Tests
1st tests to order
vaginal or speculum examination
Test
Cervical mass or cervical bleeding may be observed.
Result
may show cervical mass or bleeding
colposcopy
Test
Indicated if cervical cancer screening is abnormal, or symptoms suggest more advanced disease. Key diagnostic criteria include abnormal vascularity, white change with acetic acid, or visible exophytic lesions.
Result
may be abnormal
biopsy
Test
Confirms diagnosis histologically and identifies subtype.
Cone biopsy or loop electrosurgical excision are used for lesions that are not clinically visible; punch biopsy may be sufficient for larger, visible lesions.[89]
Result
may be abnormal
human papillomavirus (HPV) testing
Test
HPV testing is indicated with an atypical cytology test (atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance [ASC-US]).
ASC-US patients who are HPV-positive should be referred for colposcopy.
ASC-US patients who are HPV-negative are followed up in 1 year.
Result
may be positive or negative
Tests to consider
CBC
Test
Hemoglobin <12 g/dL suspicious for significant bleeding.
Result
may show anemia
renal function testing
Test
Elevated creatinine may suggest renal system involvement or obstruction.
Result
creatinine may be elevated
liver function tests
Test
Elevated alkaline phosphatase may suggest liver or bone involvement.
Result
alkaline phosphatase may be elevated
chest x-ray
Test
Round or cavitating lesions suggestive of possible metastatic lesions; may inform staging.
Order in patients with invasive or metastatic disease.[89]
Result
may show mass
intravenous pyelogram
Test
To investigate possible renal system obstruction; may inform staging.
Result
may be abnormal
renal ultrasound
Test
To investigate possible renal system obstruction; may inform staging.
Order in patients with invasive or metastatic disease.[89]
Result
may be abnormal
barium enema
Test
To investigate possible mass impinging on bowel; may inform staging.
Result
may be abnormal
sigmoidoscopy
Test
To investigate possible mass impinging on bowel if patient clinically symptomatic.[89]
Result
may show mass
cystoscopy
Test
To investigate possible mass impinging on bladder; may inform staging.
Result
may show mass
MRI pelvis
Test
Used to evaluate local/metastatic spread and aid treatment planning.[89][93]
Optimal method for evaluating the tissues adjacent to the cervix (parametria and ligaments).[94]
MRI may be more sensitive than other imaging methods for assessing tumors greater than 10 mm.[91]
For nodal involvement: sensitivity 56%, specificity 91%.[94]
For parametrial involvement: sensitivity 97%, specificity 100%; significantly higher than physical exam.[94][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: MRI for treatment planningFrom the collection of Neil S. Horowitz, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].
Result
may be abnormal
PET whole body
Test
Used to evaluate local/metastatic spread and aid treatment planning.[89][93]
Detection of recurrence: sensitivity 80%, specificity 100%.[95][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Fluorodeoxyglucose-PET for treatment planning, metastatic activityFrom the collection of Neil S. Horowitz, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].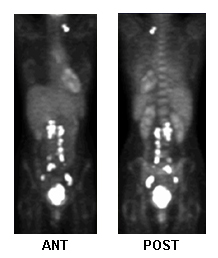
Result
may show increased metabolic activity in areas of involvement
PET/CT whole body
Test
Used to evaluate local/metastatic spread and aid treatment planning.[89][93]
For detection of nodal metastasis greater than 10 mm, PET-CT is more accurate than CT or MRI.[89]
Detection of nodal involvement: sensitivity 75%, specificity 96%.[96]
Detection of metastases: sensitivity 100%, specificity 94%.[96][97]
Result
may show nodal involvement and metastases
CT of chest/abdomen/pelvis with intravenous/oral contrast
Test
A substitute imaging modality to evaluate local/metastatic spread and aid treatment planning if MRI, PET, and PET/CT are not available.
Result
may show mass
molecular testing
Test
For patients with recurrent, progressive, or metastatic disease, molecular testing for programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and human epidermal growthfactor receptor 2 (HER2) status is recommended to determine use of targeted therapies.[90]
Molecular profiling (e.g., using a Food and Drug Administration-approved assay or validated test that includes at least HER2, mismatch repair/microsatellite instability [MMR/MSI], tumor mutational burden, and NTRK and RET gene fusions) may also be considered for recurrent or metastatic disease.[90]
Result
may show PD-L1 expression; HER2 overexpression; mismatch repair/microsatellite instability status; tumor mutational burden; presence of NTRK or RET gene fusions
Emerging tests
p16 and Ki67 biomarker expression
Test
Immunocytochemical test performed on cervical cytologic specimens to assist triage.
Coexpression of p16 and Ki67 biomarkers is highly sensitive for high-grade cervical dysplasia (CIN 2 or greater).[98] Approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in women who have tested positive for HPV.[99]
Result
may show p16 and Ki67 expression in cervical cells
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer