- none:
diagnosis usually made clinically without further investigations
More
Other investigations
- tilt-table testing:
demonstrates orthostatic fall in BP
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome
History
dizziness and palpitations on standing from a lying or sitting position, episodes are usually transient; may be fatigue, nausea, presyncope or syncope, more common in women and girls between 12-50 years of age
Exam
increase in heart rate on standing (and with tilt table study) by 30 bpm or >120 bpm and associated postural symptoms; lack of orthostatic hypotension; absence of other conditions that may cause orthostatic hypotension, such as dehydration, a primary cardiac cause, an endocrine disorder, or a nervous system disorder[60]
1st investigation
- tilt table study:
confirms excessive postural tachycardia, excludes orthostatic hypotension
Other investigations
Diabetes mellitus
History
most commonly occurs in people with a known history of diabetes mellitus; often dizziness may coincide with episodes of hypoglycemia where patient feels ill, clammy, generally weak; may be a preceding peripheral vestibular disorder and prolonged symptoms, particularly with associated peripheral neuropathy (associated numbness in feet and legs and history of painless injuries)
Exam
may be signs of peripheral neuropathy including numbness and presence of painless injuries
1st investigation
- blood glucose:
low during attacks
More
Other investigations
- serum HbA1c:
elevated compared with nondiabetic levels, but result may be lower than expected
More
Alcohol
History
acute intoxication: patients report feeling "high," dizzy, and intoxicated
Exam
smell of alcohol on the breath, disorientation, abnormal gait
1st investigation
- blood alcohol level:
may be elevated
Other investigations
- serum LFTs:
gamma glutamyl transpeptidase, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase may be deranged
Drugs
History
history of aminoglycoside antibiotics, cisplatin, or other drugs that may cause dizziness (e.g., antihypertensive or antiarrhythmic medication, diuretics, antipsychotic or antiparkinsonian medication, opioids, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, or anesthetic medication); may be hearing loss and tinnitus with aminoglycosides and cisplatin
Exam
may be orthostatic hypotension on exam if taking antihypertensive, antipsychotic or antiparkinsonian medication, opioids, or phosphodiesterase inhibitors
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
the diagnosis is often made clinically from the history and physical findings
Other investigations
- serum drug levels of aminoglycoside:
may be elevated
More - urine drug-toxicity screen:
elevated levels of drugs or their metabolites
- blood drug-toxicity screen:
elevated levels of drugs or their metabolites
- pure-tone audiogram:
may be a sensorineural hearing-loss pattern or normal
More - m.1555A>G mutation screening:
may be present
More
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
History
dizziness associated with a current or previous COVID-19 infection, typical symptoms are dry cough, fever, and dyspnea; other common symptoms include anorexia, myalgia, and sore throat; may be travel history to an affected area or close contact with a suspected or confirmed case in the 14 days prior to symptom onset
Exam
may have fever and/or dyspnea; patients with pneumonia or respiratory distress syndrome may have inspiratory crackles, rales, and/or bronchial breathing; patients with respiratory distress syndrome may have tachycardia, tachypnea, or cyanosis accompanying hypoxia
1st investigation
- real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR):
positive for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RNA
More
Other investigations
Uncommon
Cholesteatoma
History
malodorous ear discharge and hearing loss, with or without tinnitus; less commonly vertigo, otalgia, altered taste, or facial weakness
Exam
otoscopy reveals crust or keratin in the attic (upper part of the middle ear), the pars flaccida, or the pars tensa (usually posterior superior aspect), with or without perforation of the tympanic membrane; fistula test may be positive
1st investigation
- pure-tone audiogram:
normal, conductive, or mixed conductive/sensorineural hearing-loss pattern
Other investigations
- CT scan of the petrous temporal bones:
opacification of the middle ear, ossicular erosion, and erosion of the scutum; may demonstrate mastoid, cochlear, semicircular canal, or intracranial involvement
More
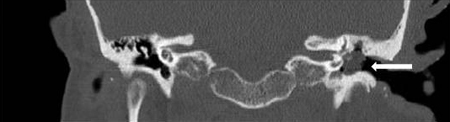
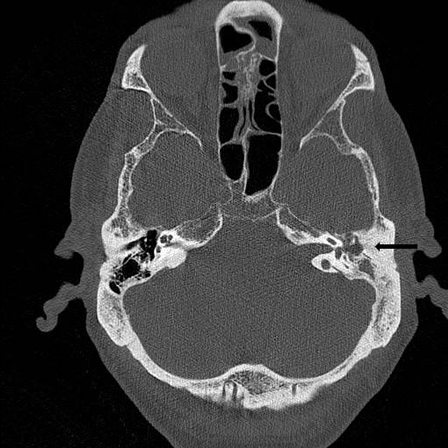
Superior semicircular canal dehiscence
History
history of episodes of vertigo associated with sound or pressure such as coughing, sneezing, straining, or sudden loud noise and hyperacusis; a feeling of the affected ear being blocked; autophony; may be preceding history of trauma
Exam
upward and torsional nystagmus evoked by Tullio (loud noise) and Hennebert (altered middle-ear pressure) tests
1st investigation
- pure-tone audiogram:
conductive hearing-loss pattern
- CT scan petrous temporal bones:
bony dehiscence of the superior semicircular canal on the affected side
More - vestibular evoked myogenic potential:
increased amplitude may be demonstrated
Other investigations
- acoustic reflexes:
normal
More
Perilymphatic fistula
History
may have a history of surgery such as stapes surgery, head trauma or barotrauma; paroxysmal vertigo, imbalance, and hearing loss with or without tinnitus
Exam
may have a positive fistula test
1st investigation
- pure-tone audiogram:
sensorineural hearing-loss pattern
Other investigations
- exploratory tympanotomy:
fistula noted at the round or oval window
Persistent postural-perceptual dizziness (PPPD)
History
Five diagnostic criteria must be satisfied to make the diagnosis: 1) History of dizziness, unsteadiness, or nonspinning vertigo on most days for ≥3 months. 2) Symptoms occurring without provocation but worse with upright posture, active or passive motion, or exposure to moving stimuli. 3) Precipitated by conditions that cause vertigo, neurologic or medical illness, or psychological distress. 4) Symptoms cause significant distress or functional impairment. 5) Symptoms not better explained by another disorder.
Exam
physical exam normal
1st investigation
- none:
diagnosis made based on clinical criteria
More
Other investigations
Posterior fossa tumor
History
typically unilateral hearing loss, dizziness, or vertigo and tinnitus
Exam
spontaneous nystagmus may be present
1st investigation
- pure-tone audiogram:
unilateral sensorineural hearing-loss pattern
- contrast-enhanced structural MRI internal auditory meatus and brain:
space-occupying lesion in cerebellopontine angle
Other investigations
- electronystagmography:
abnormal tracking and abnormal optokinetic nystagmus test
Multiple sclerosis
History
vertigo as an initial symptom (5%) or at some point during their disease (50%); prolonged spontaneous attacks of vertigo may be similar to vestibular neuritis; variety of symptoms such as dizziness, diplopia, and altered gait
Exam
variety of neurologic findings, such as nystagmus, ataxia, and cranial nerve palsies
1st investigation
- pure-tone audiogram:
sensorineural hearing-loss pattern
- MRI brain and spinal cord:
demyelinating lesions demonstrated
Other investigations
Posterior circulation stroke
History
sudden intense vertigo, nausea, and vomiting, dysarthria, unilateral limb weakness, headache, diplopia
Exam
nystagmus present and may be bilateral or vertical (suggesting a central cause), head impulse test is negative, patients usually cannot stand without support; patients may have gait and limb ataxia, facial numbness, Horner syndrome, diplopia
1st investigation
Other investigations
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency
History
episodic vertigo lasting between 30 seconds and 15 minutes and typically starting after abruptly standing or turning the head; associated with diplopia, dysarthria, ataxia, drop attack, and clumsiness of the extremities; may have risk factors for stroke such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, smoking, or heart disease
Exam
usually normal
1st investigation
- MRI brain ± angiogram:
may be lesions demonstrating areas of infarction; vascular occlusion of the cerebellar arteries may be demonstrated on angiography
Other investigations
Arnold-Chiari malformation type 1
History
occipital headache, dizziness, unsteadiness, and hearing loss, but may be asymptomatic[44]
Exam
may be downbeat nystagmus, most prominent on lateral gaze; positional testing may precipitate dizziness with downbeat nystagmus
1st investigation
- MRI brain/spine:
craniocervical lesion
Other investigations
Wallenberg syndrome (Lateral medullary infarction)
History
double vision, abnormal balance, facial or limb numbness, prolonged vertigo lasting several days
Exam
abnormal eye movements; ipsilateral Horner syndrome; diplopia; ipsilateral limb ataxia; truncal ataxia; dysphagia and hoarseness; loss of pain and temperature sensation of the ipsilateral face and contralateral trunk
1st investigation
Other investigations
Trauma
History
history of head trauma (e.g., a fall, an assault, or a motor vehicle accident), vertigo, disequilibrium, tinnitus, pressure, headache, diplopia
Exam
evidence of fluid or blood in the middle ear, evidence of a temporal bone fracture (e.g., mastoid and periorbital ecchymosis, abnormal neurologic findings, cerebrospinal fluid otorrhea).
1st investigation
- CT scan petrous temporal bones:
temporal bone fracture demonstrated
Other investigations
- electronystagmography:
abnormal response of affected side
- caloric testing:
abnormal response of affected side
- MRI scan head:
intracranial pathology
More
Vertebral artery dissection
History
more likely to be a young adult or trauma patient; dizziness, headache, and neck pain; may be history of predisposing factors, such as hypertension, recent infection, connective tissue disorder (e.g., Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Marfan syndrome, osteogenesis imperfecta, fibromuscular dysplasia)
Exam
dysarthria, visual field deficits, ataxia
1st investigation
- MRI angiogram:
may demonstrate double lumen in artery, evidence of intramural hematoma or pseudoaneurysm
- CT angiogram:
may demonstrate double lumen in artery, evidence of intramural hematoma or pseudoaneurysm
Other investigations
- carotid ultrasound with color doppler:
may demonstrate arterial dissection
More
Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration
History
history of cancer of the ovary, breast, or lung, or history of Hodgkin lymphoma; dizziness, nausea and vomiting, gait instability, altered speech, and dysphagia
Exam
nystagmus, ocular dysmetria, abnormalities of pursuit, saccadic oscillations, and an ataxic gait ± features of the associated cancer
1st investigation
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
History
often obese; headaches and transient episodes of poor vision; dizziness and tinnitus
Exam
papilledema on fundoscopy; some have bilateral 6th nerve palsy
1st investigation
- MRI brain:
slit-like ventricles demonstrated
- Visual field testing:
visual field defects; enlarged blind spot, inferonasal loss, other nerve fiber bundle defects, or constriction of the field
Other investigations
- lumbar puncture and measurement of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure:
CSF pressure elevated
More
Normal pressure hydrocephalus
History
history of abnormal balance, urinary incontinence, and cognitive dysfunction
Exam
ataxic gait, cognitive dysfunction
1st investigation
- MRI brain:
normal
Other investigations
- lumbar puncture and measurement of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure:
normal CSF pressure
More - cisternography:
no blockage of the cerebral aqueduct or of CSF outflow from the fourth ventricle
Mal de debarquement syndrome
History
swinging, swaying, unsteadiness, and disequilibrium after exposure to motion (e.g., long voyage, air travel); symptoms may last for hours, months, or years; symptoms occur after disembarking; not associated with nausea or vomiting
Exam
usually normal
1st investigation
- pure-tone audiogram:
normal pattern
Other investigations
- electronystagmography:
normal
More
Psychophysiological dizziness
History
a variety of symptoms such as rocking, floating, or swimming sensations; symptoms may worsen with stress or fatigue
Exam
anxious, may be hyperventilating, normal clinical balance tests
1st investigation
- hospital anxiety and depression scale:
may be abnormally high (>8)
Other investigations
Psychogenic dizziness
History
dizziness on standing and walking; may demonstrate anxiety reactions and avoidance behavior to specific stimuli; may be history of panic disorder with agoraphobia, personality disorders, or generalized anxiety; inappropriate or excessive anxiety or fear
Exam
normal clinical balance tests
1st investigation
- hospital anxiety and depression scale score:
abnormally high (>8)
Other investigations
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
History
history of SLE, photosensitive rash, fatigue, weight loss, alopecia, joint pain, symptoms of vertigo ± hearing loss
Exam
clinical features of SLE: malar rash, discoid rash, oral ulcers, hypertension, peripheral edema, retinal vasculitis
1st investigation
Cogan syndrome
History
history of photophobia, ocular discomfort, lacrimation, fluctuating hearing loss, imbalance or vertigo
Exam
ocular redness
1st investigation
- pure-tone audiogram:
sensorineural hearing-loss pattern
More
Other investigations
- slit-lamp exam:
may demonstrate features of interstitial keratitis, uveitis, episcleritis, or scleritis
- fluorescent treponemal antibodies absorption test:
negative
More
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly known as Wegener granulomatosis)
History
dizziness or vertigo, hearing loss, facial weakness; may have symptoms of nasal involvement with excessive nasal crusting, epistaxis or nasal discharge; lower respiratory tract symptoms of dyspnea, cough, hemoptysis or chest pain; fever, night sweats, anorexia, weight loss, malaise; neurologic symptoms of numbness, focal weakness or headache; ocular symptoms of redness, pain, diplopia, visual blurring; arthralgia, myalgia or joint swelling; purpuric, nodular, hemorrhagic or ulcerative skin lesions
Exam
serous otitis media (tympanic membrane retracted or concave, with impaired mobility), facial palsy, nasal lesions or upper respiratory tract mucosal bleeding, ulceration or crusting; may have septal perforation or saddle nose deformity; may have crackles, focal dullness to percussion or rhonchi; fever; mononeuritis multiplex; red eye, proptosis, reduced visual acuity, retinal exudates and hemorrhage; palpable purpura, cutaneous nodules, hemorrhagic and ulcerative skin lesions; joint tenderness or swelling, muscle weakness
1st investigation
- antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA):
positive
Other investigations
- biopsy of lesions for histology:
granulomatous inflammation, necrosis and vasculitis; minimal/absent immune deposits on immunofluorescence and electron microscopy
- Urinalysis and urine microscopy:
may show hematuria, proteinuria; dysmorphic red blood cells, RBC casts
More - CT chest:
lung nodules (which may cavitate); infiltrates
More
Behcet disease
History
recurrent genital and oral ulceration, eye pain, photophobia, blurred vision, headache, hearing impairment, tinnitus, dizziness
Exam
genital ulcers, oral ulcers, red eye, acne lesions, erythema nodosum, superficial thrombophlebitis
1st investigation
- none:
diagnosis is based on clinical criteria[151]
Other investigations
Carbon monoxide poisoning
History
may be history of suspected accidental exposure from residential boilers, central heating systems, cookers, fireplaces, and chimneys; often nonspecific symptoms, such as vertigo, headaches, impaired concentration, presyncope, angina, shortness of breath, nausea and vomiting, fatigue[108]
Exam
may be normal; flushed cheeks, tachycardia, hypotension
1st investigation
- carboxyhemoglobin level:
elevated
Other investigations
- chest x-ray:
may be signs of noncardiogenic pulmonary edema
- ECG:
may be tachycardia, arrhythmias, features of cardiac ischemia
- blood glucose:
may be elevated
- lactate:
may be elevated in severe poisoning
- cardiac biomarkers:
may be elevated
Postsurgery
History
history of a surgical procedure (e.g., stapedectomy, middle-ear surgery, or cochlear implantation)
Exam
positive fistula test
1st investigation
- pure-tone audiogram:
elevated hearing thresholds or severe-to-profound hearing-loss pattern
More
Other investigations
- exploratory tympanotomy:
perilymphatic fistula may be present at the round or oval window
More
Secondary syphilis
History
hearing loss or vertigo with or without other variable symptoms (e.g., malaise, myalgia, rash); late neurosyphilis: may present with hearing loss, fluctuating hearing, or dizziness or vertigo with or without other variable symptoms (e.g., personality change, altered mood, loss of anal and bladder sphincter control)
Exam
variable signs, including lymphadenopathy, rash, mucosal ulceration with or without signs of more specific organ involvement (e.g., uveitis, meningism, seizures, nephrotic syndrome); late neurosyphilis: signs of tabes dorsalis (e.g., ataxia, Argyll-Robertson pupils, areflexia, loss of vibration/proprioception, positive Romberg sign), may have signs of memory impairment, confusion, tremor
1st investigation
Other investigations
- caloric test:
abnormal
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer