Tests
1st tests to order
CBC with differential
Test
CBC and differential are used in initial evaluation and follow-up monitoring.
Over 90% of patients with ALL have clinically evident hematologic abnormalities at the time of initial diagnosis.
Normocytic normochromic anemia with low reticulocyte count is present in 80% of patients.
Leukocytosis is found in 50% of patients. In 25% of these patients, WBC count is >50,000/microliter. High WBC at presentation is associated with a poorer prognosis.
Despite the elevation in WBC, many patients have severe neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count <500 cells/microliter), thus placing them at high risk for serious infections.[56] See Febrile neutropenia.
Thrombocytopenia is very common, affecting 75% of patients.[1][2][8]
Result
anemia, leukocytosis, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia
peripheral blood smear
Test
Leukemic lymphoblasts may be detected on peripheral blood smear.
The presence of leukemic lymphoblasts ≥1000/microliter in the peripheral blood is sufficient to defer a bone marrow exam at presentation.[57]
Result
presence of leukemic lymphoblasts (≥1000/microliter)
serum electrolytes
Test
Measured at initial evaluation and monitored during follow-up.
Hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, and hypocalcemia (together with hyperuricemia and elevated serum LDH) may occur due to tumor lysis syndrome (TLS), particularly during treatment and if WBC count (tumor burden) is high. This can lead to cardiac arrhythmias, seizures, acute renal failure, and death, if untreated. TLS is an oncologic emergency. See Tumor lysis syndrome.
Hypercalcemia may occur due to bony infiltration or ectopic release of a parathyroid hormone-like substance.
Result
serum potassium and phosphorus may be elevated; serum calcium may be elevated or decreased
serum uric acid
Test
Measured at initial evaluation and monitored during follow-up.
Hyperuricemia (together with hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, and elevated serum LDH) may occur due to tumor lysis syndrome (TLS), particularly during treatment and if WBC count (tumor burden) is high. This can lead to cardiac arrhythmias, seizures, acute renal failure, and death, if untreated. TLS is an oncologic emergency. See Tumor lysis syndrome.
Result
may be elevated
serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
Test
Measured at initial evaluation and monitored during follow-up.
Elevated serum LDH (together with hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperuricemia, and hypocalcemia) may occur due to tumor lysis syndrome (TLS), particularly during treatment and if WBC count (tumor burden) is high. This can lead to cardiac arrhythmias, seizures, acute renal failure, and death, if untreated. TLS is an oncologic emergency. See Tumor lysis syndrome.
Result
may be elevated
renal function tests
Test
Important baseline investigation.
Includes measurement of BUN and creatinine.
Result
may be abnormal if there is renal dysfunction caused by leukemic lymphoblasts
liver function tests
Test
Important baseline investigation.
Includes measurement of total bilirubin, albumin, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and aspartate aminotransferase (AST).
Result
may be abnormal if there is liver dysfunction caused by infiltration of leukemic lymphoblasts
coagulation profile
Test
Prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, and levels of fibrinogen and D-dimers should be measured in any patient with bleeding or petechiae.
Result
results are variable
bone marrow evaluation
Test
Required to establish a diagnosis. Peripheral blood may be used for cytomorphology assessment instead of bone marrow specimens if sufficient numbers of circulating lymphoblasts are present.[57]
Bone marrow aspiration specimens should be stained with Wright-Giemsa stain, and trephine biopsy specimens should be stained with hematoxylin and eosin.
Biopsy specimens should also be stained with myeloperoxidase, which will be negative in patients with ALL.[59]
A biopsy demonstrating bone marrow hypercellularity and infiltration by lymphoblasts is characteristic for ALL. There is a lack of consensus regarding the proportion of lymphoblasts in the bone marrow that is required to make a diagnosis of ALL; however, a threshold of ≥20% is generally advised.[57]
The proportion of lymphoblasts in the marrow can help distinguish between ALL and lymphoblastic lymphoma. See Differential diagnosis.
A defined number of lymphoblasts in the bone marrow (or peripheral blood) is not always required for the diagnosis of ALL (e.g., T-ALL can be diagnosed based on immunophenotyping). See Classification.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Lymphoblasts in bone marrow smear from 3-year-old male with ALL (Wright-Giemsa stain)Image and description are from the AFIP Atlas of Tumor Pathology [Citation ends].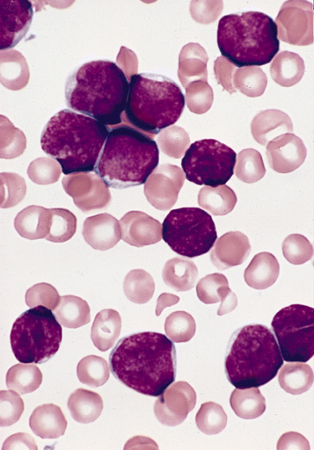
Result
bone marrow hypercellularity and infiltration by leukemic lymphoblasts; ≥20% lymphoblasts in the bone marrow; negative myeloperoxidase stain
immunophenotyping
Test
Immunophenotyping (on bone marrow specimens, or peripheral blood if sufficient numbers of circulating lymphoblasts are present) using flow cytometry is required to assess cell surface markers to:[1][3][8]
determine lymphoid lineage (B-cell or T-cell);
define an aberrant phenotype for measurable residual disease (MRD) assessment; and
detect clinically important cell surface antigens (e.g., CD20).
Leukemic cells typically exhibit markers of one cell type. Rarely, simultaneous expression of lymphoid and myeloid markers occurs in ALL, either as ALL with aberrant expression of myeloid antigens (My+ ALL) or true biphenotypic acute leukemia.
Result
presence of lymphoid lineage cell surface markers (e.g., CD19, CD22, and CD79a in B-ALL; CD3 and CD7 in T-ALL; terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase [TdT] in B- and T-ALL); clinically important cell surface antigens (e.g., CD20)
cytogenetic analysis (karyotyping and fluorescence in situ hybridization [FISH])
Test
Required to detect genetic abnormalities associated with ALL (e.g., BCR::ABL1 fusion gene encoded by the Philadelphia chromosome; ETV6::RUNX1 [also known as TEL::AML1]; KMT2A rearrangement).[58]
Genetic abnormalities are common in ALL and can guide diagnosis, risk stratification, treatment planning, and measurable residual disease (MRD) assessment during treatment. See Diagnostic criteria.
Complementary test to molecular studies.
Result
may detect cytogenetic abnormalities (e.g., Philadelphia chromosome)
molecular studies (reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction [RT-PCR])
Test
Required to detect genetic abnormalities associated with ALL (e.g., BCR::ABL1 fusion gene encoded by the Philadelphia chromosome; ETV6::RUNX1 [also known as TEL::AML1]; KMT2A rearrangement).[58]
Genetic abnormalities are common in ALL and can guide diagnosis, risk stratification, treatment planning, and measurable residual disease (MRD) assessment during treatment. See Diagnostic criteria.
Complementary test to cytogenetic analysis.
Result
may detect important genomic abnormalities (e.g., BCR::ABL1; ETV6::RUNX1; KMT2A rearrangement)
next-generation sequencing (NGS) assay
Test
Can be used to detect certain gene fusions and mutations with prognostic significance (e.g., NOTCH1/FBXW7 mutation in T-ALL).[57][59] See Diagnostic criteria.
Genetic abnormalities are common in ALL and can guide diagnosis, risk stratification, treatment planning, and measurable residual disease (MRD) assessment during treatment.
Complementary test to cytogenetic analysis and molecular studies.
Result
may detect gene fusions and mutations with prognostic significance (e.g., NOTCH1/FBXW mutation)
blood group and antibody screening
Test
Blood group and antibody screening are required for transfusion support.
Transfusion support is a near-universal requirement of patients with ALL, either as a consequence of their disease or of its treatment.
Result
blood group type; alloantibodies to red blood cell and/or platelet antigens may be detected
antibody testing for infection
Test
Antibody testing for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, HIV, and cytomegalovirus (CMV) is required to establish underlying viral infection.
Result
may be positive for antibodies for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, HIV, or CMV
Tests to consider
chest radiograph
Test
May be performed to identify a mediastinal mass, pleural effusion, and lower respiratory tract infections.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray of patient presenting with dyspnea, showing widened mediastinum and tracheal displacementFrom the personal collection of CR Kelsey [Citation ends].
Result
may reveal a mediastinal mass, pleural effusion, or lower respiratory tract infection; a widened mediastinum may indicate mediastinal lymphadenopathy
lumbar puncture
Test
Required in all patients given the relatively high frequency of central nervous system (CNS) involvement. Signs or symptoms of CNS involvement include focal neurologic deficits, headache, papilledema, nuchal rigidity, and meningismus.
Lumbar puncture should only be performed once raised intracranial pressure has been ruled out.
Lumbar puncture should be carried out at a time consistent with the treatment protocol being used. Pediatric-inspired protocols typically include lumbar puncture at diagnostic workup. However, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) ALL Panel recommends the first lumbar puncture be performed concomitantly with initial intrathecal therapy to avoid seeding the CNS with circulating leukemic blasts, unless symptoms require a lumbar puncture to be performed earlier.[57]
How to perform a diagnostic lumbar puncture in adults. Includes a discussion of patient positioning, choice of needle, and measurement of opening and closing pressure.
Detection of lymphoblasts in the initial cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) sample by multiparameter flow cytometry can identify patients at high risk of CNS relapse.[66][67]
CNS involvement at diagnosis can be graded based on the presence of lymphoblasts, WBCs, and red blood cells (RBCs) in the CSF, using the Children’s Oncology Group classification.[68][69] Higher grade (i.e., increased lymphoblasts, WBCs, and RBCs [traumatic lumbar puncture] in the CSF) is associated with poorer outcomes. See Diagnostic criteria.
Result
may reveal leukemic lymphoblasts in the CSF
pleural tap
Test
Pleural effusions should be tapped and samples sent for cytology and immunophenotyping. A mediastinal biopsy should be avoided if possible, though this may be the primary site of involvement for some patients and in such cases is unavoidable.
Result
may reveal leukemic lymphoblasts
CT/MRI brain
Test
Central nervous system (CNS) imaging should be performed in patients with major neurologic signs and symptoms (e.g., lowered consciousness level, meningismus, or focal neurologic deficits) to identify meningeal involvement or CNS bleeding.
Spinal cord and parenchymal brain involvement may occur, but is very rare.
Result
may reveal CNS infiltration or CNS bleeding
CT chest
Test
The findings of stridor, wheezing, pericardial effusion, and superior vena cava syndrome may be associated with mediastinal masses (most commonly caused by T-ALL).
CT thorax should be performed in the presence of a widened mediastinum on chest radiograph.
CT thorax, abdomen, and pelvis should be performed if there is palpable lymphadenopathy or other evidence of extramedullary disease.
Result
CT thorax may reveal a mediastinal mass; CT thorax, abdomen, and pelvis may reveal widespread lymph node involvement or extramedullary disease
scrotal ultrasound
Test
In males with an abnormal testicular exam or symptoms, scrotal ultrasound should be performed to characterize the nature of the abnormality and to establish a baseline prior to treatment initiation.[57]
Testicular involvement typically presents with painless unilateral testicular enlargement, and occurs most commonly in children and adolescents with T-ALL.[49]
Result
may reveal testicular involvement
baseline measurable residual disease (MRD) testing
Test
It is important to establish a baseline for MRD testing based on immunophenotypic, molecular, and/or cytogenetic features of the leukemic cell.
MRD testing enables depth and speed of remission to be assessed during treatment. It is prognostically important and can guide therapeutic decisions.
The exact tests for MRD depend on the patient, and assays available to the treating center.
The preferred sample for MRD testing is the first small volume (of up to 3 mL) pull of the bone marrow aspirate and/or peripheral blood.[57]
Result
may include immunoglobulin heavy chain or T-cell receptor re-arrangements; fusion genes; or leukemia-associated immunophenotype
thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT) phenotyping
Test
TPMT phenotyping may be carried out once a diagnosis of ALL is confirmed. Results of this test will help guide dosing of mercaptopurine during maintenance therapy.[70]
Result
varying expression in population; dose reduction required for mercaptopurine if TPMT activity is low
nudix hydrolase 15 (NUDT15) phenotyping
Test
NUDT15 phenotyping may be carried out once a diagnosis of ALL is confirmed. Results of this test will help guide dosing of mercaptopurine during maintenance therapy.[70]
Result
varying expression in population; dose reduction required for mercaptopurine if NUDT15 activity is low
HLA-typing
Test
HLA-typing is required to identify a suitable donor for stem cell transplantation.
Class I typing allows HLA-matched platelets to be provided in the event of platelet alloimmunization.
Result
variable
echocardiogram or multigated acquisition (MUGA) scan
Test
Echocardiogram or MUGA scan should be considered in all patients to assess cardiac function before initiating treatment.[57]
Anthracyclines are used in most treatment regimens for ALL, and are potentially cardiotoxic.
Result
baseline cardiac function
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer
