Criteria
Colposcopy findings
Key diagnostic criteria include:
Abnormal vascularity
White change with acetic acid
Visible exophytic lesions.
Preinvasive disease
Older terminology (mild, moderate, severe dysplasia) was replaced with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) for histologic classification based on biopsy.
CIN 1: low grade lesion with mildly atypical cellular change in lower third of epithelium
CIN 2: high-grade lesion with moderately atypical cellular changes confined to basal two-thirds of epithelium
CIN 3: severely atypical cellular changes encompassing greater than two-thirds of the epithelial thickness and includes full-thickness lesions (severe dysplasia or carcinoma in situ)
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) staging of cervical cancer[100][101]
Stage I: carcinoma confined to the cervix (extension to the uterine corpus disregarded) [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Cervical cancer stage IFrom the collection of Richard T. Penson, MD, MRCP; used with permission [Citation ends].
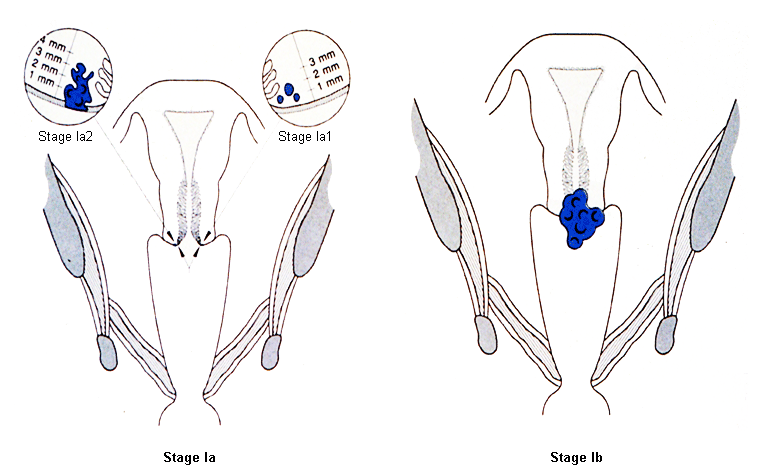
Stage IA: invasive carcinoma diagnosed only by microscopy; maximum depth of invasion <5 mm
Stage IA1: stromal invasion ≤3 mm in depth
Stage IA2: stromal invasion >3 mm and ≤5 mm in depth
Stage IB: invasive carcinoma with measured deepest invasion >5 mm; lesion limited to cervix
Stage IB1: invasive carcinoma >5 mm depth of stromal invasion, and ≤2 cm in greatest dimension
Stage IB2: invasive carcinoma >2 cm and ≤4 cm in greatest dimension
Stage IB3: invasive carcinoma >4 cm in greatest dimension
Stage II: carcinoma invades beyond the uterus, but has not extended onto the lower third of the vagina or to the pelvic wall [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Cervical cancer stage IIFrom the collection of Richard T. Penson, MD, MRCP; used with permission [Citation ends].
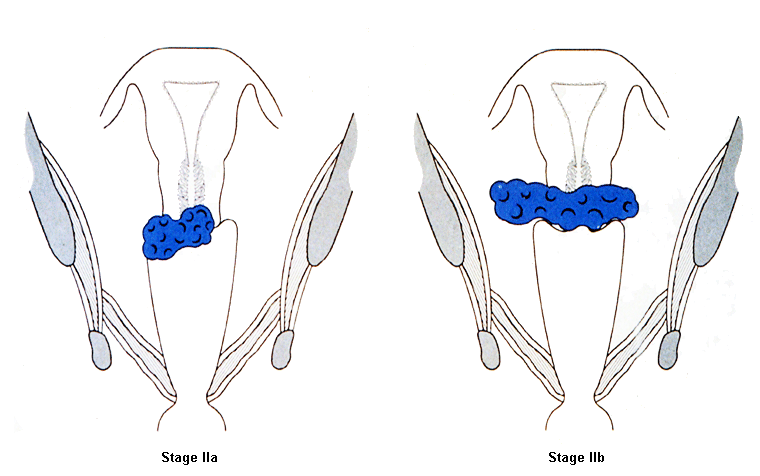
Stage IIA: involvement limited to the upper two-thirds of the vagina without parametrial involvement
Stage IIA1: invasive carcinoma ≤4 cm in greatest dimension
Stage IIA2: invasive carcinoma >4 cm in greatest dimension
Stage IIB: with parametrial involvement but not up to the pelvic wall
Stage III: carcinoma involves the lower third of the vagina and/or extends to the pelvic wall and/or causes hydronephrosis or nonfunctioning kidney and/or involves pelvic and/or para-aortic lymph nodes [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Cervical cancer stage IIIFrom the collection of Richard T. Penson, MD, MRCP; used with permission [Citation ends].
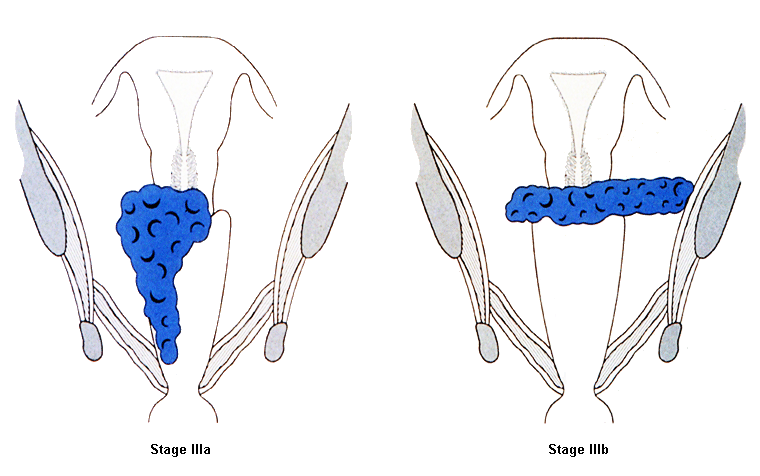
Stage IIIA: carcinoma involves the lower third of the vagina, with no extension to the pelvic wall
Stage IIIB: extension to the pelvic wall and/or causes hydronephrosis or nonfunctioning kidney (unless known to be due to another cause)
Stage IIIC: involvement of pelvic and/or para-aortic lymph nodes (including micrometastases), irrespective of tumor size and extent (use r and p notations to indicate findings on radiography and pathology, respectively)
Stage IIIC1: pelvic lymph node metastasis only
Stage IIIC2: para-aortic lymph node metastasis
Stage IV: carcinoma has extended beyond the true pelvis or biopsy-proven involvement of the mucosa of the bladder or rectum (bullous edema does not permit assignment of stage IV)
Stage IVA: spread to adjacent pelvic organs
Stage IVB: spread to distant organs.
Union for International Cancer Control Classification[102]
Staging based on clinical examination, and imaging and pathology (where available). Staging corresponds to FIGO classification.
T - primary tumor
TX primary tumor cannot be assessed
T0 no evidence of primary tumor
Tis carcinoma in situ
T1 tumor confined to the cervix
T1a1 invasive carcinoma diagnosed by microscopy, depth of stromal invasion <3 mm
T1a2 invasive carcinoma diagnosed by microscopy, depth of stromal invasion >3 mm and <5 mm
T1b1 lesion confined to the cervix >5 mm and <2 cm
T1b2 lesion confined to the cervix >2 cm and <4 cm
T1b3 lesion >4 cm in diameter.
T2 tumor invades beyond uterus but not to pelvic wall or to lower 3rd of vagina
T2a tumor without parametrial invasion
T2a1 lesion <4 cm
T2a2 lesion >4 cm
T2b tumor with parametrial invasion
T3a tumor involves lower third of vagina
T3b tumor or extends to pelvic wall or causes hydronephrosis
T4 tumor invades mucosa of bladder or rectum or extends beyond the true pelvis.
N - regional lymph nodes
NX regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
N0 no regional lymph node metastasis
N1 regional lymph node metastasis to pelvic lymph nodes only
N2 regional lymph node metastasis to para aortic lymph nodes with or without positive pelvic lymph nodes.
M - distant metastasis
M0 no distant metastasis
M1 distant metastasis.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer