Images and videos
Images
Vitamin D deficiency
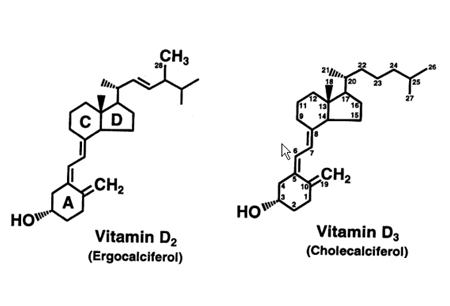
Chemical structure of vitamin D
From the collection of M.F. Holick, PhD, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Vitamin D deficiency
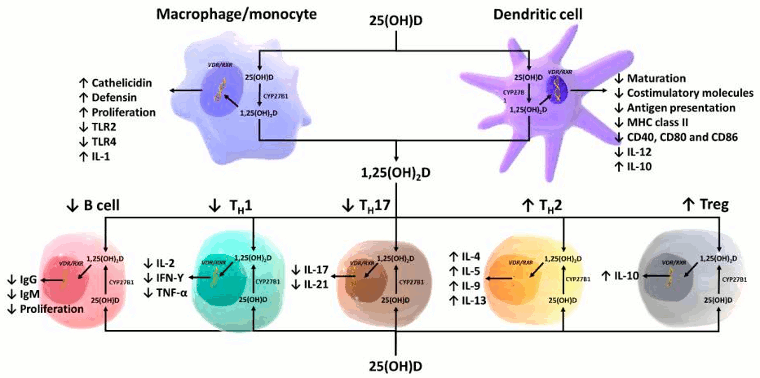
Schematic representation of paracrine and intracrine function of vitamin D and its metabolites and actions of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D on the innate and adaptive immune systems. Abbreviation: 1,25(OH)2D: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D; 25(OH)D: 25-hydroxyvitamin D, IFN-Ƴ: interferon- Ƴ; IL: interleukin; MHC: membrane histocompatibility complex, TH1: T helper 1; TH2: T helper 2; TH17: T helper 17; Treg: regulatory T cell, TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor- α; TLR2: toll-like receptor 2; TLR4: toll-like receptor 4
Reproduced with permission from Holick MF, copyright 2020
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Vitamin D deficiency
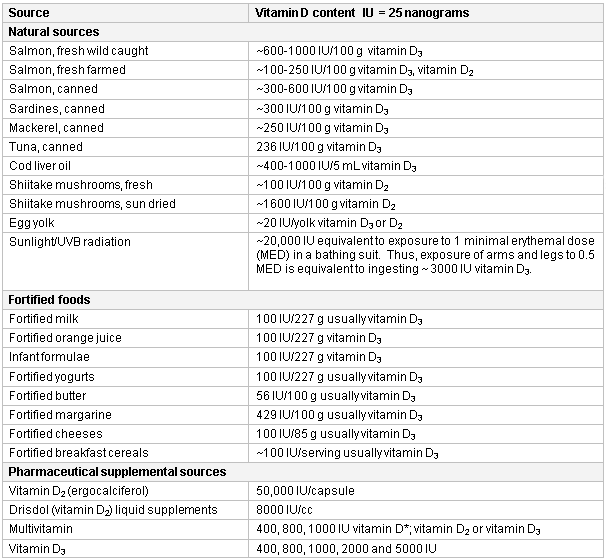
Sources of vitamin D
Created by M.F. Holick, PhD, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Vitamin D deficiency
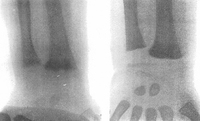
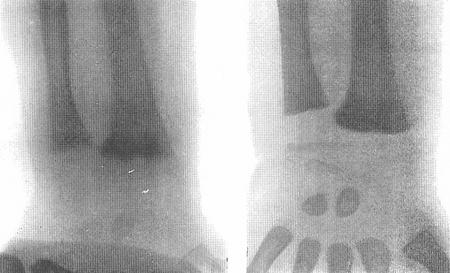
X-rays of a wrist from a child with vitamin D-deficiency rickets before (left panel) and after (right panel) treatment with vitamin D
From the collection of M.F. Holick, PhD, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Vitamin D deficiency
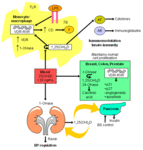
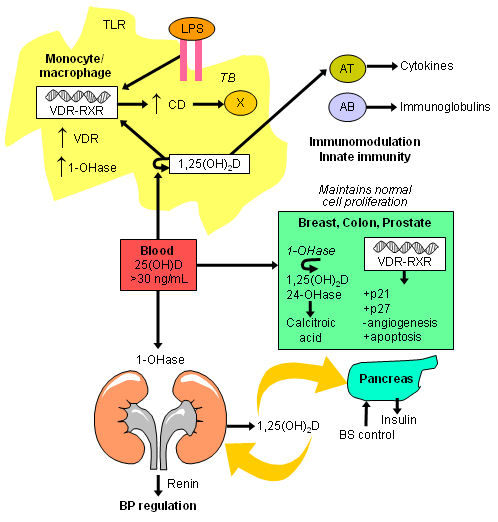
Extrarenal production of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D to modulate immune function, cell growth, and insulin production. Abbreviations: AB, activated B lymphocyte; AT, activated T lymphocyte; BS, blood sugar; CD, cathelicidin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; TLR, toll-like receptor; VDR-RXR, vitamin D receptor-retinoid X receptor; 1,25(OH)2D, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D; 1-OHase, 25-hydroxyvitamin-1-hydroxylase; 24-OHase, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-24-hydroxylase; 25(OH)D, 25-hydroxyvitamin D
Created by M.F. Holick, PhD, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Vitamin D deficiency
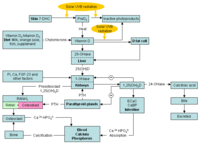
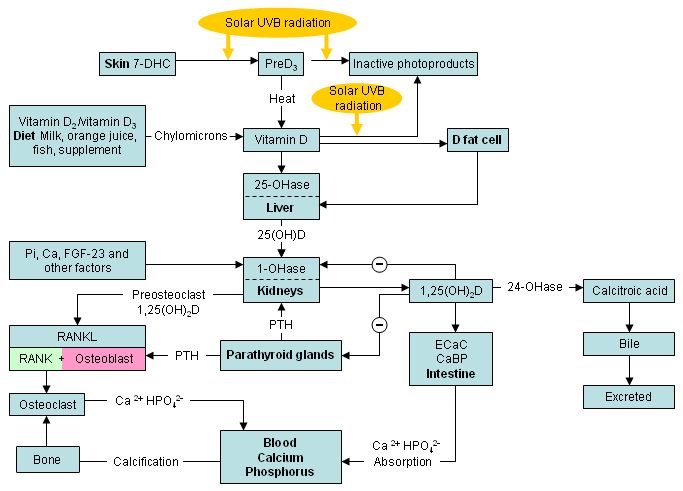
Production, metabolism, and biologic functions of vitamin D on calcium metabolism and bone health (D represents D2 and D3). Abbreviations: CaBP, calbindin; ECaC, epithelial calcium channel; FGF-23, fibroblast growth factor 23; preD3, previtamin D3; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand; 1,25(OH)2D, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D; 1-OHase, 25-hydroxyvitamin-1-hydroxylase; 7-DHC, 7-dehydrocholesterol; 24-OHase, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-24-hydroxylase; 25-OHase, vitamin D-25-hydroxylase; 25(OH)D, 25-hydroxyvitamin D
Created by M.F. Holick, PhD, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Vitamin D deficiency
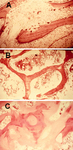
Bone biopsy of trabecular bone demonstrating (A) increased osteoclastic activity due to secondary hyperparathyroidism; (B) normal; and (C) wide osteoid seams (light-pink area), which are classic for osteomalacia
From the collection of M.F. Holick, PhD, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Vitamin D deficiency
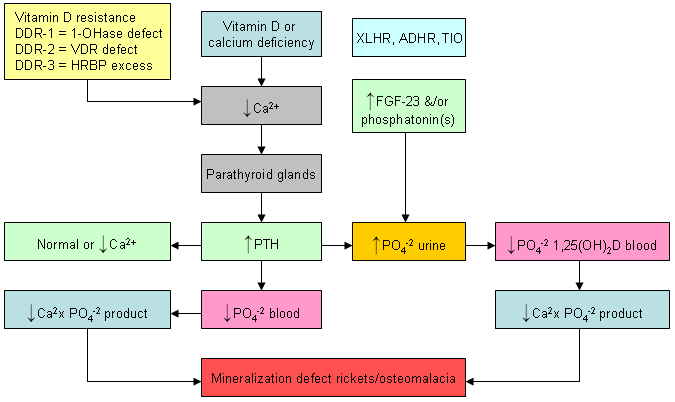
Differential effects of various disorders of calcium, phosphate, bone, and vitamin D metabolism on serum levels of calcium, phosphate, and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. Abbreviations: ADHR, autosomal-dominant hypophosphatemic rickets; FGF-23, fibroblast growth factor 23; HRBP, heterologous ribonuclear binding protein; VDR, vitamin D-resistant; XLHR, X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets, TIO, tumor-induced osteomalacia; 1-OHase, 25-hydroxyvitamin-1-hydroxylase
Created by M.F. Holick, PhD, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Vitamin D deficiency
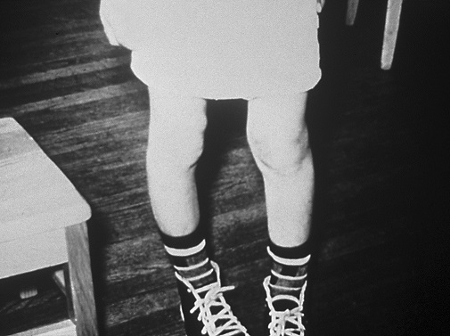
Inward or outward bowing of the legs is a typical sign of classic rickets
CDC
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Vitamin D deficiency
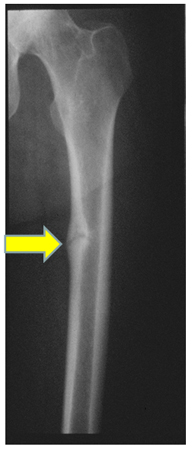
Radiograph of the femoral shaft in a patient with osteomalacia demonstrating a "pseudofracture" (also known as Looser's zone) on the medial aspect of the mid-femoral shaft
From the collection of Bridget Sinnott, MD
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer