Differentials
Asbestosis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
History of exposure to asbestos. In certain workplaces, such as foundries and mines, workers may be exposed to both silica and asbestos.[42] The clinical presentation may be similar.
INVESTIGATIONS
Chest x-ray appearance of asbestosis: there is lower zone linear interstitial fibrosis, progressively involving the entire lung, with pleural thickening.
Chest x-ray appearance of silicosis: there are small rounded opacities, initially beginning in the upper lobes, and with progression, these smaller nodules conglomerate into large opacities (progressive massive fibrosis). Unlike in asbestos exposure, there are no pleural changes seen on chest x-ray, although pleural fibrosis may be seen from a pathologic specimen of silicosis.
Lung biopsy in patients with asbestosis will not show silicotic nodules, which are pathognomonic for silicosis.
Some patients with exposure to asbestos and silica may have radiographic and or pathologic changes of mixed dust.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CXR showing changes consistent with simple silicosis or coal workers' pneumoconiosisFrom the personal collection of Kenneth D. Rosenman, Michigan State University [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CXR of progressive massive fibrosis due to silica or coal exposureFrom the personal collection of Kenneth D. Rosenman, Michigan State University [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CXR of progressive massive fibrosis due to silica or coal exposureFrom the personal collection of Kenneth D. Rosenman, Michigan State University [Citation ends].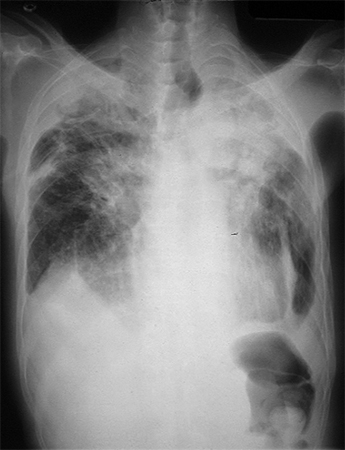 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CXR of asbestosisFrom the personal collection of Kenneth D. Rosenman, Michigan State University [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CXR of asbestosisFrom the personal collection of Kenneth D. Rosenman, Michigan State University [Citation ends].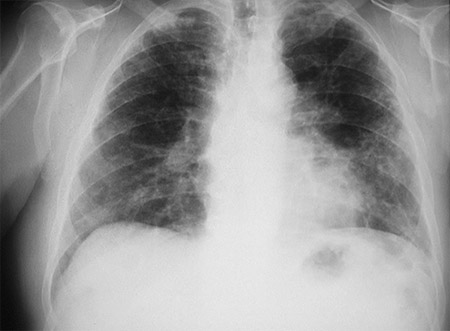 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CXR demonstrating pleural thickening (indicated by arrows)From the personal collection of Kenneth D. Rosenman, Michigan State University [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CXR demonstrating pleural thickening (indicated by arrows)From the personal collection of Kenneth D. Rosenman, Michigan State University [Citation ends].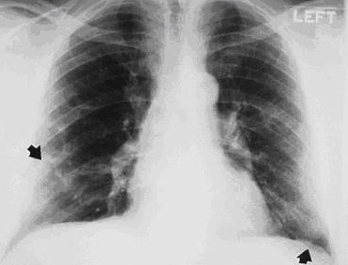
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Complete workup and environmental history reveals an absence of history of significant exposure to mineral dust or metal.
May be no other differentiating signs and symptoms.
INVESTIGATIONS
Imaging (chest x-ray or high-resolution CT scan [HRCT]) shows lower lobe linear fibrosis.
There is a negative beryllium lymphocyte proliferation test (BeLPT).
Lung biopsy does not show increased mineral content.
Sarcoidosis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Complete workup and environmental history reveals an absence of history of significant exposure to beryllium.
There may be no other differentiating signs and symptoms. Sarcoidosis may also involve nonrespiratory organs, this does not occur with acute or chronic beryllium disease. Patients with coal workers' pneumoconiosis or silicosis may have involvement of their joints and skin seen with rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, and systemic lupus erythematosus.
INVESTIGATIONS
Imaging (chest x-ray or HRCT scan) shows hilar lymphadenopathy and predominately linear, not rounded, upper lobe scarring.
May be associated with hypercalcemia.
Granulomas demonstrated on lung biopsy (granulomas also present in chronic beryllium disease).
There is a negative beryllium lymphocyte proliferation test (BeLPT).[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Sarcoidosis: CXR demonstrating bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy plus pulmonary infiltratesAdapted from BMJ (2009); used with permission [Citation ends].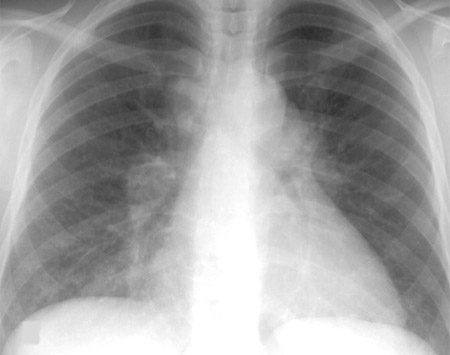
Rheumatoid arthritis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Although patients may have rheumatoid arthritis without pneumoconiosis, the diagnosis is sometimes mixed. Patients with pneumoconiosis may develop rheumatoid arthritis or connective-tissue disease. Also, patients with a history of rheumatoid arthritis may develop pulmonary fibrosis.
Complete workup and environmental history reveals an absence of history of significant exposure to mineral dust or metal in patients with rheumatoid arthritis without pneumoconiosis.
Specific signs and symptoms of arthritis, rheumatoid nodules, pleuritis, pericarditis, and inflammatory eye disease may be present in people with rheumatoid arthritis, but not in people with pneumoconiosis that is not complicated by connective-tissue disease.
INVESTIGATIONS
Lung biopsy does not show pathology of pneumoconiosis or increased mineral content in people who have rheumatoid arthritis without pneumoconiosis.
Immunologic markers, such as rheumatoid factor (RF), are nonspecific and may be present in patients with silicosis and coal workers' pneumoconiosis without connective-tissue disease, thus are not differentiating tests.[35][43]
Smooth rounded opacities may be seen on the chest x-ray in people with silicosis or coal workers' pneumoconiosis who also develop rheumatoid arthritis (Caplan syndrome).[30][31] The opacities seen in Caplan syndrome are smooth and typically golf-ball size. They differ from the opacities seen in progressive massive fibrosis (PMF), which have irregular borders. PMF may occur as coal workers' pneumoconiosis or silicosis progress. As the opacities of PMF increase in size, they may occupy the whole upper lobe and cause distortion in the lung structure.
Scleroderma
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Although patients may have scleroderma without pneumoconiosis, the diagnosis is sometimes mixed. Patients with pneumoconiosis may develop rheumatoid arthritis, connective-tissue disease, or vasculitides. Also, patients with a history of scleroderma may develop pulmonary fibrosis.
Complete workup and environmental history reveals an absence of history of significant exposure to mineral dust or metal in patients with scleroderma without pneumoconiosis.
Specific signs and symptoms of Raynaud phenomenon, digital pits or ulcers, sclerodactyly, heartburn, reflux, or arthralgia may be present in people with scleroderma, but not in people with pneumoconiosis that is not complicated by connective-tissue disease.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Hands demonstrating Raynaud phenomenonFrom the collection of Maureen D. Mayes, University of Texas [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Fingers demonstrating sclerodactyly with finger curling, shiny skin at the fingers, and telangiectasiasFrom the collection of Maureen D. Mayes, University of Texas [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Fingers demonstrating sclerodactyly with finger curling, shiny skin at the fingers, and telangiectasiasFrom the collection of Maureen D. Mayes, University of Texas [Citation ends].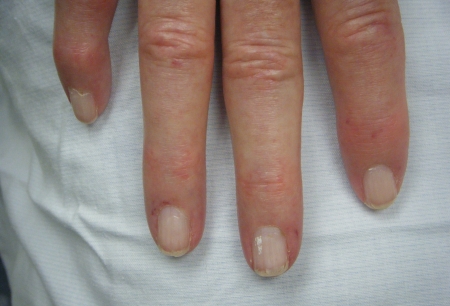
INVESTIGATIONS
Lung biopsy does not show pathology of pneumoconiosis or increased mineral content in patients with scleroderma without pneumoconiosis.
Immunologic markers, such as antinuclear antibody (ANA), are nonspecific and may be present in patient with silicosis and coal workers' pneumoconiosis without connective-tissue disease, thus are not differentiating tests.[35][43]
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Patients with a history of SLE may develop pulmonary fibrosis, making a clear diagnosis sometimes more difficult.
Complete workup and environmental history reveals an absence of history of significant exposure to mineral dust or metal.
Specific signs and symptoms of malar, discoid, or photosensitive rash; arthritis; Raynaud phenomenon; hypertension; edema; or abdominal pain may be present in people with SLE, but not in people with pneumoconiosis that is not complicated by connective-tissue disease.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Hands demonstrating Raynaud phenomenonFrom the collection of Maureen D. Mayes, University of Texas [Citation ends].
INVESTIGATIONS
Lung biopsy does not show pathology of pneumoconiosis or increased mineral content.
Immunologic markers, such as antinuclear antibody (ANA), are nonspecific and may be present in patients with silicosis and coal workers' pneumoconiosis without connective-tissue disease, thus are not differentiating tests.[35][43]
Drug- or radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
History of medications such as amiodarone, nitrofurantoin, methotrexate, bleomycin, and cyclophosphamide, or history of receiving radiation therapy.
Complete workup and environmental history reveals an absence of history of significant exposure to mineral dust or metal.
May be no other differentiating signs and symptoms.
INVESTIGATIONS
Imaging (chest x-ray or high-resolution CT scan) shows lower lobe linear fibrosis.
There is a negative beryllium lymphocyte proliferation test (BeLPT).
Lung biopsy does not show increased mineral content.
COPD
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
COPD not from pneumoconiosis is no different from COPD from pneumoconiosis, except there will be a history of prolonged exposure to a mineral dust or metal when such an exposure is a significant contributing factor.
INVESTIGATIONS
There are typically no distinguishing tests. If lung tissue is available, the dust/mineral content can be determined and quantified to identify exposures not identified in the exposure history, or to confirm the exposures that were identified from the history.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer