Tests
1st tests to order
arthrocentesis with synovial fluid analysis
Test
Important to confirm the diagnosis, exclude septic arthritis, and differentiate from gout.
The sample should be collected in a sodium heparin-containing tube and can be stored for several days if tightly sealed.
Result
intracellular or extracellular positively birefringent rhomboid-shaped crystals under polarized light confirms CPPD; fluids are often bloody
radiographs of affected joints
Test
Cartilage calcification on x-ray is suggestive but not diagnostic of CPP arthritis and detects only about 40% of articular CPP crystal deposits.[8]Therefore, its absence does not rule out the diagnosis. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Knee radiograph with linear calcific deposits of cartilage calcificationFrom the personal collection of Ann K. Rosenthal, MD [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Wrist radiograph from a patient with chronic calcium pyrophosphate arthritis showing severe degenerative changesFrom the personal collection of Ann K. Rosenthal, MD [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Wrist radiograph from a patient with chronic calcium pyrophosphate arthritis showing severe degenerative changesFrom the personal collection of Ann K. Rosenthal, MD [Citation ends].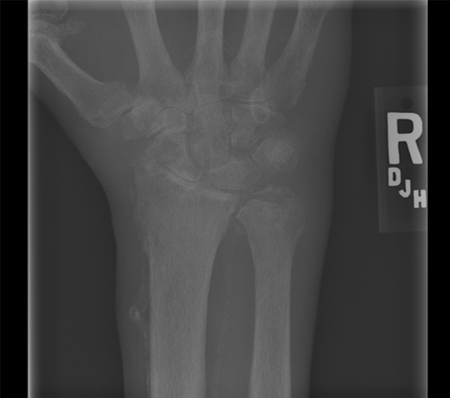
Result
linear, stippled radiopaque deposits in the fibrocartilage or hyaline articular cartilage of joints, calcified tendons, subchondral cysts, progressive rapid joint degeneration or bony collapse, and predominant involvement of the patellofemoral joint in the knee suggests CPPD
serum calcium
Test
Excludes hyperparathyroidism.
Result
may be normal or elevated in CPPD
serum parathyroid hormone
Test
Excludes hyperparathyroidism.
Result
may be normal or elevated in CPPD
iron studies
Test
Would include analysis of serum ferritin, iron, serum transferrin saturation and total iron-binding capacity. Excludes hemochromatosis, although if there is strong clinical suspicion of hemochromatosis, repeat fasting serum transferrin saturation and consideration of further testing is recommended.
Result
may be normal or elevated in CPPD
serum magnesium
Test
Excludes hypomagnesemia.
Result
may be normal or decreased in CPPD
serum alkaline phosphatase
Test
Excludes hypophosphatasia.
Result
may be normal or decreased in CPPD
Tests to consider
ultrasonography
Test
When x-rays or joint aspiration is negative but there is a strong clinical suspicion, ultrasound of affected joints may be confirmatory and can detect small calcific deposits sometimes missed by plain radiographs.[45][46] The double-contour sign on ultrasound identifies crystal-related arthropathies, but it cannot reliably distinguish between gout and CPPD in routine clinical practice. The diagnostic value is increased, however, when it is combined with hypervascularization on ultrasound, and serum uric acid levels.[47]
Result
calcified deposits in articular tissues confirms CPPD
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer