Tests
1st tests to order
renal function testing
Test
Renal dysfunction is usual in rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis.
Result
abnormal
renal biopsy
Test
If clinical suspicion of antiglomerular basement membrane (anti-GBM) disease is high, a renal biopsy for definitive diagnosis should be performed as soon as contraindications are ruled out. Contraindications to renal biopsy include uncontrolled bleeding disorder, uncontrolled hypertension, and an unwilling patient.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Immunofluorescence of renal biopsy staining for IgG in a linear pattern in patient with antiglomerular basement membrane (anti-GBM) diseaseFrom the collection of Michael S. Gersch [Citation ends].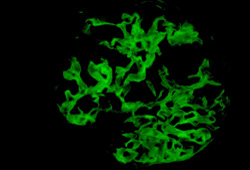
Result
crescentic glomerulonephritis, and characteristic linear IgG staining on immunofluorescence
antiglomerular basement membrane (anti-GBM) antibody titer
Test
Anti-GBM serologies are a useful confirmatory diagnostic test in addition to the renal biopsy. Additionally, this test is used to monitor response to treatment and to gauge when to stop plasma exchange.[27] Continue plasma exchange until the antibody titer is negative (usually requires 2-3 weeks).[27][28]
Serology is occasionally negative when the more sensitive indirect immunofluorescence on a renal biopsy is positive.
Result
positive
antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)
Test
Positive ANCA test suggests a diagnosis of Wegener granulomatosis, Churg-Strauss, or microscopic polyarteritis. Between 30% and 50% of patients with anti-GBM disease also have a positive ANCA test and about 5% to 14% of patients with ANCA-positive disease have circulating anti-GBM antibodies.[5] Positive ANCA in anti-GBM disease does not alter initial treatment but will change subsequent management.
Result
variable
serum complement (C3 and C4)
Test
Necessary to rule out nephritic syndrome related to lupus, infection, endocarditis, or cryoglobulinemia.
Result
normal
antinuclear antibody
Test
Used to rule out lupus nephritis.
Result
normal
cryoglobulins
Test
Sample must be kept at 37º C while being transported to the laboratory to prevent precipitation of the cryoglobulins. Used to rule out cryoglobulin-associated renal disease.
Result
negative
hepatitis panel
Test
Used to rule out hepatitis B and C, which can cause renal disease.
Result
negative
antistreptolysin O titer
Test
Used to rule out poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis.
Result
negative
clotting screen
Test
Necessary to rule out coagulopathy before proceeding with biopsy.
Result
normal
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer