Tests
1st tests to order
ECG
cardiac enzymes
Test
Important to exclude myocardial infarction; however, myocardial ischemia and infarction can occur if the dissection extends to the coronary ostium. See ST-elevation myocardial infarction.
Result
cardiac enzymes usually negative
computed tomography angiography (CTA)
Test
Should be ordered as soon as diagnosis suspected because of the patient's history or widened mediastinum on chest x-ray.[24][10][11][14][34][32][33] CTA is the primary modality used to confirm the diagnosis, given its wide availability, accuracy, and speed, as well as the extent of anatomic detail it provides.[4] Also shows the full extent of the dissection and, in some cases, the entry tear site. CTA can detect the presence and mechanism of aortic branch vessel involvement, as well as vessel patency, signs of malperfusion, pericardial effusion and hemopericardium, periaortic or mediastinal hematoma, and pleural effusion.[4] For patients who cannot receive iodinated contrast, CT without contrast is an acceptable alternative. Should include chest, abdomen, and pelvis to visualize extent of the dissection. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan showing dissecting aneurysm in a 45-year-old patient with Marfan syndrome experiencing chest painSanyal K, Sabanathan K. Chest pain in Marfan syndrome. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.07.2008.0431 [Citation ends].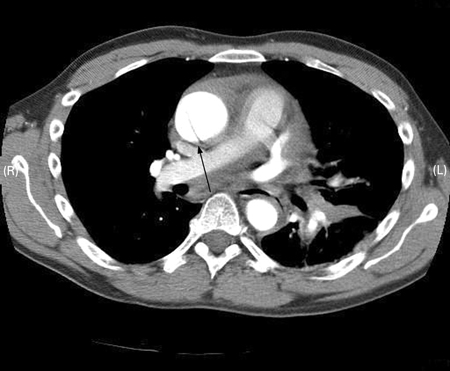 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT of a 71-year-old man showing type II dissecting aneurysm of the ascending aorta. Hematoma around the proximal segment of the ascending aorta (panels A-D) compressed the right pulmonary artery, almost occluding its patency and limiting the perfusion of the reciprocal lungStougiannos PN, Mytas DZ, Pyrgakis VN. The changing faces of aortic dissection: an unusual presentation mimicking pulmonary embolism. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.2006.104414 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT of a 71-year-old man showing type II dissecting aneurysm of the ascending aorta. Hematoma around the proximal segment of the ascending aorta (panels A-D) compressed the right pulmonary artery, almost occluding its patency and limiting the perfusion of the reciprocal lungStougiannos PN, Mytas DZ, Pyrgakis VN. The changing faces of aortic dissection: an unusual presentation mimicking pulmonary embolism. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.2006.104414 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 3D CT, distal dissectionFrom the collection of Dr Eric E. Roselli; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 3D CT, distal dissectionFrom the collection of Dr Eric E. Roselli; used with permission [Citation ends].
Result
intimal flap
renal function tests
Test
May show renal failure; either pre-existing, or developing if renal perfusion is compromised.[10]
Result
elevated creatinine and blood urea nitrogen
liver function tests
Test
May be elevated if hepatic perfusion is compromised.
Result
elevated aspartate transaminase and alanine transaminase
lactate
Test
Indicative of bowel ischemia or metabolic acidosis due to ischemia caused by aortic dissection
Result
elevated or normal
complete blood count
type and cross
Test
Surgical intervention/transfusion may be necessary in some cases.
Result
preparation for surgery
Tests to consider
chest x-ray
Test
Neither sufficiently sensitive nor specific for aortic dissection to be used as a diagnostic tool. Excludes pneumonia and may also reveal other causes of chest pain.[4][10][32][33] Widening of the mediastinum or pleural effusion can indicate aortic dissection but is of limited diagnostic value for diagnosis of aortic dissection, particularly if the dissection is confined to the ascending aorta; chest x-ray is normal in up to 40% of patients with aortic dissection.[11][14][34][35]
Result
may show widened mediastinum or pleural effusion, disruption of the normally distinct contour of the aortic knob, calcium sign (separation of the intimal calcification from the aortic wall of >5 mm, tracheal deviation to the right, double density appearance within the aorta, deviation of the nasogastric tube to the right)
D-dimer
Test
Despite a high sensitivity, D-dimer is not recommended as the sole screening tool for acute aortic dissection; while negative D-dimer may be helpful to rule out aortic dissection in low-risk patients, particularly when used within an integrated decision support tool, a positive D-dimer lacks specificity when used in isolation.[29][30] However, D-dimer will be of value when considering the differential diagnosis (e.g., pulmonary embolus).[27]
Result
positive
transthoracic echocardiography
Test
Can be ordered as supplementary test, or in unstable patients when acute proximal dissection is suspected.[32] TTE can show pericardial effusion or aortic regurgitation, and a dissection flap can sometimes be visualized; however, more complete imaging of the aortic arch requires transesophageal echocardiography or CTA.[4] Aids diagnosis if the patient presents with an incidental finding of chronic dissection (such as mediastinal widening or prominent aortic knob on chest x-ray).
Result
intimal flap
transesophageal echocardiography
Test
Can be used to confirm the diagnosis and better evaluate the aortic valve, or if computed tomography angiography is unavailable. Sensitivity and specificity are higher than for transthoracic echocardiography.[32] Aids diagnosis if the patient presents with an incidental finding of chronic dissection (such as mediastinal widening or prominent aortic knob on chest x-ray).
Result
intimal flap
MRI
intravascular ultrasound
Test
In the setting of type B dissections, if medical therapy fails and surgery required, helps define morphology of the dissection and assists in treatment plan.
Result
intimal flap
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer