Differentials
Carotid dissection or subintimal hematoma
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Often, but not exclusively, younger age groups <50 years.
Neck pain in some patients.
Associated with trauma, vigorous exercise, or an event that sustains severe neck movement (e.g., roller coaster ride, motor vehicle accident).
May have Horner syndrome or history of genetic collagen abnormality.[25]
INVESTIGATIONS
Duplex ultrasound, computed tomography angiography, or magnetic resonance angiography may show the intimal flap and intramural thrombus.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Magnetic resonance time of flight image of brain. The arrow shows the right carotid artery with a crescent-shaped appearance. This is consistent with intramural hematoma consequent upon dissection of the right carotid arteryUsed with permission from BMJ Case Reports 2012; doi:10.1136/bcr.01.2012.5636 [Citation ends].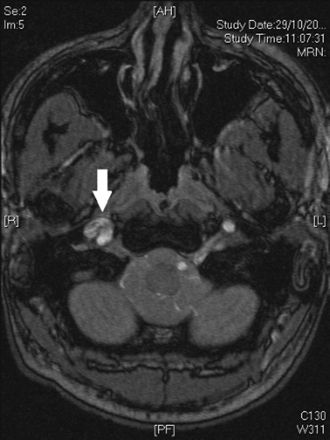 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: MRI of carotid artery. The arrow shows narrowing of the lumen of the carotid artery caused by intramural hematomaUsed with permission from BMJ Case Reports 2012; doi:10.1136/bcr.01.2012.5636 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: MRI of carotid artery. The arrow shows narrowing of the lumen of the carotid artery caused by intramural hematomaUsed with permission from BMJ Case Reports 2012; doi:10.1136/bcr.01.2012.5636 [Citation ends].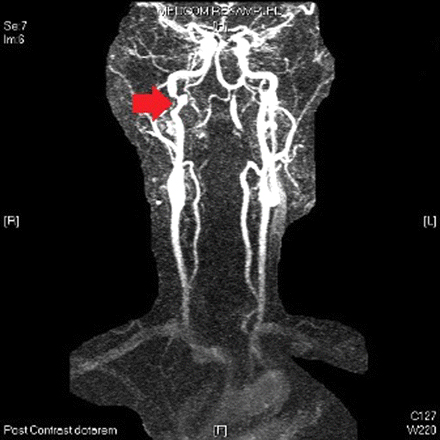
Thrombotic occlusion of the carotid artery resulting from plaque rupture
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
No differentiating symptoms/signs except in the patient who also has common carotid artery occlusion when pulsation of the carotid artery in the neck may be absent.
INVESTIGATIONS
Duplex ultrasonography, computed tomography angiography, or magnetic resonance angiography will show an occluded carotid artery filled with thrombus.
Fibromuscular dysplasia
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Asian ancestry.
Younger age group <50 years.
Female sex.
Evidence of additional arch vessel occlusive disease (e.g., absent radial pulses as a result of subclavian artery stenosis).
INVESTIGATIONS
Duplex ultrasound may show homogenous intramural lesions without calcification.
Computed tomography angiography or magnetic resonance angiography may show characteristic "string of beads" appearance in the distal carotid artery and may show additional occlusive lesions in the arch vessels.
Carotid web
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Variant of fibromuscular dysplasia.
Fairly rare. More common in younger patients.
INVESTIGATIONS
Carotid web has a typical appearance on computed tomography angiograph.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer