History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
common
urethral discharge in men
Early symptom of gonorrhea.
uncommon
tenderness and/or swelling of the epididymis
Suggests epididymitis. This requires specialized treatment and needs to be distinguished from testicular torsion.
mucopurulent or purulent exudate at the endocervix
Mucopurulent cervicitis is the classical sign of gonorrhea infection in women but as a sign it is not common enough nor specific enough for the predictive value to be sufficient to make a diagnosis without supportive laboratory tests.
Physical findings include frank mucopus on swab and cervical os friability.
Other diagnostic factors
common
pelvic pain in women
Considered for an STI and needs a bimanual exam. A significant number of women may have endometritis without overt symptoms.[41] If no overt pelvic pain is reported it also important to elicit whether pain occurs with sex.
urethral irritation in men
Early symptom of gonorrhea usually followed by discharge hours to days later.[18]
dysuria in men
The most common symptom of gonorrhea in men and will precede discharge.
uncommon
tenderness and/or swelling of testis
Orchitis is usually one-sided.
tenderness and/or swelling of prostate
Prostatitis is an uncommon finding with gonorrhea but is suspected if urinary obstructive symptoms or pelvic pain is present.
anal pruritus
Associated with rectal gonorrhea infection.
mucopurulent discharge from the rectum
Associated with rectal gonorrhea infection. Usually occurs with a bowel movement.
rectal pain
Associated with rectal gonorrhea infection. More common in men who have sex with men.
tenesmus
Associated with rectal gonorrhea infection. More common in men who have sex with men.
rectal bleeding
Associated with rectal gonorrhea infection. More common in men who have sex with men.
vaginal discharge
Women with gonorrhea may have some vaginal discharge, but lack of a discharge does not exclude infection.
In most vaginal discharges, other types of vaginitis such as trichomonas, yeast, and bacterial vaginosis predominate.
The discharge should be sent for microscopy. Leukorrhea is defined as >10 white blood cell count on high-power field of a vaginal fluid smear.[23]
cervical friability
Bleeding that occurs with gentle passage of a cotton swab through the cervical os suggest cervicitis.[23]
uterine, adnexal, or cervical motion tenderness
Tenderness suggests pelvic inflammatory disease, which requires specialized treatment.
uterine mass
The presence of a mass suggests pelvic inflammatory disease, which requires specialized treatment.
anterior cervical lymphadenopathy
May be present in pharyngeal gonorrhea infection.
conjunctivitis
Gonococcal conjunctivitis presents with thick/white yellow discharge.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Gonococcal conjunctivitis of the right eyeCDC/ Joe Miller, VD [Citation ends].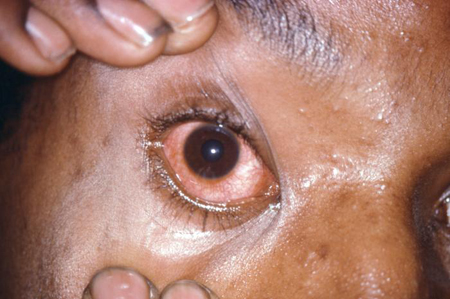
fever
Can be seen with ascending gonorrhea infection or disseminated gonorrhea infection.
skin lesions (papules, bullae, petechiae, or necrotic) at extremities
Indication of disseminated gonococcal infection.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Cutaneous lesions on the left ankle and calf due to a disseminated Neisseria gonorrhoeae infectionCDC/ Dr S. E. Thompson, VDCD/ J. Pledger [Citation ends].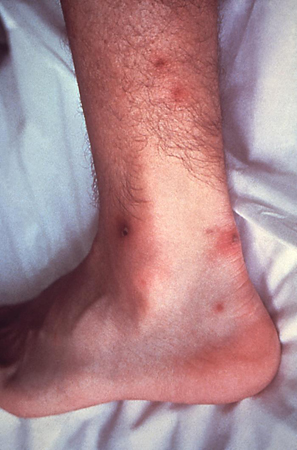
polyarthritis
Indication of disseminated gonococcal infection. Most commonly affected joints are wrists, ankles, and small joints of hands and feet.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Gonococcal arthritis of the hand, which caused the hand and wrist to swellCDC/ Susan Lindsley, VD [Citation ends].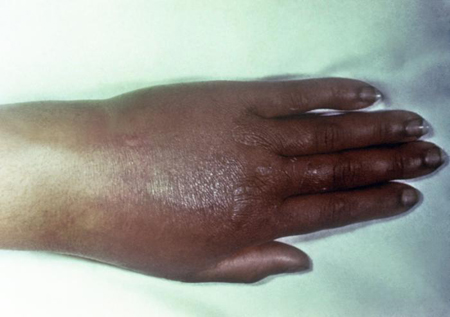
purpuric rash
Manifestation of gonococcal meningitis.
positive Brudzinski and Kernig sign
Manifestation of gonococcal meningitis.
seizures
Manifestation of gonococcal meningitis.
focal cerebral signs
Manifestation of gonococcal meningitis.
murmur
Manifestation of gonococcal endocarditis
ophthalmia neonatorum
Neonatal conjunctivitis. One of the most severe manifestations of pediatric gonococcal infection.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: A newborn with gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum caused by a maternally transmitted gonococcal infectionCDC/ J. Pledger [Citation ends].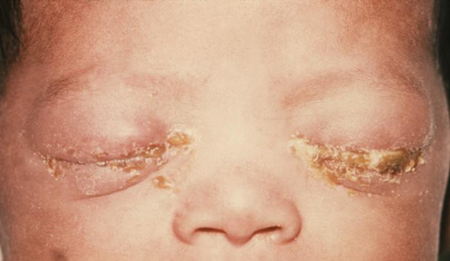
rhinitis
Less severe manifestation of pediatric gonococcal infection.
urethritis (infantile)
Less severe manifestation of pediatric gonococcal infection.
vaginitis
Most common manifestation of gonococcal infection in preadolescent girls. May occur in infants with gonococcal infection.
Risk factors
strong
age 20 to 24 years
One of the strongest predictors of gonorrhea, with rates 4 to 5 times higher than the national average. According to US data, the highest rates in men and women are seen in the 20 to 24 years age group.[3]
men who have sex with men (MSM)
In the US, about one third of gonorrhea cases are reported in MSM.[3]
In 2016, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's MSM Prevalence Monitoring Project in several urban STI clinics in the US showed high median site-specific positivity for rectal gonorrhea (15.9%) and pharyngeal gonorrhea (8.8%) among MSM.[24]
black ancestry
In the US, people of black ancestry have a rate that remains higher than other races/ethnicities and is between 8 and 9 times higher than the rate in white people (652.9 vs. 78.9 cases per 100,000).[3] There is no biologic basis for this; rate differences by race/ethnicity may represent contextual factors such as geography, socioeconomic status, and social structure that affect sexual networks.[25] In the US-based National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health (Add Health) study the highest rate among those ages 18 to 26 years was seen in black people (2.13%).[26]
current or prior history of STI
This is consistently found to be a risk factor for repeat infections and therefore is a clear indication for screening.[27][28][29] In the Add Health study (a US-based cohort study of adults ages 18 to 26 years), chlamydia was found as a coinfection in 69% of those with gonorrhea.[26] In this study most gonorrhea was asymptomatic, which may be because symptomatic people had received treatment. Women with prior bacterial vaginitis had a 26% increased risk of having gonorrhea. Bacterial vaginosis is associated with an increased risk of subsequent gonorrhea infection.[30]
multiple recent sex partners
inconsistent condom use
risk factors of partner
Unprotected sex is required for gonorrhea infection, but it does not constitute a high risk on its own if it is within a monogamous relationship. However, it is important to also consider the partner's risk factors because even if the patient has one partner, that partner may be linked to a high-risk sexual network by any of the same factors listed.
history of sexual or physical abuse
Reinfection of women with gonorrhea or chlamydia is associated with a history of physical or sexual abuse.[33]
weak
substance use
past incarceration
Some studies have demonstrated that people with a history of imprisonment may have higher rates of STIs (including gonorrhea) than those with no history of imprisonment.[23] In the US, 4.4% of females and 1.2% of males entering a juvenile correctional institution in 2011 were positive for gonorrhea.[34]
high-morbidity community
It is always important to consider the local epidemiologic factors in a decision to screen a person. Within the context of a local outbreak of gonorrhea the threshold to initiate screening may be different.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer