Tests
1st tests to order
ECG
Test
Essential for the clinical diagnosis of atrial flutter.
In the typical form (counterclockwise atrial flutter), negatively directed saw-tooth atrial deflections (f waves) in leads II, III, and aVF, and positive deflections in V1 with atrial rates of 240 to 320 bpm are seen.
2:1 atrioventricular block is usually present in the typical form, resulting in the characteristic ventricular rate of 150 bpm. However, variable block may occur, leading to an irregular rate.
In the reverse typical form (clockwise isthmus-dependent flutter), positive flutter waves in leads II, III, and aVF, and negative flutter waves in lead V1 are seen.
Atypical flutter has an ECG pattern of continuous undulation of the atrial complex, not meeting criteria for typical or reverse typical flutter, with atrial rates >240 bpm.
Carotid massage or giving adenosine during ECG recording generally slows the ventricular rate to allow better visualization of the flutter waves if the diagnosis is not clear.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Typical atrial flutter with variable (3 to 4:1) blockFrom the collection of Dr K.C. Wu [Citation ends].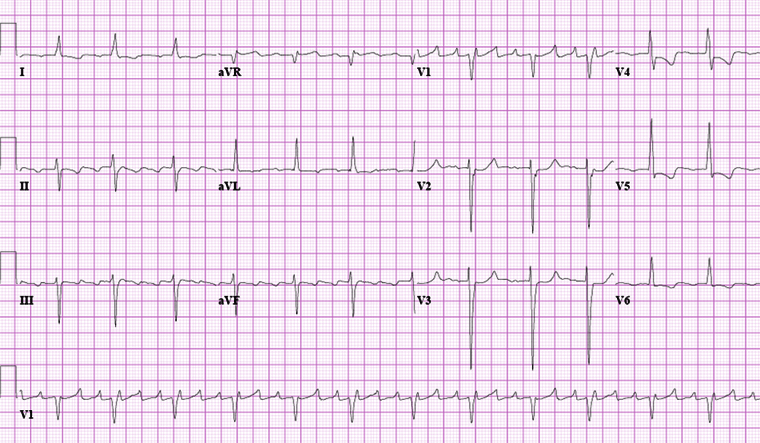 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Close-up images of leads V1, II, III, aVF demonstrating the features of typical atrial flutter: positive saw-tooth deflections in lead V1 and negative deflections in leads II, III, aVF (arrows)From the collection of Dr K.C. Wu [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Close-up images of leads V1, II, III, aVF demonstrating the features of typical atrial flutter: positive saw-tooth deflections in lead V1 and negative deflections in leads II, III, aVF (arrows)From the collection of Dr K.C. Wu [Citation ends].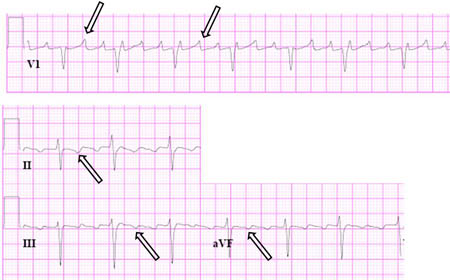 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Reverse typical atrial flutterFrom: Waldo AL. Heart. 2000 Aug;84(2):227-32; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Reverse typical atrial flutterFrom: Waldo AL. Heart. 2000 Aug;84(2):227-32; used with permission [Citation ends].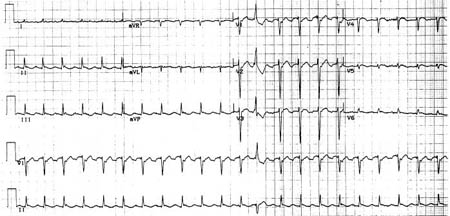 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Selected leads from a patient with reverse typical atrial flutter confirmed at electrophysiologic study. The atrial deflections are negative in lead V1 and positive in leads II, III, aVF (arrows)Adapted from: Waldo AL. Heart. 2000 Aug;84(2):227-32; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Selected leads from a patient with reverse typical atrial flutter confirmed at electrophysiologic study. The atrial deflections are negative in lead V1 and positive in leads II, III, aVF (arrows)Adapted from: Waldo AL. Heart. 2000 Aug;84(2):227-32; used with permission [Citation ends].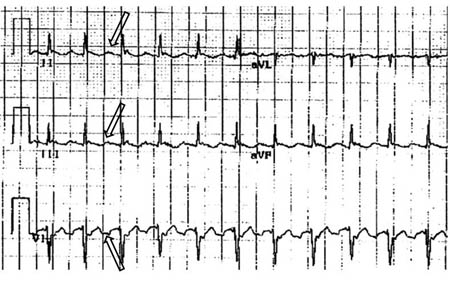 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Atypical flutter with right bundle branch blockFrom the collection of Dr K.C. Wu [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Atypical flutter with right bundle branch blockFrom the collection of Dr K.C. Wu [Citation ends].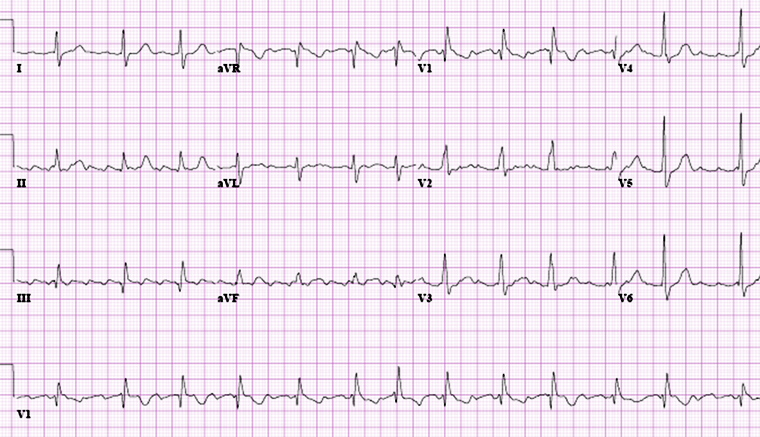 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Close up of leads II, III, V1 showing the continuously undulating pattern of atrial deflections not fitting the criteria for typical or reverse typical atrial flutterFrom the collection of Dr K.C. Wu [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Close up of leads II, III, V1 showing the continuously undulating pattern of atrial deflections not fitting the criteria for typical or reverse typical atrial flutterFrom the collection of Dr K.C. Wu [Citation ends].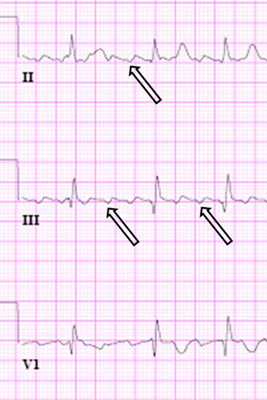
Result
changes diagnostic of typical, reverse typical, or atypical atrial flutter
thyroid function tests
Test
To rule out underlying thyroid disease.
Result
normal; abnormal if underlying thyroid disease is present
serum electrolytes
Test
Electrolyte abnormalities are generally not the sole cause of atrial flutter, but imbalances should be checked and corrected.
Result
normal; abnormal if underlying electrolyte disturbances are present
Investigations to avoid
imaging stress tests
coronary CT angiography
Tests to consider
pulmonary function tests
Test
Should be ordered if there is clinical suspicion of lung disease as a cause.
Result
normal; abnormal if underlying lung disease is present
CXR
Test
Should be ordered if there is clinical suspicion of lung disease as a cause.
Result
normal; may be abnormal if underlying lung disease is present
digitalis level
Test
Rarely a cause of atrial flutter, but digitalis toxicity may be considered in patients taking digitalis drugs (e.g., digoxin).
Result
normal; elevated in digitalis toxicity
cardiac enzymes
Test
May be considered if acute myocardial infarction (MI) is suspected.
Result
normal; elevated in MI
spiral CT with pulmonary embolism protocol
Test
May be considered if pulmonary emboli are suspected.
Result
normal; direct visualization of thrombus in a pulmonary artery in pulmonary embolism
transthoracic echocardiogram
Test
Atrial sizes can be measured.
Can also assess for valvular disease, ventricular function, and pericardial disease.
Right ventricular systolic pressures (RVSP) can also be measured.
Elevated RVSP indicates the presence of pulmonary hypertension, which can be seen in pulmonary processes.
Result
possible structural heart disease
atrial electrogram recording
Test
Recorded by postsurgical epicardial leads, dual chamber pacemaker, or esophageal lead.
Can help visualize flutter waves when the diagnosis is not clear.
Result
flutter waves
electrophysiologic studies
Test
Requires the input of electrophysiologists.
May be required for diagnosis, mapping of the critical isthmus (i.e., the cavotricuspid isthmus), and therapeutic ablation.
Result
map of reentrant circuit
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer