Etiology
Pathophysiology
The presence of a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, resulting in an abnormal chromosome 22 (termed the Philadelphia chromosome), is pathognomonic. The BCR gene on chromosome 22 is fused to the ABL1 gene originating from the distal portion of chromosome 9, resulting in a BCR::ABL1 fusion oncogene. The end product is usually a p210 BCR::ABL1 protein, which is the hallmark of CML.[20] p190 BCR::ABL1, the isoform found in the majority of Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL) patients, occurs in a minority of CML patients and is associated with distinct hematologic features and poor outcomes.[21][22]
BCR::ABL1 is a constitutively active tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates and alters activity of downstream signal transduction proteins. This fusion protein transforms normal hematopoietic stem cells into malignant cells. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: BCR::ABL1 translocationFrom the collection of Dr Han Myint and Dr Robert Chen; used with permission [Citation ends].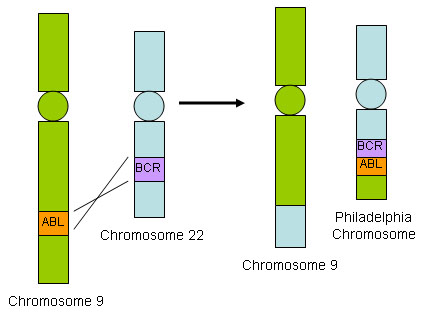
Classification
European treatment and outcome study long-term survival (ELTS) score[4]
Risk assessment using a validated scoring system is recommended before starting tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy in patients with chronic-phase CML.[5]
The ELTS scoring system can be used to stratify patients into low-, intermediate-, and high-risk categories.[4] Scores are based on age, spleen size, platelet count, and percentage of blasts in peripheral blood. The ELTS score was developed in patients treated with imatinib. It estimates the risk of CML-related death.
Studies suggest that the ELTS score is superior to the Sokal scoring system for predicting outcomes and discriminating between risk groups.[6][7][8]
ELTS score: [ EUTOS long-term survival (ELTS) score Opens in new window ]
Low risk ≤1.5680
Intermediate risk >1.5680 to ≤2.2185
High risk >2.2185.
Sokal risk score[9]
The Sokal scoring system can be used to stratify patients into low-, intermediate-, and high-risk categories.[9] Scores are based on age, spleen size, platelet count, and percentage of blasts in peripheral blood. The Sokal scoring system was developed before TKI treatment was available. It estimates the risk of death (any cause).
Sokal score: [ Sokal score for chronic myeloid leukemia Opens in new window ]
Low risk <0.8
Intermediate risk 0.8 to 1.2
High risk >1.2.
Hasford (Euro) risk score[10]
The Hasford (Euro) scoring system can be used to stratify patients into low-, intermediate-, and high-risk categories.[4][10] Scores are based on age, spleen size, platelet count, and percentage of blasts, basophils, and eosinophils in peripheral blood. The Euro scoring system was developed before TKI treatment was available. It estimates the risk of death (any cause).
Euro score:
Low risk ≤780
Intermediate risk >780 to ≤1480
High risk >1480.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) treatment response thresholds[5]
Complete hematologic response (CHR):
Normalization of peripheral blood count (leukocyte count <10 x 10⁹/L)
Platelet count <450 × 10⁹/L
No immature cells (e.g., myelocytes, promyelocytes, or blasts) in peripheral blood
No signs or symptoms of disease
Cytogenetic response:
Complete cytogenetic response (CCyR): no Ph-positive metaphases
Major cytogenetic response (MCyR): 0% to 35% Ph-positive metaphases
Partial cytogenetic response (PCyR): 1% to 35% Ph-positive metaphases
Minor cytogenetic response: >35% to 65% Ph-positive metaphases
Molecular response:
Early molecular response (EMR): BCR::ABL1 (IS) ≤10% at 3 and 6 months
Major molecular response (MMR): BCR::ABL1 (IS) ≤0.1%
Deep molecular response (DMR): MR4.0: BCR::ABL1 (IS) ≤0.01% or MR4.5: BCR::ABL1 (IS) ≤0.0032%
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer