Case history
Case history #1
A 23-year-old woman complains of diarrhea lasting several weeks. She has lost weight, but has not had a fever, and has not noticed blood in the stool. The diarrhea started while she was traveling in Mexico.
Case history #2
A 39-year-old man presents to the ER with right shoulder pain that he has been experiencing for 2 months. He reports that the pain has radiated to his back. He has been having night sweats and chills and has lost around 5 kg in weight. He also has had abdominal pain for 3 days and a nonproductive cough. He was born in Iran and recently emigrated to the US. Physical examination identifies hepatomegaly and decreased breath sounds over the lower two-thirds of the right lung. Neurologic examination is normal.
Other presentations
Amebiasis is asymptomatic in 80% of cases. Diarrhea is the most common illness caused by Entamoeba histolytica, although intestinal disease may present as dysentery (diarrhea with blood or mucus) rather than diarrhea alone. An ameboma, which is a mass of granulation tissue in the colon that can be similar in appearance to colonic carcinoma, may also be detected.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Cyst of Entamoeba histolytica: unstained (A), and iodine stained (B) after formalin-ether concentration of stool sample.Original photos from National Center for Global Health and Medicine, Tokyo, Japan. [Citation ends].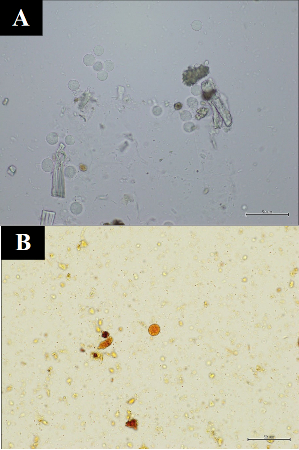
Less common extraintestinal manifestations are peritonitis from perforation of the intestine, which sometimes mimics acute appendicitis, and pleural or pericardial effusions from direct extension of a liver abscess and brain abscess (almost all patients with brain abscess due to E histolytica also have a liver abscess).[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8] Amebic acute appendicitis is also a possible but rare manifestation of amebiasis; amebic appendicitis is more likely to be complicated than non-amebic appendicitis.[8]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Amebic appendicitis with skin fistula two weeks after appendectomy (enhanced computed tomography).Original photo from National Center for Global Health and Medicine, Tokyo, Japan. [Citation ends].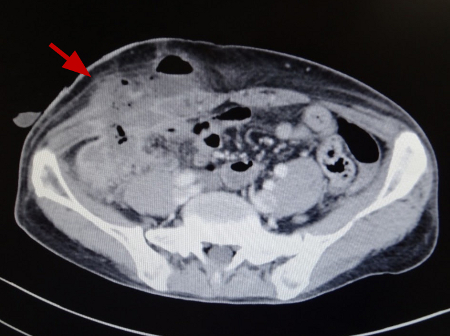 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Hematoxilin-Eosin stain (A-C) and Periodic acid-Schiff stain (D-F) of resected appendix of amebic appendicitis. Entamoebas are deeply dyed by Periodic acid-Schiff stain.Original photo from National Center for Global Health and Medicine, Tokyo, Japan. [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Hematoxilin-Eosin stain (A-C) and Periodic acid-Schiff stain (D-F) of resected appendix of amebic appendicitis. Entamoebas are deeply dyed by Periodic acid-Schiff stain.Original photo from National Center for Global Health and Medicine, Tokyo, Japan. [Citation ends].
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer