Complications
Your Organizational Guidance
ebpracticenet urges you to prioritize the following organizational guidance:
Acute KeelpijnPublished by: Werkgroep Ontwikkeling Richtlijnen Eerste Lijn (Worel)Last published: 2017Mal de gorge aiguPublished by: Groupe de Travail Développement de recommmandations de première ligneLast published: 2017Scarlet fever is simply the presence of a characteristic "scarlatiniform" rash due to infection with an erythrogenic toxin-producing strain of streptococci (usually group A but also can be type B or C). The rash is a diffuse papular eruption that has a characteristic "sandpaper" feel. The rash generally starts in the inguinal creases and axillae and spreads diffusely, then desquamates. Circumoral pallor and strawberry tongue can also be present.
Treatment does not differ from that of group A Streptococcuspharyngitis.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Scarlatiniform rash on the forearm due to group A Streptococcus bacteriaCourtesy of the CDC Public Health Image Library [Citation ends].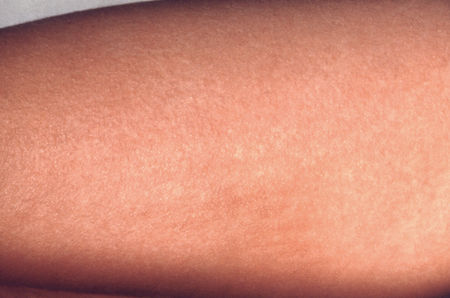
A very rare but life-threatening condition characterized by rapidly progressing multiple organ failure and shock associated with an exaggerated inflammatory reaction to streptococcal antigens.
In a December 2022 UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) report, rates of invasive group A streptococcus (GAS) disease (which includes streptococcal toxic shock syndrome and necrotizing fasciitis) in England were higher than expected for the time of year.[99]
Relatively higher rates of invasive GAS in children during the 2022-2023 season have been documented in the UK and in the USA. Clinicians are advised to maintain a high index of suspicion, as early recognition and prompt initiation of specific and supportive therapy for patients with invasive GAS infection can be life-saving.[99]
Rheumatic fever presents as polyarthritis, carditis, subcutaneous nodules, erythema marginatum, and chorea. It is a rare complication of group A Streptococcus and is mostly seen between the ages of 3 and 21 years. Symptomatic treatment may shorten the acute inflammatory phase, particularly polyarthritis, which can be very painful. Penicillin is the first-line choice for secondary prophylaxis.
Acute glomerulonephritis is associated with group A Streptococcus infection of the pharynx or skin 1 to 3 weeks after infection. Treating the underlying disorder and managing hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and proteinuria is the mainstay of therapy. Most individuals recover without long-term renal impairment. Some patients may eventually need dialysis or transplant. Antibiotics probably do not prevent glomerulonephritis.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer